A Pirani gauge is a device used to measure low pressure or vacuum levels.
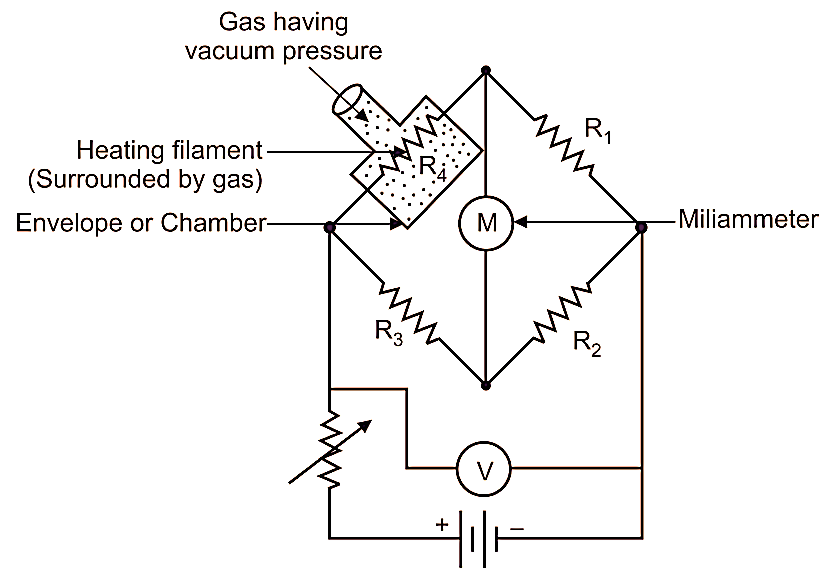
Fig. 1: Pirani Gauge.
Working Principle of Pirani Gauge
Pirani gauge works on the principle that, “Thermal conductivity decreases with decreasing pressure.” The heat loss from a heated filament to the surrounding gas is proportional to the pressure of the gas. As the pressure changes, the filament’s temperature and resistance change, which is then measured to determine the pressure.
Construction of Pirani Gauge
Pirani gauge is also a thermal conductivity gauge, like thermocouple vacuum gauge. Pirani gauge consists of a heating filament enclosed in chamber. Heating element or filament is a platinum wire, which forms an arm of Wheatstone bridge. Refer the Fig. 1.
- Heating Filament: Typically made of tungsten or platinum, placed inside the vacuum system.
- Wheatstone Bridge: Used to detect changes in the filament’s resistance due to pressure variations.
- Vacuum Chamber: Encloses the heating filament and allows the gas to surround it.
- Milliammeter and Voltmeter: Measure the output signal corresponding to pressure changes.
Working of Pirani Gauge
The heating filament is heated by a constant current. Therefore, Temperature of heating filament will increase. For a given magnitude of current, temperature of heating filament depends upon rate of heat dissipation to surrounding medium, i.e. Gas by means of conduction and convection. After heating, the heating filament is placed or connected to vacuum or low-pressure surrounding gas medium. Now since, the heating filament is surrounded by vacuum or low-pressure gas, then thermal conductivity (i.e. ability of heating filament to give away heat to surrounding medium) of heating filament will also decrease. In such condition, the heating filament will be hotter. Change in temperature of heating filament will lead to change in resistance of wire, which can be measured by using Wheatstone bridge. The current under unbalanced condition is indicated by an ammeter in mA. We obtain an output reading, which is a function of temperature of heating filament and hence, the function of pressure of surrounding gas.
Advantages of Pirani Gauge
- Rigid Construction.
- Can read very low pressure from 1.33 × 10-6 bar to 1.33 × 10-3 bar (i.e. 0.133 Pa to 13.3 Pa).
- More accurate as compared to thermocouple vacuum gauge.
- Shows linear characteristic for most of its operating range.
- Portable.
Disadvantages of Pirani Gauge
- More expensive than thermocouple type gauges.
- Needs individual and frequent calibration for different gases.
- Dependent on electrical power to operate.
- It has poor transient response. In short, it takes several minutes for obtaining thermal equilibrium at low pressure.
Application of Pirani Gauge
- Used to measure low pressure of range 0.133 Pa to 13.3 Pa, i.e. 1.33 × 10-6 bar to 1.33 × 10-3 bar.
- Vacuum Systems: Monitoring and controlling pressure in vacuum chambers.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: Used in processes requiring precise vacuum control.
- Thin Film Deposition: Ensures optimal conditions for coating applications.
- Industrial Processes: Used in food packaging, pharmaceuticals, and other industries requiring vacuum environments.