In this topic, you study Universal Motor – Types, Construction, Diagram Applications & Characteristics.
Universal motors are small capacity series motors designed to operate on either direct current or single phase alternating current supply of approximately the same voltage, with nearly similar operating characteristics. Normally the frequency of the ac supply used is upto 50 Hz. A side-sectional view of a universal motor shown in Figure 1.
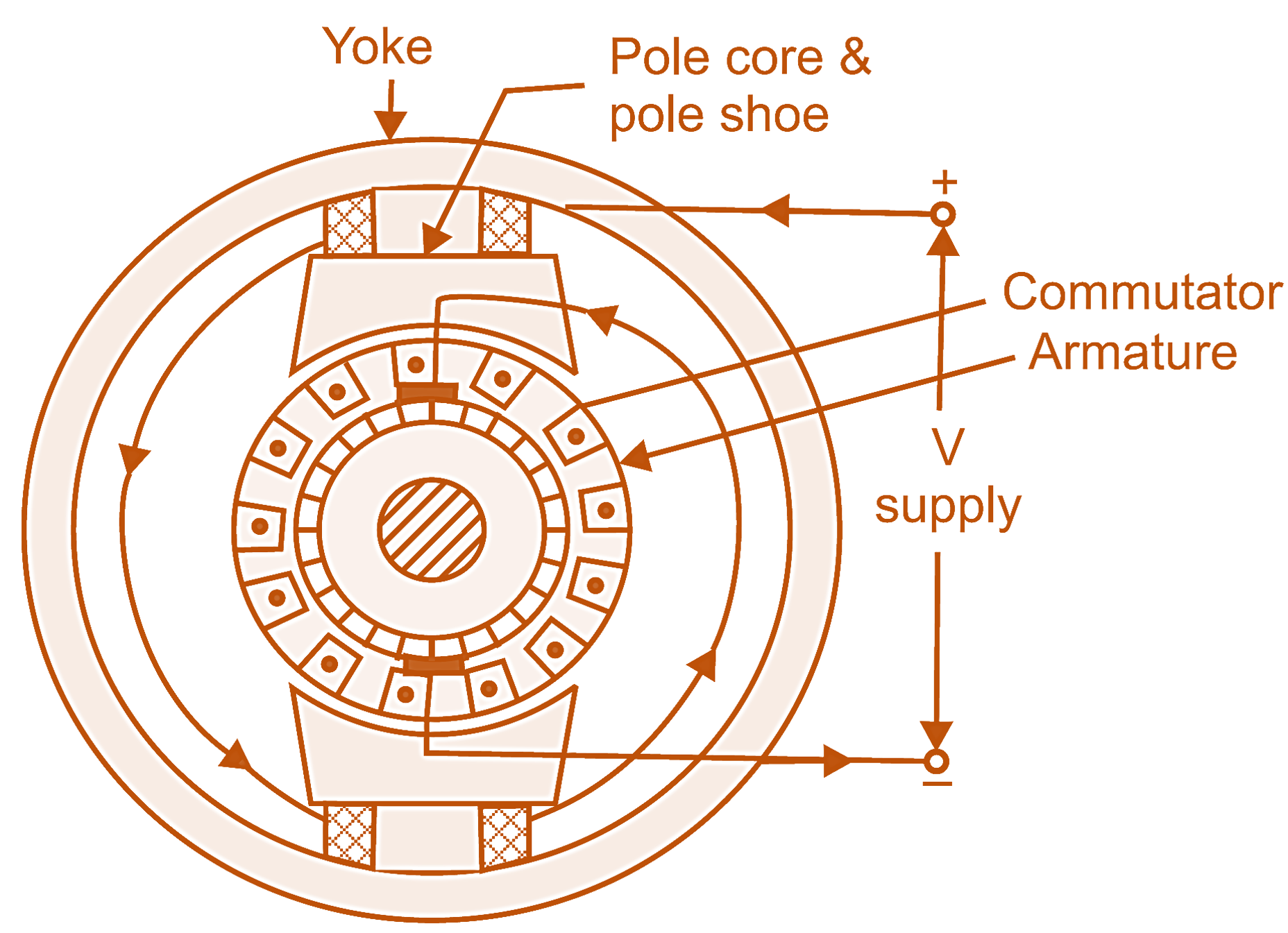
Fig. 1: Side-sectional view of a universal motor
Constructional Features and Types of Universal motor
Two types of universal motors are in use, namely, non-compensated and compensated. The non-compensated motor is usually built with concentrated or salient poles (Fig. 2). On the other hand, the compensated motor has distributed field windings (main field and compensating winding). Hence, the stator of such a motor resembles to that of a split-phase induction motor. Both these types of motors have a wound armature similar to that of a small dc motor. Fig. 3 shows the connection diagrams for these motors.
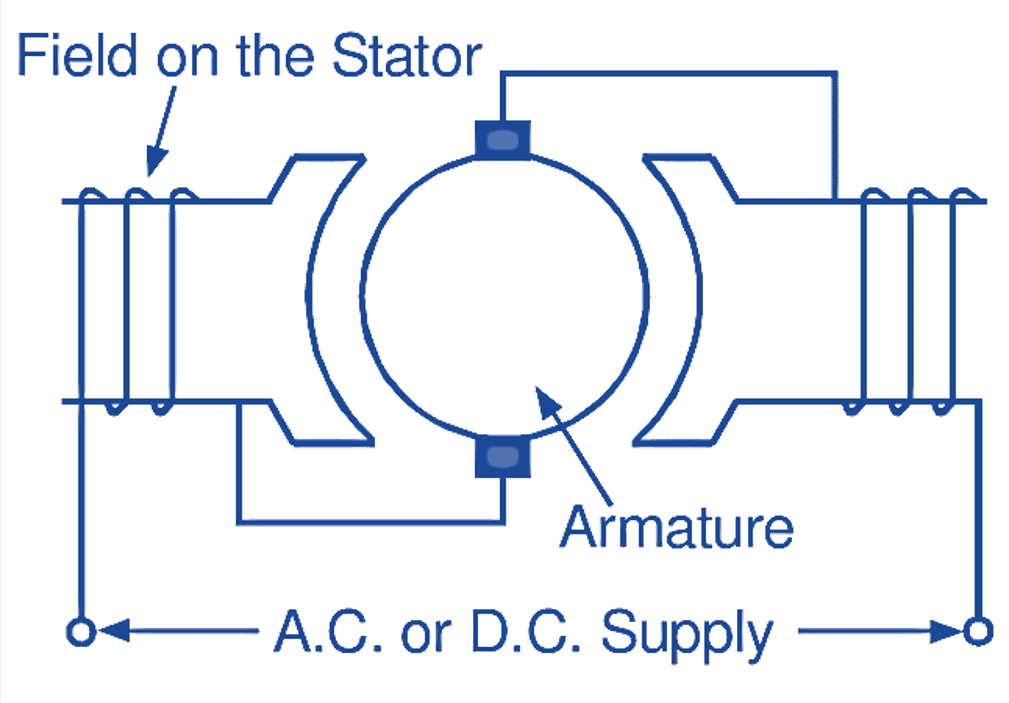
Fig. 2. Cross-sectional view of a non-compensated type universal motor
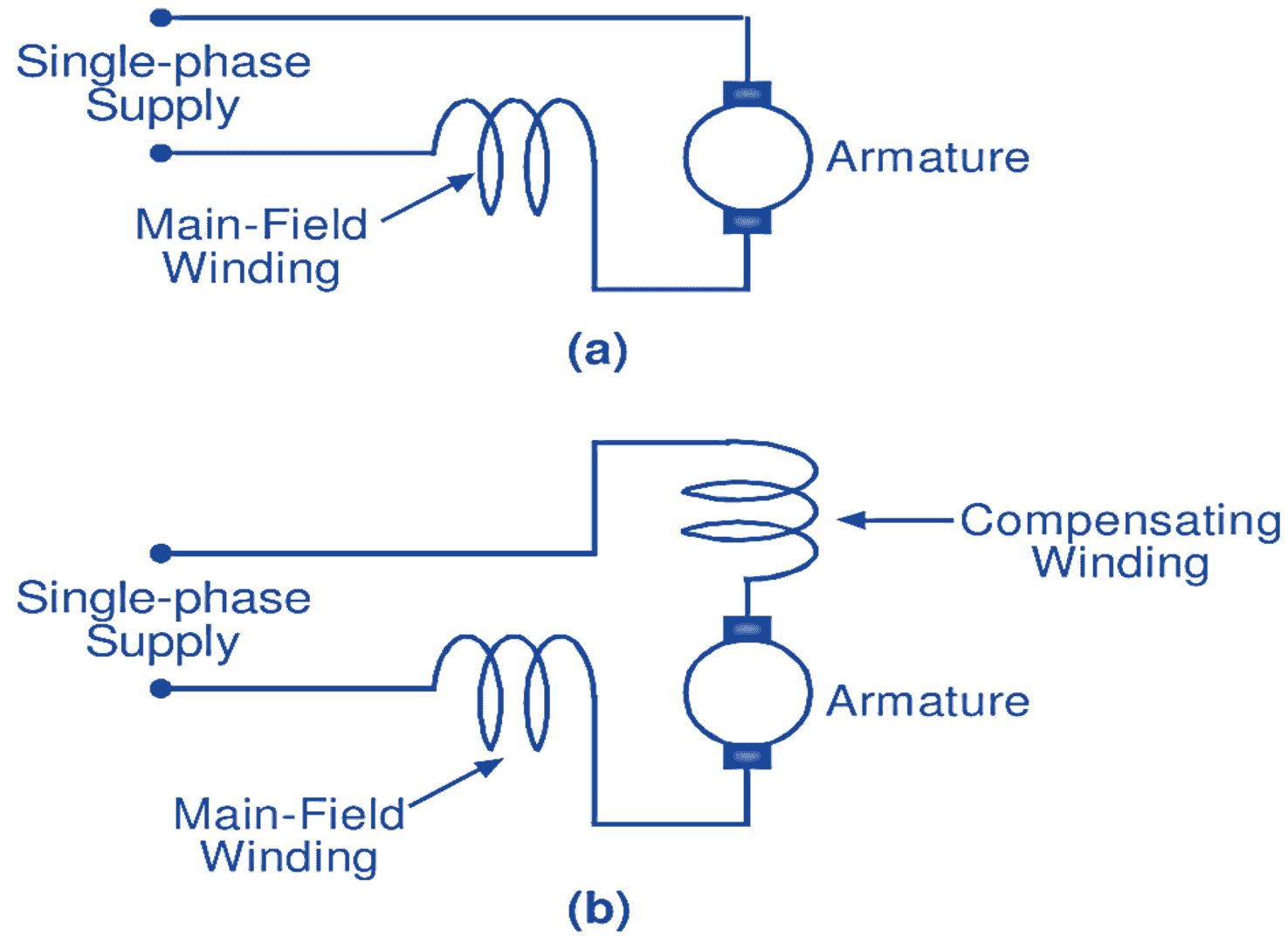
Fig. 3: Connection diagram of a universal motor (a) Non-compensated type, (b) Compensated type
Speed-Torque Characteristics of Universal motor
Speed-torque characteristics of a non-compensated universal motor, for both ac and dc operations, are shown in Fig. 4 (a). Similarly, Fig. 4 (b) shows the speed-torque characteristics of a compensated universal motor. From these figures, it will be observed that the compensated motor has better universal characteristics i.e. it has nearly the same operating characteristics on dc as well as on ac supply. Depending upon their ratings, universal motors are usually designed for full-load operating speeds ranging between 3000 to 20000 r.p.m. and if necessary, are provided with in built speed reduction gears for low speed applications. Normally, the friction and windage losses in small universal motors are sufficient to limit their no-load speeds to a safe value.
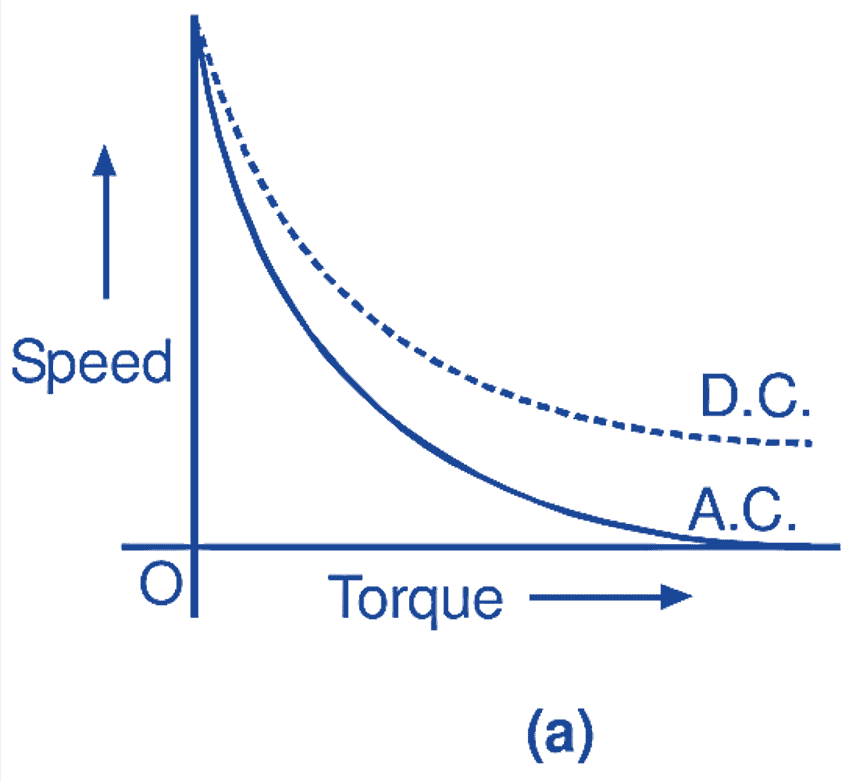
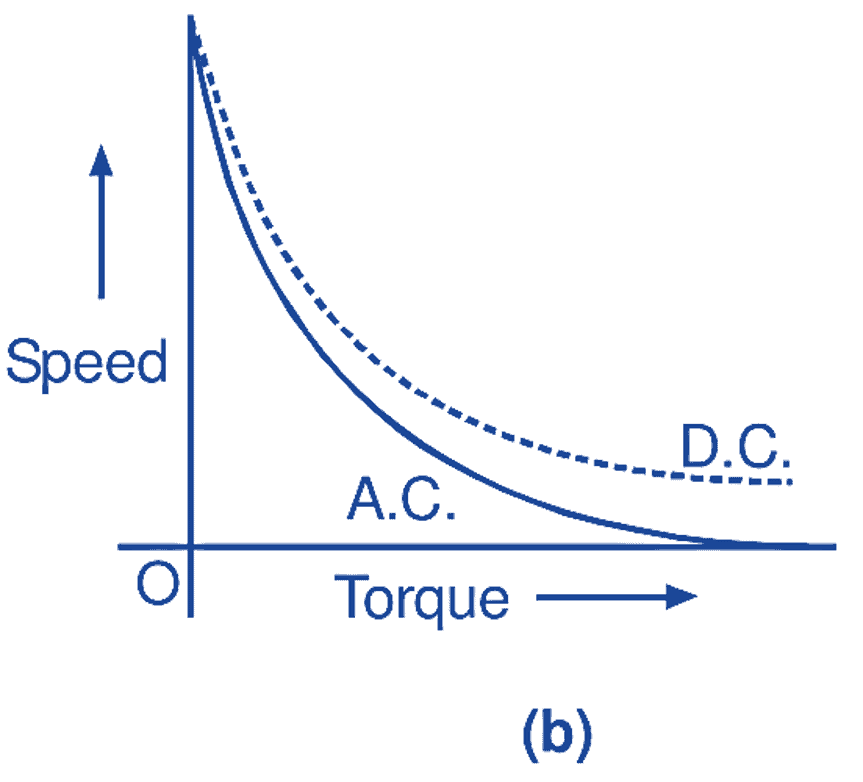
Fig. 4: (a) Speed-torque characteristics of a non-compensated universal motor, (b) Speed-torque characteristics of a compensated universal motor
Reversal of Rotation of Universal motor
For universal motors also, the reversal can be achieved by reversing the connections to either the field or the armature winding.
Applications of Universal motor
Even though compensated type universal motors have more superior characteristics, non-compensated motors are in more general use, particularly for small power applications. This is because they are less expensive and simpler in construction. Being high-speed motors, universal motors are smaller in size than other types for a given output. Hence, these motors are used where lightweight is important. High starting torque is also their outstanding feature. The usual applications of the universal motors are for domestic appliances like vacuum cleaners, food mixers, coffee grinders, sewing machines, hair driers, electric shavers, etc. Their other applications include blowers, mechanical computing machines, portable tools like drilling machines, and other small power drives.