Gear drive is used, when centre to centre distance between driver and driven shafts is very small. Gears are defined as, “toothed wheels, which can transmit power and motion from one shaft to another shaft by means of successive engagement of teeth. ”
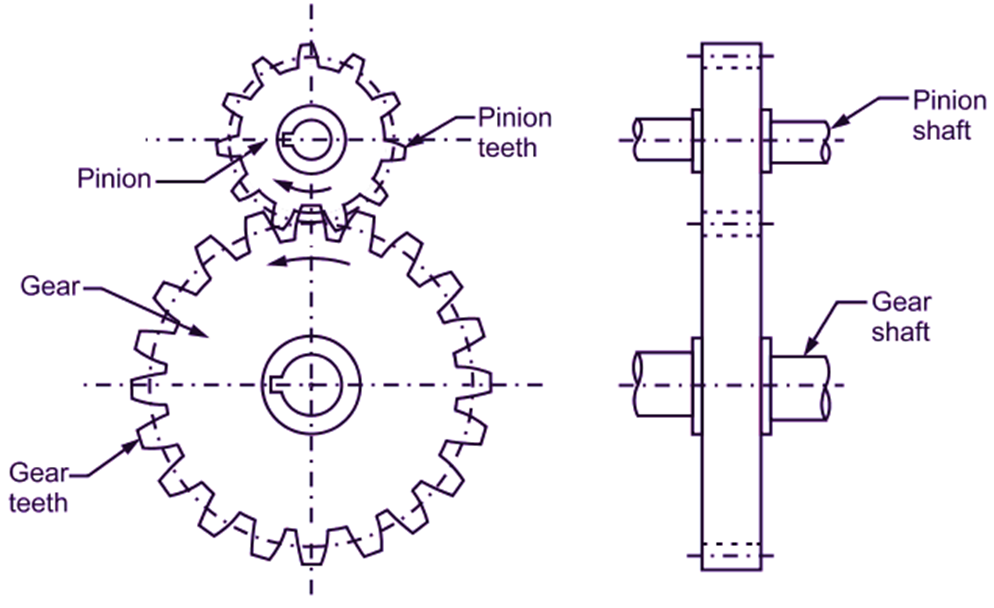
Fig. 1: Gear Drive
It is important to note that, both the gears, which are engaged, always rotate in opposite direction. Gear drive consists of two wheels. The smaller wheel is called as pinion and the larger wheel is called as gear. Refer Fig. 1. In gear drive, slip is absent. Therefore, it gives exact and uniform velocity ratio. Due to this ability of maximum power transmission and exact velocity ratio, gear drive is called as perfect positive drive.
Advantages of Gear Drive
- Exact velocity ratio.
- High efficiency.
- Compact layout.
- Ability of transmitting large power.
- Reliable service.
Disadvantages of Gear Drive
- Manufacturing of gears requires special tools and equipment. This leads to high production cost.
- Complicated manufacturing process.
- Gear drive requires precise alignment of shafts.
- Costly lubrication system is required for smooth operation and longer life of gear teeth.
- Any error induced in gear during the process of teeth cutting leads to noisy operation with severe vibrations.
Applications of Gear Drive
- Gear box of vehicle,
- Machine tools,
- Dial indicator,
- Gear mechanism of wrist watches,
- Differential mechanism of automobile,
- Cement mixing unit.
Difference between Gear Drive and Belt Drive
| Comparative Point | Gear Drive | Belt Drive |
| Power transmitted | Suitable for high power transmission, when the distance between two shafts is short. | Suitable for moderate power transmission, when the distance between two shafts is large. |
| Torque transmitted | More. | Less. |
| Space required | Requires less space due to small centre to centre distance between the shafts. | Requires more space due to large centre to centre distance between the shafts. |
| Velocity ratio | Perfect velocity ratio may be obtained. | Perfect velocity ratio may not be obtained due to effect of slip. |
| Noise | Operation is noiseless. | Operation is noisy. |
| Manufacturing | Complicated and difficult. | Simple and easy. |
| Cost | More. | Less. |