In this topic, you study the extension of range of the voltmeter by voltage multipliers.
A multiplier is employed for extension of a voltmeter’s range. A multiplier is a resistance of high value connected in series with the voltmeter. The combination then is connected across the circuit, whose voltage is to be measured. The multiplier limits the current through the voltmeter and value of its resistance be calculated as under: See Fig. 1.
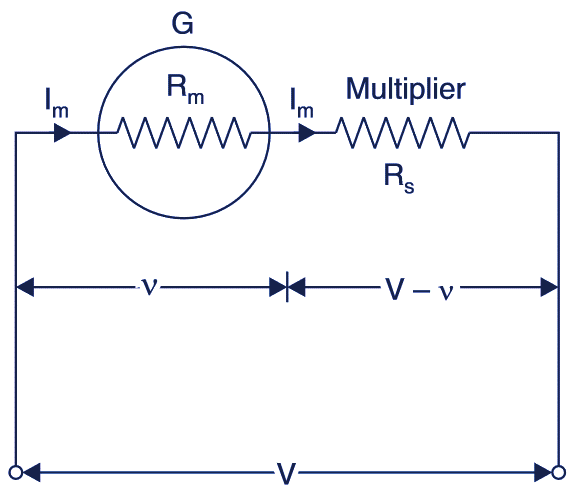
Fig. 1. Extension of Voltmeter Range.
Let,
Rm = The internal resistance of the Multi Range Voltmeter
Im = Full scale deflection (f.s.d) current of the meter which can safely be carried by the instrument. The same current will flow through multiplier.
Rs = Resistance of the multiplier.
v = voltage drop across the meter
V = The voltage measured V > v,
Dividing (ii) by (i)
or
V -IR
-R
The ratio of total voltage to be measured and the voltage across the meter is called “multiplying factor” of the multiplier.
multiplying factor m —
(from eq, (iif)l
R,n.m – + or, Rs- l)
Hence, Resistance of the multiplier
The value of the multiplier resistance Rs can be calculated; if Rm and m are known.
Required Properties for Multiplier’s Material
The requirements for the multiplier’s material are same i.e., they should have low temperature coefficient of resistance, and their resistance should not have the ageing effect and their value should not change with time.
The material used for multipliers are also manganin and constantan. For low voltage, the multipliers are enclosed within the meter, but for above 500 V, the multipliers are mounted externally.