Generator is the most important and costly equipment in power system. The cost is high because the alternator unit is accompanied by prime mover, excitation system, voltage regulator, cooling system etc. The protection system provided should therefore becomes elaborate and complex. As soon as the fault develops on an alternator, it should be immediately disconnected from the other generating plant to avoid the faulty machine from being fed by other sources. Following Table 1 shows abnormal conditions (faults) and protection schemes employed for the alternator.
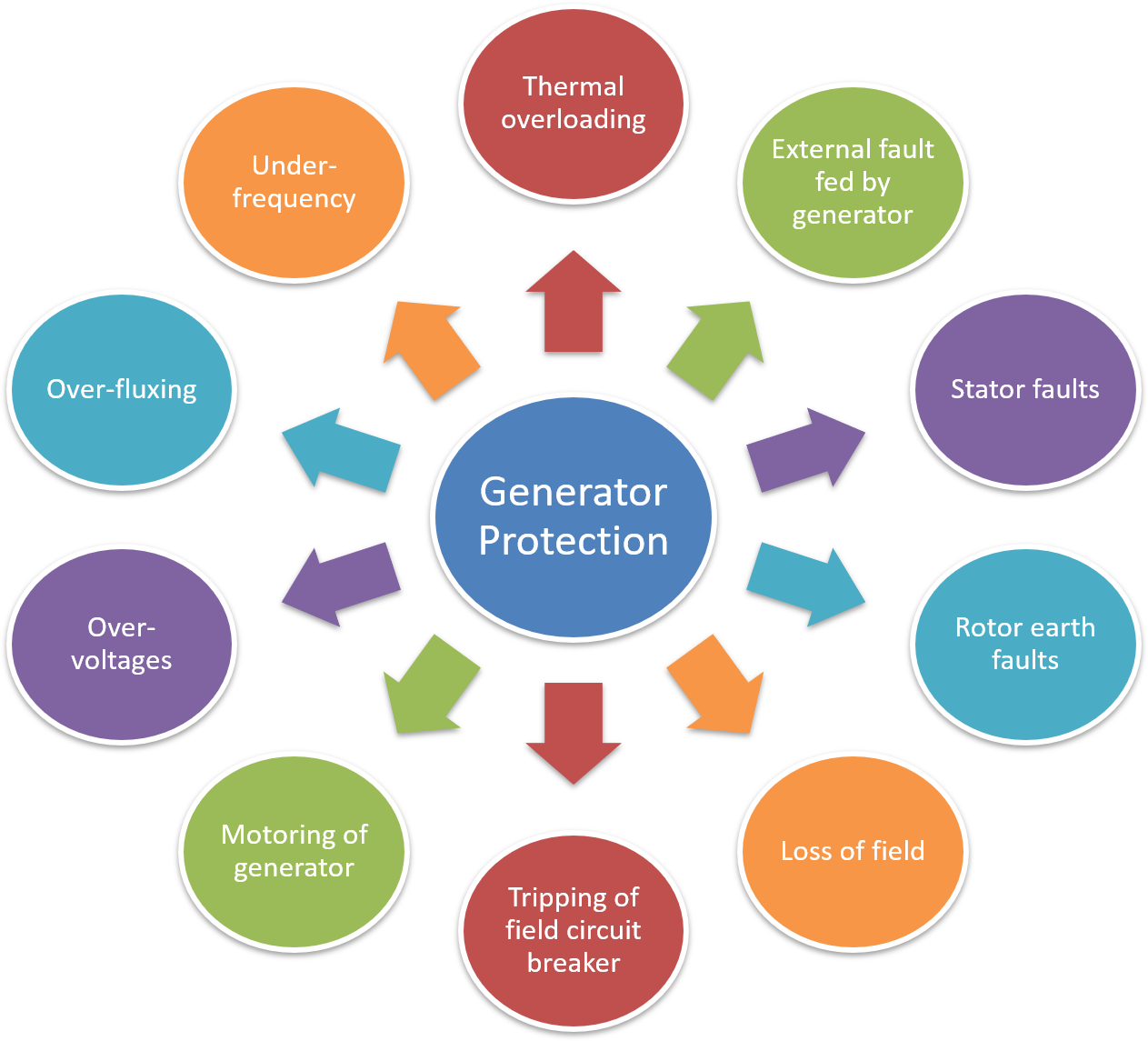
Table 1
| Abnormal Condition | Effect | Protection |
| Thermal overloading:
(i) Continuous over-loading. (ii) Failure of cooling system. |
Overheating of stator winding and insulation failure. | Thermocouples of resistance thermometer embedded in stator slots and cooling system. Stator overload protection with overcurrent relays. |
| External fault fed by generator | Unbalanced loading stresses on winding and shaft, excessive heating for prolonged short circuit. | Negative phase sequence protection for large machines. Overload protection for small generators. |
| Stator faults:
(i) phase to phase (ii) phase to earth (iii) inter-turn. |
Winding burn-out, welding of core laminations, shut down | Biased differential protection, sensitive earth fault protection, inter-turn fault protection |
| Rotor earth faults | Single fault does not harm second fault, causes unbalanced magnetic forces causing damage to shaft, bearings. | Rotor earth fault protection. |
| Loss of field:
Tripping of field circuit breaker |
Generator runs as induction generator deriving excitation currents from bus-bar. Speed increases slightly. | ‘Loss of field’ or ‘Field failure’ protection. |
| Motoring of generator. When input to prime mover stops, the generator draws power from bus-bars and runs a synchronous motor in the same direction. | Effect depends upon type of prime mover and the power drawn from the bus during motoring. | Reverse power protection by directional power relays direct the reversal of power. |
| Over-voltages | Insulation failure | Lightning arrestors connected near generator terminals. |
| Over-fluxing of generator transformer and auxiliary transformer. | Heating of core relay | Connected in voltage regulator circuit generator. |
| Under-frequency | Failure of blades of steam turbines. | Frequency relays. |