Bourdon tube pressure gauge consists of bourdon tube bent into an arc of circle. Cross-section of the tube is elliptical. One end of tube is connected to the point, whose pressure is to be measured. Other end is connected to the rack and pinion through mechanical linkage. The pointer is pivoted on the pinion (Fig. 1).
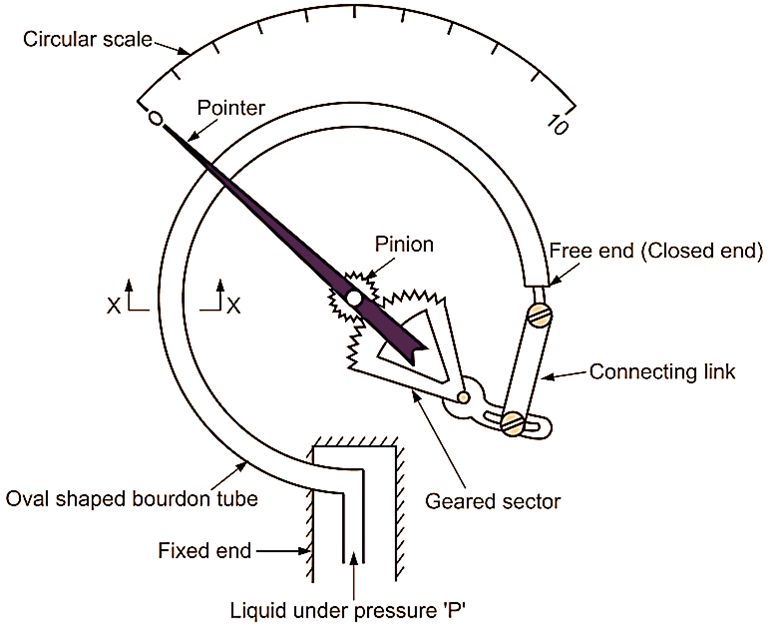
(a) Schematic view of Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge.
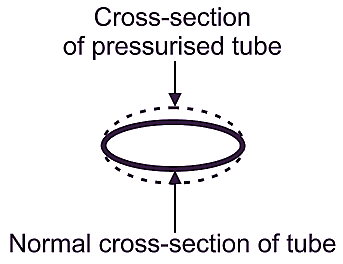
(b) X-X Section
Fig. 1: Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge
Construction of Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge
- Bourdon Tube:
- The primary sensing element.
- A curved, hollow, oval-shaped tube made of materials like brass, phosphor bronze, or stainless steel.
- One end is fixed and connected to the pressure inlet; the other end is free and closed.
- Connecting Link:
- A mechanical link connecting the free end of the Bourdon tube to the geared sector.
- Geared Sector:
- A toothed, arc-shaped component that converts the linear movement of the Bourdon tube into rotational motion.
- Pinion:
- A small gear mounted on the same axis as the pointer.
- Engages with the geared sector to rotate the pointer.
- Pointer and Dial:
- The pointer indicates pressure on a circular scale (dial) graduated in appropriate pressure units.
- Casing:
- The entire mechanism is enclosed in a protective casing, often made of metal or plastic, with a transparent front for visibility.
Working of Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge
When the fluid (either liquid or air or gas), whose pressure is to be measured, is made to flow through bourdon tube, its original elliptical cross-section tends to become circular. This makes the tube straighten itself out with an increase in radius of curvature. This causes the free end of the tube to move/displace. This displacement of free end of tube creates angular movement in rack and pinion through mechanical linkage. The pointer, which is pivoted on the pinion, moves over a calibrated scale, which directly indicates pressure in terms of N/m2 or ‘m’ head of mercury.
Advantages of Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge
- Low cost.
- Simple construction.
- Available in wide variety of range.
- High accuracy as compared with cost.
Disadvantages of Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge
- Low spring gradient.
- Highly sensitive to shock, vibration and Hysteresis.
- Slight lag in pointer movement due to repeated pressure cycling can reduce precision over time.
- Overpressure can permanently deform the Bourdon tube, leading to inaccurate readings.
- Not suitable for dynamic or rapidly fluctuating pressure measurements.
Applications of Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge
The Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge is widely used across various industries for measuring pressure due to its reliability, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness.
- Monitoring pressure in boilers, steam turbines, and heat exchangers in power plants.
- Measuring pressure in pneumatic systems and hydraulic systems in manufacturing industries.
- Used in process industries (chemical, petrochemical, and oil & gas) for pressure monitoring of fluids and gases in pipelines and reactors.
- Monitoring pressure in ship propulsion systems, including steam and diesel engines.
- Measuring pressure in ballast tanks and other fluid systems on vessels.
- Monitoring gas pressures in oxygen cylinders and anesthesia machines.
- Checking pressure in medical compressors and pumps.
- Testing pressure in gas cylinders and storage tanks during maintenance.
- Calibration of other pressure-measuring devices in laboratories and workshops.
- Used in air compressors and water pumps for pressure control.
- Pressure monitoring in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems.
Factors to be Considered, While selecting Material for Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge
- Elastic characteristics suitable for pressure measurement.
- Range of measurement.
- Pressure of medium.
- Temperature of medium.
- Corrosive resistance of medium