In this topic, you study HRC Fuse Definition, Working, Diagram, Construction, Advantages, & Applications.
In an HRC (High-Rupturing capacity) fuse, the fuse element surrounded by an inert arc quenching medium is completely enclosed in an outer body of ceramic material having good mechanical strength. The unit in which the fuse element is enclosed is called fuse link. The fuse link replaced when it blows off. The pictorial view of an H.R.C. cartridge fuse is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1: The pictorial view of HRC Fuse
Construction of HRC Fuse
In its simplest form, an HRC fuse consists of a cylindrical body of ceramic metal usually stealite, pure silver element, pure quartz powder, brass end-caps, and copper contact blades. The fuse element fitted inside the ceramic body and space within the body surrounding the element is completely fitted with pure powdered quartz. The essential parts of a typical H.R.C. cartridge fuse are shown in Figure 2. The fuse element is either of pure silver or bimetallic in nature. Normally it has two or more joints of tin. Fuse element in the form of a long cylindrical wire is not used, because after melting, it will form a string of droplets and an arc will be struck between each droplets. The tin joint prevents the formation of a long arc. As the melting point of tin, much lower than that of silver from attaining high temperature.
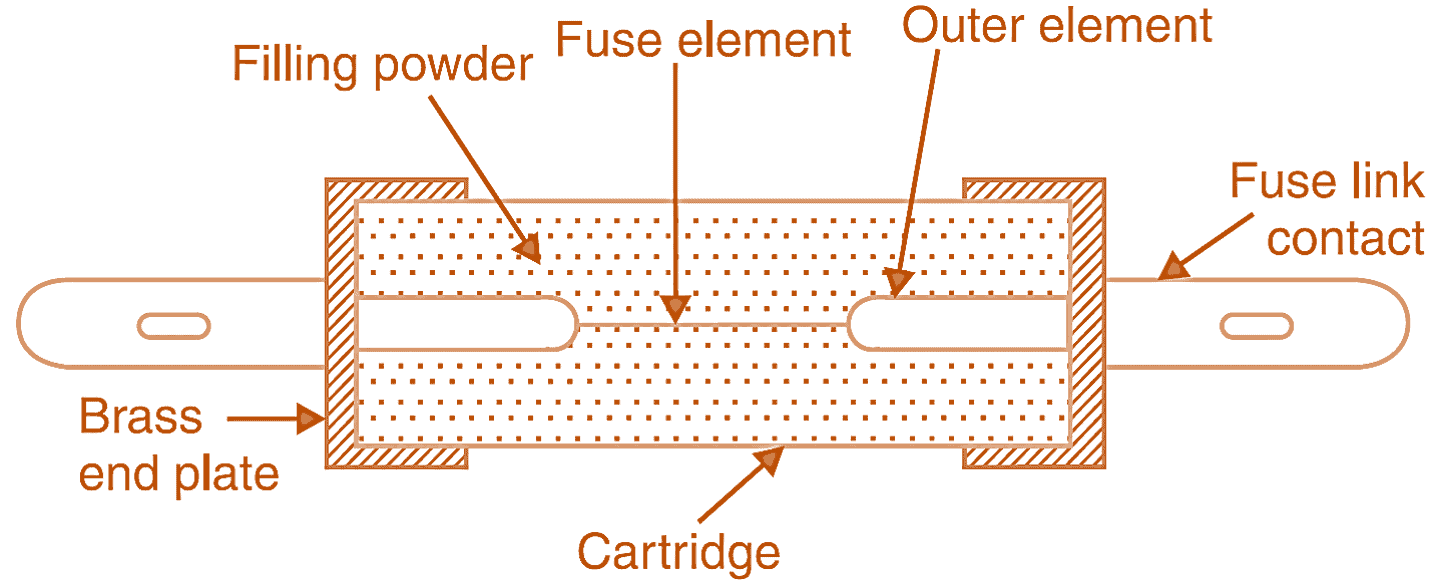
Figure 2: Essential parts H.R.C. cartridge fuse.
Working of HRC Fuse
When the fuse current increased due to fault, the fuse element melts before the fault current reaches its first peak. As the element melts, it vaporizes and disperses. During the arcing period, the chemical reaction between the metal vapour and quartz powder forms a high resistance substance which helps in quenching the arc. Thus the current is interrupted.
Advantages of HRC Fuse
The capability of clearing high values of fault currents.
- Fast operation.
- Non-deterioration for long periods.
- No maintenance needed.
- Reliable discrimination.
- Consistent in performance.
- Cheaper than other circuit interrupting devices.
- Current limitation by cut-off action.
- Inverse time-current characteristic.
Disadvantages of HRC Fuse
- It requires replacement after each operation.
- Inter-locking is not possible.
- It produces overheating of the adjacent contacts.
Applications of HRC Fuse
- Protection of cables.
- Protection of bus-bars.
- Protection of industrial distribution system.
- Contactor gear for the motor control system.
- Earth fault of low and high magnitudes.
- Semiconductor rectifiers and aircrafts.