In Direct arc furnace, an electric arc is struck between carbon or graphite electrodes which produces intense heat. The impurities are oxidized from the charge by melting and absorbed by slag. The slag is run off by tilting the furnace.
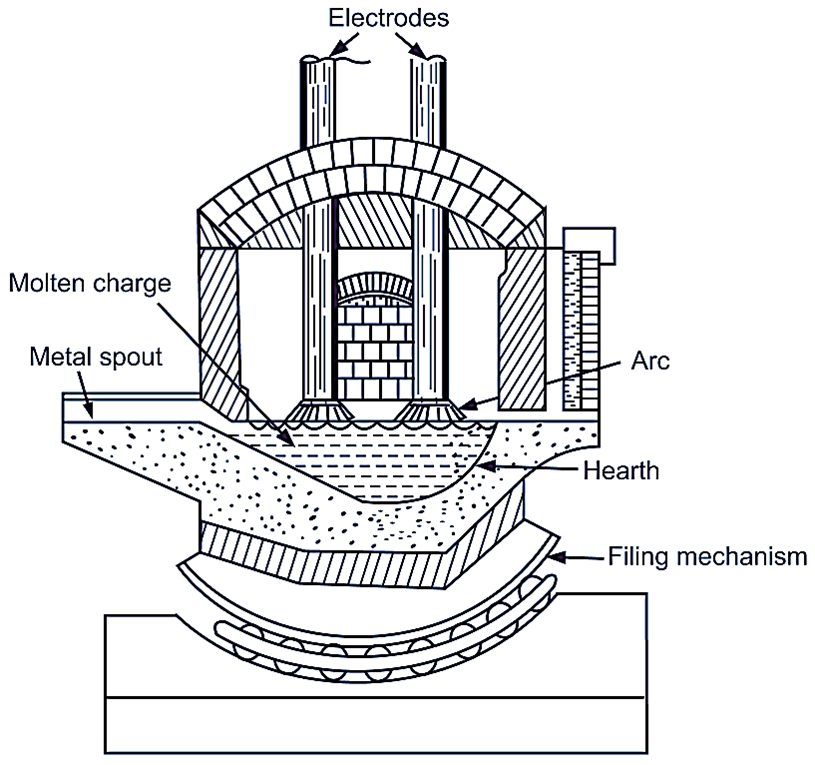
Fig. 1: Direct arc furnace
Construction & Working of Direct arc furnace
The furnace consists of a steel cylindrical shell with a spherical or flat bottom. The bottom is mounted on rollers, so as to enable the furnace to be tilted by operating a hand wheel.
The charge is contained in a bowl shaped hearth, lined with suitable basic material like magnetic bricks (see Figure 1). There are two spouts opposite each other, one for pouring the molten metal and other for taking out the slag. Three large vertical electrodes are arranged in triangular pattern which can be raised or lowered by an automatic device. The charge consists of steel scrap and iron oxide in the form of iron ore. After charging, the top is closed and electrodes are lowered and current is switched on.
A powerful spark is produced between the electrode and metallic charge. High temperature of about 2000°C is produced. This intense heat melts the charge. To get desired composition, alloying elements are added. The process is suitable for both ferrous and non-ferrous metals. But process is costly because of high cost of electricity, so process is used for making high grade alloy steels, heat resisting steels and stainless steels.
Advantages of Direct Arc Furnace
- Because of high quality fuel i.e. electricity more refined high grade steel can be prepared.
- The temperature can be controlled easily.
- No loss of expensive alloy element like nickel, tungsten, chromium etc.
- A variety of steel can be prepared.
Disadvantages of Direct Arc Furnace
- Process is costly.
- The output is from 30 to 80 tonnes/day which is low.