In this topic, you study the Bounded and Unbounded Signals theory, definition & solved examples.
Bounded Signal
A continuous-time signal $x(t)$ having finite value at any instant of time is said to be bounded signal i.e. if $x(t) < M$ ; where $M$ is the finite value for all time $t$. The bounded signal example with $M=1$ shown in Figure 1.
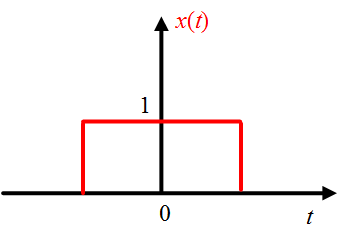
Figure 1: Bounded signal.
Unbounded Signal
A continuous-time signal $x(t)$ having infinite value at any instant of time is said to be the unbounded signal. The unbounded signal example is shown in Figure 2.
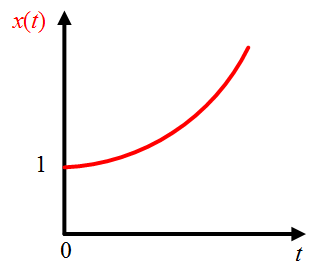
Figure 2: Unbounded signal.