Unbonded strain gauges do not have backing material, so strain is transferred to the resistance wire directly.
Construction of Unbonded Strain Gauge
Unbonded strain gauge consists of a fixed frame and a movable frame (armature). Movable frame is connected to a rod or bar, which is able to move in either direction under the application of force and strain to be measured. Four strain gauge wires are made up of platinum tungsten alloy having high tensile strength. They have uniform cross-sectional area and equal length and they are connected in such a manner that; one end of each wire is connected to fixed frame and another end is connected to armature or movable frame. Refer wires aa’, bb’, cc’ and Cd’ in the Fig. 1. These wires form a Wheatstone’s bridge circuit and the galvanometer is calibrated in terms of quantity being measured.
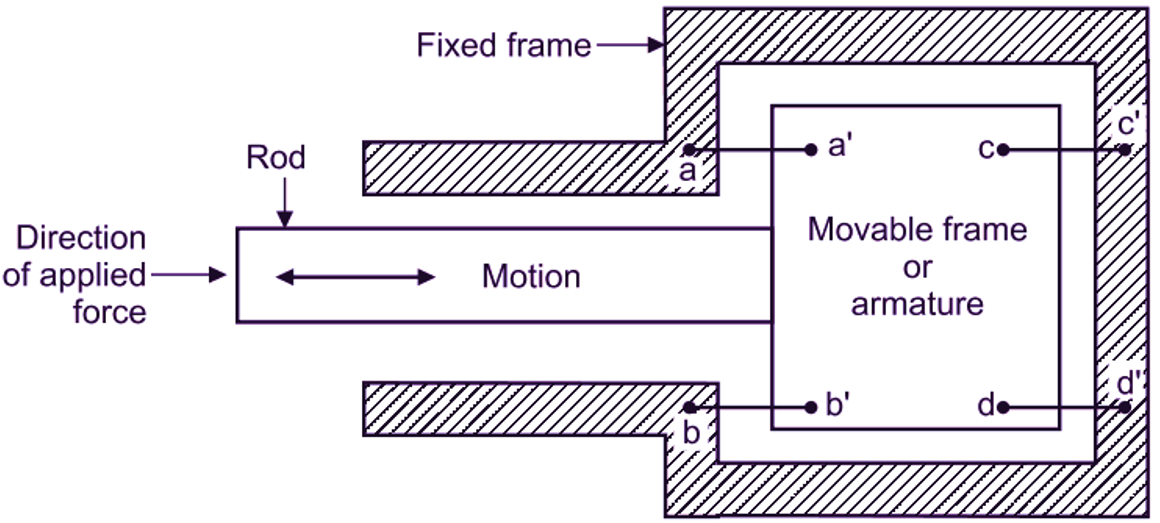
(a) Arrangement of Unbonded Strain Gauge
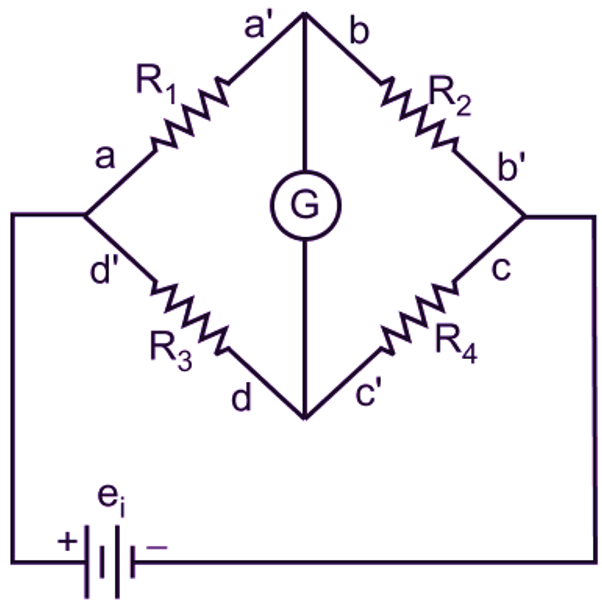
(b) Electrical Circuit
Fig. 1: Unbonded Strain Gauge
Working of Unbonded Strain Gauge
Initially, no force is applied. At this condition of preloading, it is assumed that, all the wires are equally stretched. Since there is no force, there will be no stress and strain. The resistance offered by each strain gauge wire is equal in magnitude. Therefore, the galvanometer shows null position (i.e. zero reading). When force to be measured is applied on the rod, then due to applied force, the rod and hence, armature gets moved (say rightwards). Due to this movement of armature, the length of aa’ and bb’ increases (tension), whereas, length of cc’ and dd’ decreases (compression). Due to change in lengths, the resistances of strain gauge wires are changed, which causes unbalancing of Wheatstone’s bridge. The galvanometer reading is directly calibrated to read the magnitude of displacement of rod or strain and hence, force applied.
Advantages of Unbonded Strain Gauges
- Simple in construction.
- Freedom from faulty insulation.
- Small creep.
- Low hysteresis.
- Due to absence of organic substances, they can be used in high temperature installations.
Disadvantages of Unbonded Strain Gauge
- High cost.
- poor heat dissipation.
- Very low sensitivity.
- Resistance of contact lead decreases accuracy.
Applications of Unbonded Strain Gauge
- It is used for measurement of force, strain etc.
- It is used for measurement of pressure, displacement etc.
- In accelerometers.