In this topic, you study Shaded Pole Induction Motor – Working Principle, Construction, Diagram, Characteristic & Applications.
A shaded pole motor is a self start single-phase induction motor. This property of self start is achieved by splitting the phase by induction principle using shaded ring. So, this motor is thereby named as shaded pole motor.
Construction of Shaded Pole Induction Motor
Shaded Pole Motor has a rotor (G) of squirrel cage type and the stator (M) with salient poles (P1, P2). In addition to its own exciting coil (C1, C2) each pole carries a copper shading coil, band or ring (B1, B2) on one of its unequally divided parts (Fig. 1). Production of torque in this type of motor can be explained as below:
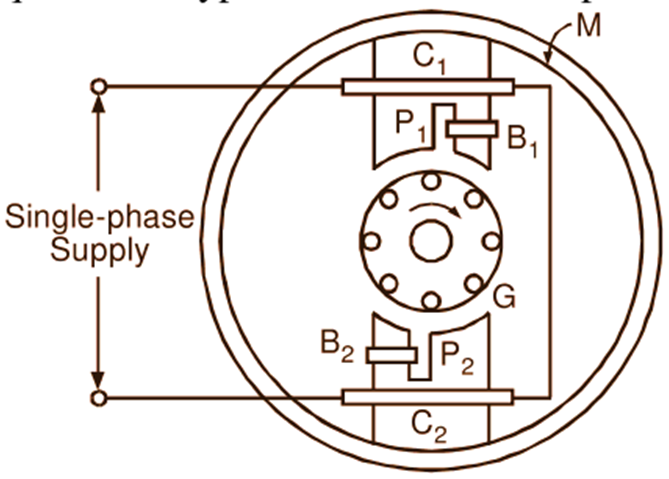
Fig. 1: Shaded pole type, single-phase induction motor
Working Principle of Shaded Pole Induction Motor
When the single-phase supply is given to the stator winding, an alternating flux is produced. Fig. 2 (a) shows the waveform for the sinusoidally varying alternating stator current and the flux produced by it. The distribution of this flux in the pole area is greatly influenced by the magnitude of the induced e.m.f. in the shading ring by transformer action. To examine this, let us consider three instants of time, namely t1, t2 and t3 on the waveform for the stator current. At the instant when t = t1 the rate of rise of stator current and hence that of stator flux being high, large e.m.f. is induced in the shading ring. The direction of this induced e.m.f. and hence the current set up by it in the short-circuited shading ring will be such as to oppose the rise of the stator current (Lenz’s law). The opposing flux produced by the induced current in the shading ring makes stator flux distribution in the pole area non-uniform. There is crowding of flux in the non-shaded portion of the pole and magnetic axis (MA) lies along the middle of this part (Fig. 2 b).
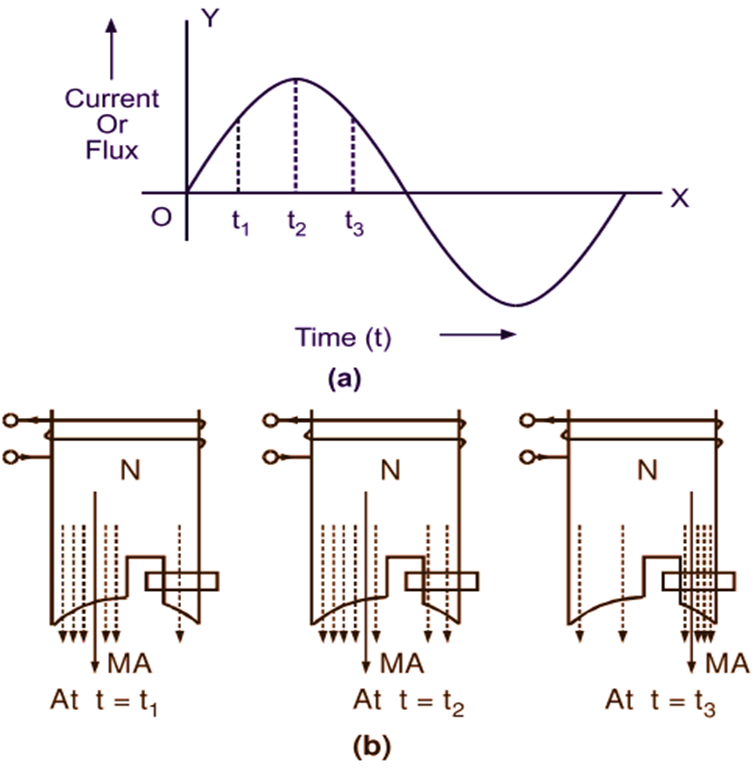
Fig. 2. Production of torque in a shaded pole type, single-phase induction motor
At the instant when t = t2, even though the stator current is at its maximum, the rate of change of current and hence that of stator flux is minimum. Under this condition, the induced e.m.f. in the shading ring is negligible and there being practically no opposing flux, stator flux distribution in the pole area will be uniform. As a result of this, the position of magnetic axis (MA) is shifted towards the centre line of the pole. At the instant when t = t1, the stator current which is rapidly decreasing, again induces large e.m.f. in the shading ring. The direction of this e.m.f. and resulting induced current in the shading ring is now such as to oppose the decrease in the Stator current. The flux produced by a current in the shading ring, therefore, strengthens the flux in the shaded portion of the pole. Consequently, the magnetic axis gets shifted to the middle of the shaded part of the pole. This sequence is repeated even in the negative half cycle of the stator current. This periodic shift in the stator flux from the unshaded to the shaded part of the pole gives to some extent rotating field effect and produces a low-starting torque.
Torque Speed Characteristic of Shaded Pole Induction Motor
Fig. 3 shows the typical torque-speed characteristic of this type of motor. The starting torque of this type of motor is only about 40 to 50
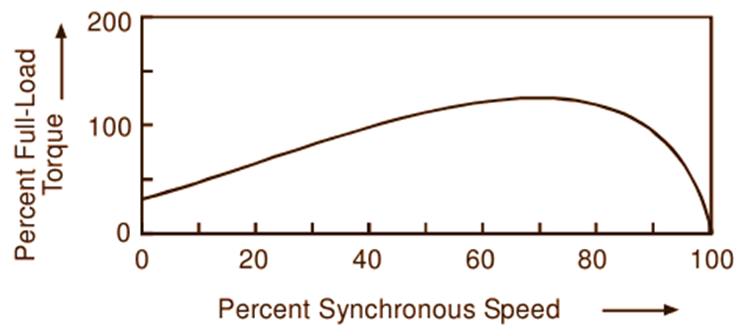
Fig. 3: Typical torque-speed characteristic of a shaded pole motor
Reversal of Rotation of Shaded Pole Induction Motor
The shaded pole motor generally has a definite direction of rotation which cannot be reversed. However, if such reversal is essential, it can be achieved by providing two shading coils, one on each end of every pole. Then by open-circuiting one set of shading coils and short-circuiting the other set, desired direction of rotation can be achieved.
Applications of Shaded Pole Induction Motor
Due to absence of centrifugal switch, construction of the motor of this type is simple and robust. However, the motor has low efficiency and low power factor and its starting torque is very poor. Therefore, such motors are suitable for only small powers and where the starting conditions are easy e.g. they are commonly employed for driving small fans, motorised valves, recording instruments, record players, gramophones, toy motors, photocopying machines, hair dryers, advertising displays, etc. The motors may be continuously rated or intermittently rated. Intermittently rated motors carry a time rating, generally 5, 15, 30 or 60 minutes).
Limitations of Shaded Pole Induction Motor
The following are the limitations of shaded pole motors.
- Compact size
- Less power rating
- Poor starting torque
- Less power factor
- Less efficiency due to losses in the shading ring
- Complexity in speed reversal.