Process instrumentation is a branch of engineering, which deals with various types of instruments to record, monitor, indicate and control of various physical parameters such as temperature, pressure, PH value, level etc.
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF PROCESS INSTRUMENTATION SYSTEM
The Fig. 1 shows a simple block diagram of process instrumentation.
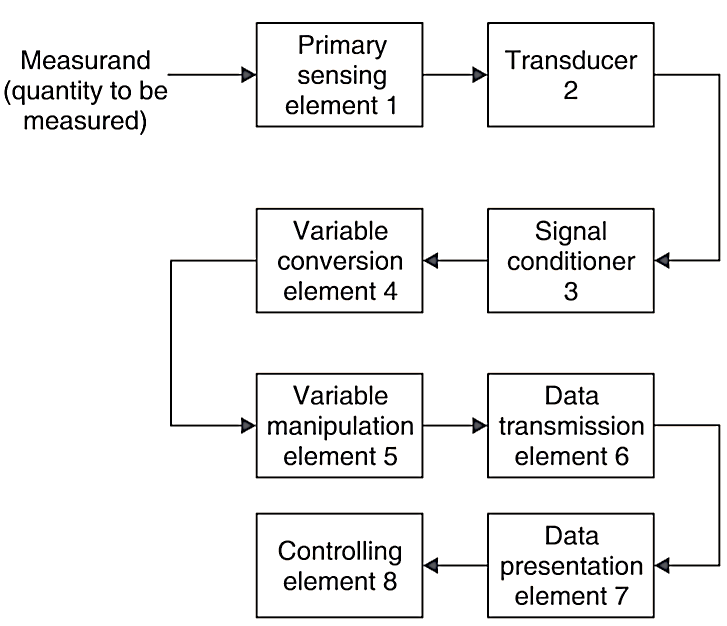
Fig. 1. Block diagram of process instrumentation
1. Primary Sensing Element: The quantity under measurement (called measurand)becomes the input to the primary sensing element.
2. Transducer: In case, the primary sensing element has a “non-electrical” input, it is converted into an electrical signal by means of a Transducer. This is a device, which converts an energy in one form into the other form.
3. Signal Conditioner: This device converts the output of transducer into a quantity suitable for the next block. The process involved in signal conditioning may be rectification, modulation etc.
Note that either a transducer or a signal conditioner is required after the primary sensing element.
4. Variable Conversion Element: Sometimes the electrical signal obtained from the above needs further conversion. e.g. If the input is in analog form and the next stage can accept only in digital form, in that case in this block, we will require an “analog to digital converter” (ADC).
5. Variable Manipulation System: This block further “manipulates” the signal obtained into a fonu acceptable to the next block e.g., it can amplify the signal to the required level.
6. Data Transmission Element: When elements of an instrument are to be physically separated, it becomes necessary to transmit data from one element to the other. This job is performed by “data transmission element”.
7. Data Presentation Element (Display): This displays the quantity under measurement in a suitable fonìi e.g., in analog or digital. which can be understood by the observer or operator.
8. Controlling element: In case, a “control device” is employed, then it becomes necessary to apply some “feedback” to the input system.
Note that all the stages may not be required in all processes, moreover their sequence may also be changed as per the need.
OBJECTIVES OF PROCESS INSTRUMENTATiON
A typical process instrumentation system may have the following objectives:
1. Monitoring of Process: Some instrumentation process monitors the process or operations going on. For example, ammeter monitors the value of current flowing in the system at an instant.
2. Control of Process: In order to control a signal in a process, the same is continuously measured then this is compared with the “reference or desired sial” and the “error signal” is amplified to operate the “actuator” as shown in Fig. 2. This corrective action goes on till the output is same as required, at this stage, there is no reference signal and the actuator stops working.
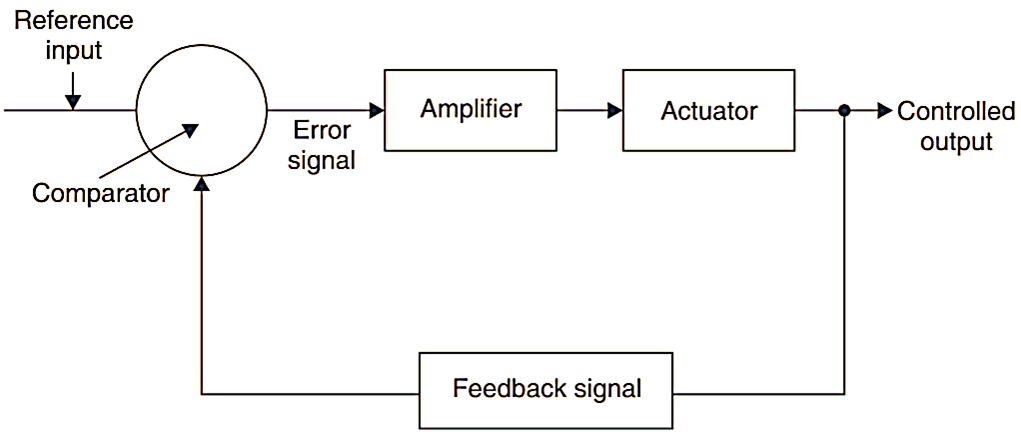
3. EngIneering Analysis: Some instrument processes carry out research work such as,
- Improvement in the process
- Development of mathematics model
- Determination of system parameters
- Storage of data