In this topic, you study Self Induction.
The property of the circuit by virtue of which an e.m.f. is induced in the same circuit in which the current is changed is known as self inductance. This induced e.m.f. is known as self induced e.m.f. and the phenomenon is known as self induction.
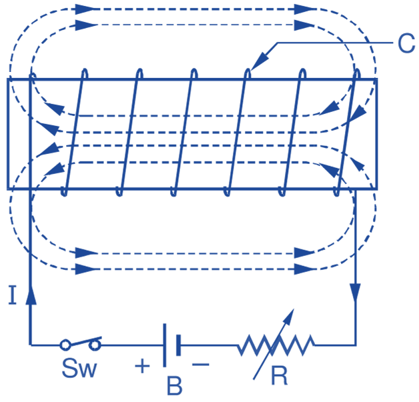
Fig.1: Self Induction.
Fig. 1 shows a coil (C) having N turns connected in series with a switch (Sw), a battery (B) and a variable resistor (R). On closing the switch, let the current in the coil be I amperes. The coil will have its Own flux threading through it due to passage of this Current. The lines of force which form complete loops as indicated are said to be linked with the coil. If φ webers is the resultant flux linking with the coil, then the total flux linkages (product, flux × turns) will be Nφ.
If now the current flowing through the coil is changed by varying R, then the number of lines of force linking with the coil will also change. Hence, according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, an e.m.f. is induced in the coil. This phenomenon is known as self-induction. The emf induced in the coil is, therefore, called a self induced emf or emf of self induction. This e.m.f. lasts till the current in the coil is changing.
The phenomenon of self-induction is most important in alternating current circuits, since in these, the current is changing from instant to instant. The action of the choke (an inductive coil) used in a fluorescent tube or filter circuit of a rectifier depends on self-induction.
Uses: The phenomenon of the self induction is used for the followings:
- In autotransformer.
- In lightning arrester.
- In fluorescent tube for starting purpose, i.e., choke.
- In fan regulators.
- For smoothing the d.c. pulsating values.