Vane pump is a rotary and positive displacement pump. The limitation of gear pump, i.e., leakage of fluids is greatly reduced using vane pumps (See Figure 1).
Figure 1: Vane pump.
A vane pump is a rotary pump, which is provided with different radial slots along with an eccentrically placed rotor. The eccentricity of the rotor causes the displacement of high quantity of fluid during delivery stroke compared to suction stroke. Thus, due to this fluid flow rate vane pump is utilized as variable displacement pump, by varying the eccentricity. The maximum discharge a vane pump can have is 1.5 lit/sec, whereas, its maximum pressure is 7 MPa.
Types of Vane Pumps
Vane pumps are classified as follows,
- Unbalanced vane pump
- Balanced vane pump.
Unbalanced Vane Pump
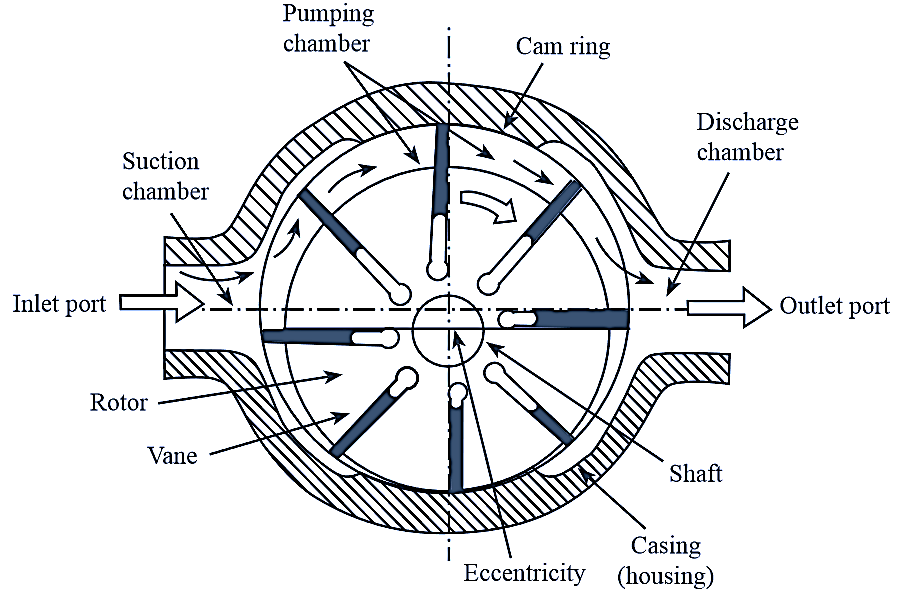
Figure 2: Unbalanced vane pump.
The pump is termed as unbalanced vane pump because all the pumping actions takes place only at one side of the rotor which leads to bearing side loads (Figure 2).
The main parts of the pump are.
- Rotor
- Rectangular vanes
- Cam ring
- Inlet and outlet ports.
The rotor consists of equally spaced radial slots and is positioned at a certain offset distance (eccentricity) from the centre of cam ring. The rotor slots consists of rectangular vanes, which slide in and out, due to the centrifugal force. These vanes do not come out of the slots completely due to design of cam ring and vanes.
Working of Unbalanced Vane Pump
Initially, the rotor is connected to a driving shaft is rotated using external power source. The rectangular vanes commies 0111 of the slots due to centrifugal force and touches the surface of the cam ring. Thus, the pumping chamber is divided into equal number of small chambers.
First Half of Rotor Rotation
During the initial rotation of the rotor, the volume of chamber increases due to the outward movement of the vanes and the pressure is less than the atmospheric pressure. This creates suction at the inlet and the fluid enters into the suction chamber. Then, the fluid is transferred to the pumping chamber.
Second Half of Rotor Rotation
During the second half of rotor rotation, the rectangular vanes are pushed back into the slots of rotor. Thus, volume is reduced and the pressure is increased. The fluid is forced out of the pump positively through the discharge chamber (i.e., outlet port). The pumping action of unbalanced vane pump i.e., delivery rate of the pump can be varied by changing the offset distance (eccentricity) between rotor and cam ring.
Advantages of Unbalanced Vane Pump
- Compact in shape
- Relatively less weight
- Can be used for less viscosity fluids i.e., vapour and gases.
- High volumetric and mechanical efficiencies.
- Leakage of fluids is greatly reduced.
- It is a bi-directional pump.
- Replacemeiìt of vanes is very easy.
- Check valves are not required.
Disadvantages of Unbalanced Vane Pump
- Cannot be used for the fluids with solid particles (abrasive fluids).
- Requires relief valves.
- Good seals and filtration systems are required.