It is necessary for air conditioning designers to know about the heat sources and their nature before taking the job of design of air conditioning systems. The natures of heat sources, which contribute heat to the air conditioning systems used for summer season, are studied here. The details of the heat sources are used for comfort air-conditioning, industrial airconditioning, product storage systems as well as product freezing systems. The air conditioning systems used have to take up two types of loads, known as ‘Sensible Heat Load and Latent Heat Load’.
The sources of sensible heat
“When there is direct addition of heat to the enclosed space, a gain in the sensible heat is said to occur”. Here, temperature increases and no phase change occurs. This sensible heat is to be removed during process of conditioning the air during summer season. The various sources of sensible heat loads are,
- Several flows of heat through the exterior walls, ceilings, floors, windows and doors due to the temperature difference between their two sides.
- Load due to solar radiation (sun load) is divided into two forms.
- Heat transmitted directly by radiation through glass of windows and ventilators.
- Heat from sun will be absorbed by the walls and roof and later on, it will be transferred to room by conduction.
- Sensible heat received from the occupants.
- Heat received from different equipments, which are commonly used in the air conditioned building.
- Heat gain due to lightening load.
- Heat received from the infiltrated outdoor air through cracks in doors, windows and ventilators and through their frequent openings.
- Miscellaneous heat sources, Which include the following:
- Heat gain by the ducts carrying the conditioned air and passing through unconditioned space.
- Heat transferred through interior partition of rooms in the same building, which are not air conditioned.
The sources of latent heat load (vapour added)
“When there is an addition of water vapours to air of enclosed space, the gain in latent heat is said to occur. ” OR
Latent heat load can be defined as, “heat of evaporation, which depends upon vapour pressure difference between the body and surrounding air.
The various sources of latent heat loads are,
- Latent heat load from the outdoor air entering into the air conditioned space by infiltration.
- Latent heat load from the occupants.
- Latent heat load from cooking foods and from stored materials.
- Moisture passing directly into the air conditioned space through permeable walls, where the water vapour pressure is higher.
Extra loads
- The fresh air taken from outside adds the sensible and latent heat loads on the air conditioner, and not in the room.
- Heat gain from the fan work (sensible heat) is added in the fresh air and it is removed in the air conditioner, if the fan is installed before the air conditioner.
- The total heat to be removed by the air conditioning system is the sum of the loads (B) and extra loads (C),
Tota load on air conditioning system = Load (A) + Load (B) + Load (C)
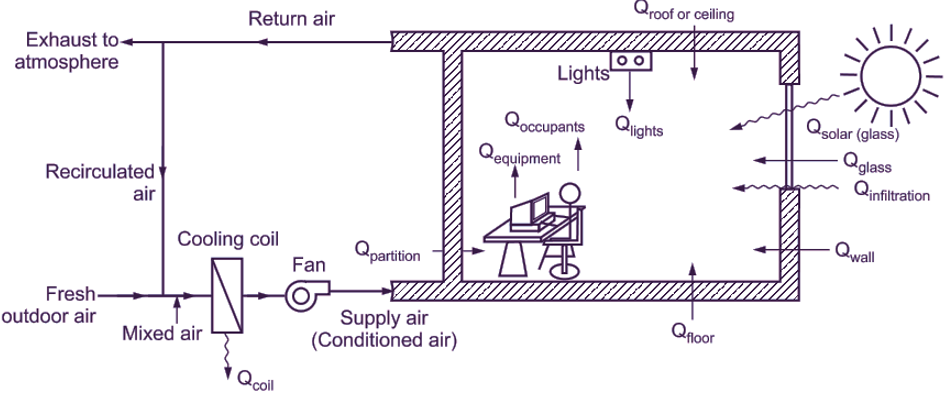
Fig. 1: Schematic diagram showing heat gains in the room from internal and external sources