In this topic, you study Stator Voltage Control of Induction Motor.
The slip and therefore the speed of the induction motor can be varied by changing the applied stator voltage. For an induction motor operating at or near full-load slip,
That is torque developed by an induction motor varies as the square of the applied voltage. Therefore, if the voltage is reduced, the torque is also reduced. Consequently, the speed drops down i.e. slip increases until the increased rotor current and hence the increased current drawn by the motor compensates for the reduction in torque due to reduced applied voltage. Thus, the motor produces the required load torque at a lower speed. Fig. 1 shows the typical speed-torque curves with stator-voltage control.
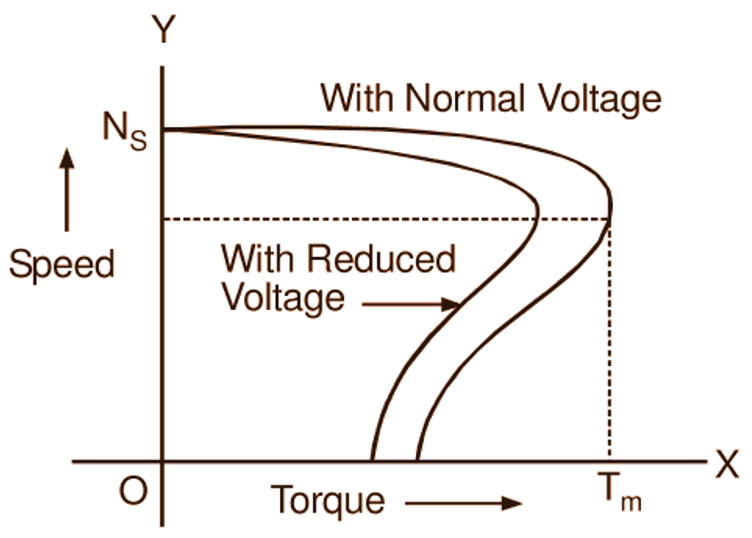
Fig. 1. Speed-torque curves of an induction motor with stator-voltage control
Applications of Stator Voltage Control of Induction Motor
Inspite of being most simple, this method is rarely used in actual practice except for small single-phase induction motors used for fans, home appliances, etc.
Advantages of Stator Voltage Control of Induction Motor
The principal reasons are as follows :
- A large change in voltage is required for a relatively small change in speed.
- When the supply voltage is reduced by a large percentage Of the rated voltage, the induction motor gets overheated due to increase in the current drawn under constant load torque condition.
- A large change in supply voltage seriously affects the magnetic conditions Of the motor.
- Need of additional voltage changing auxiliary equipment makes the method expensive.