The Cartesian coordinate robot is also referred to as rectilinear robot or X-Y-Z robot of the spherical configuration because it is equipped with three sliding joints for assembling XYZ axes. The Cartesian coordinate robot arm and body configuration is shown in Fig. 1. The arm movement of a robot using the Cartesian configuration can be described by three intersecting perpendicular straight lines, referred to as the X, Y and Z axes. In the Cartesian coordinate configuration, the robot arm has following movements:
- Linear movement that allows vertical lift to the arm because of one linear joint.
- Two sliding movements those are perpendicular to each other because of two orthogonal joint.
This configuration robot will process in a rectangular workspace by means of this three joints movement. Because movement of the arm can start and stop simultaneously along all three axes, motion of the tool tip is smoother. This allows the robot to move directly to its designated point, instead of following trajectories parallel to each axis.
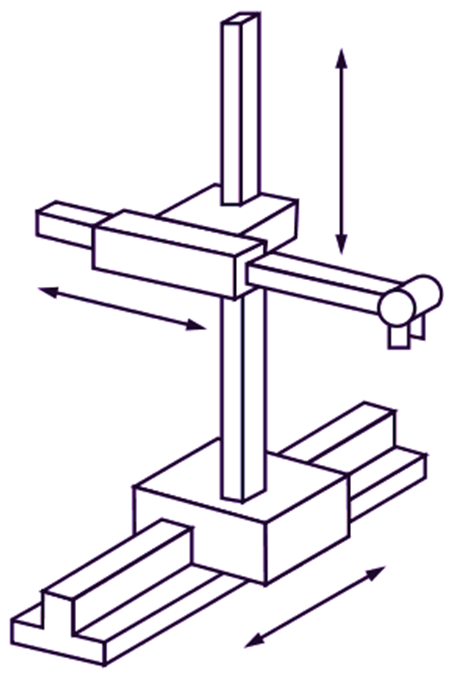
Fig. 1: Cartesian Robot
Advantages of Cartesian Robot Configuration
The Cartesian Robot Configuration has following advantages:
- It has high load carrying capability.
- It provides a rigid structure and also a high degree of mechanical rigidity and accuracy.
- It can produce high repeatability with least error and at a good speed.
Limitations of Cartesian Robot Configuration
The Cartesian Robot Configuration has following limitations:
- It has a small and rectangular work envelope.
- It has a reduced flexibility.
Applications of Cartesian Robot Configuration
The Cartesian co-ordinate configuration finds applications in inspection, assembly, machining operations, welding, finishing operations etc. This configuration also get a name of Gantry Robot as it is capable of carrying high loads with the help of its rigid structure and this weight lifting capacity does not vary at different locations within the work envelope.