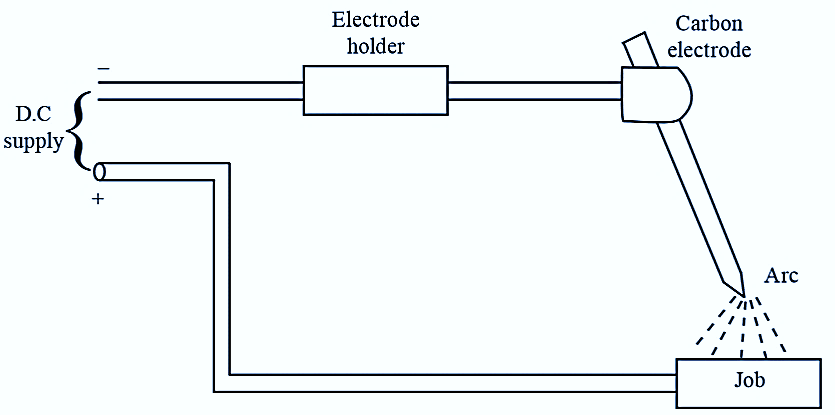
Figure. 1: Carbon Arc Welding.
In the Carbon Arc Welding process, the welding is accomplished by heating the workpiece (or job) with an electric arc, produced between the carbon electrode and the workpiece. A carbon or graphite rod is used as a negative electrode and the workpiece as positive. The carbon electrode generates lesser amount of heat, when compared to graphite at the electrode tip. It will not fuse and mix up with the workpiece. For this type of welding, D.C is preferred as no fixed polarity can be maintained in case of A.C.
The carbon electrode is held in the holder. The arc is struck instantly between the electrode and workpiece. Then, the electrode is moved away from the workpiece to a definite distance. The arc is allowed to impinge on the surface to be welded, till a molten pool is formed. Then, the holder is steadily moved along the joint. Filler metal and flux may or may not be used, depending upon the type of joint and the material to be welded. CO2 that is used for welding must be free from moisture because it effects the formation of porosity in the weld.
Advantages of Carbon Arc Welding
- CO2 gas is inexpensive and capable for producing high quality welding.
- The equipment and operation costs are low
- Less skilled operator is required
- Automation of process can be easily obtained
- Workpieces are subjected to low distortion.
Limitations of Carbon Arc Welding
- CO2 is effective if the electrode contains manganese, silicon and also aluminium in sufficient quantities.
- The quality of weld is poor, as the carbon particles contaminates the weld and results in porous and brittle weld.
- It consumes large amount of current, as the current required to bring the workpiece to welding temperature is more.
- Its use is economical only when DC supply is employed.
- Excess CO2 fumes are harmful to the operator.