Operating Range: 200°C to 1600°C.
Construction of Thermocouple
Thermocouple consists of two dissimilar metal conductors, which are electrically insulated except the hot junction. Refer Fig. 1. At hot junction, the conductors may be soldered or welded together. A refractory/metal sheath is used to protect thermocouple from mechanical damage. Two metal wires are extended as compensating leads or extension leads, which allows the meter or read-out device (Reference junction) to be placed at a considerable distance away from hot junction of thermocouple.
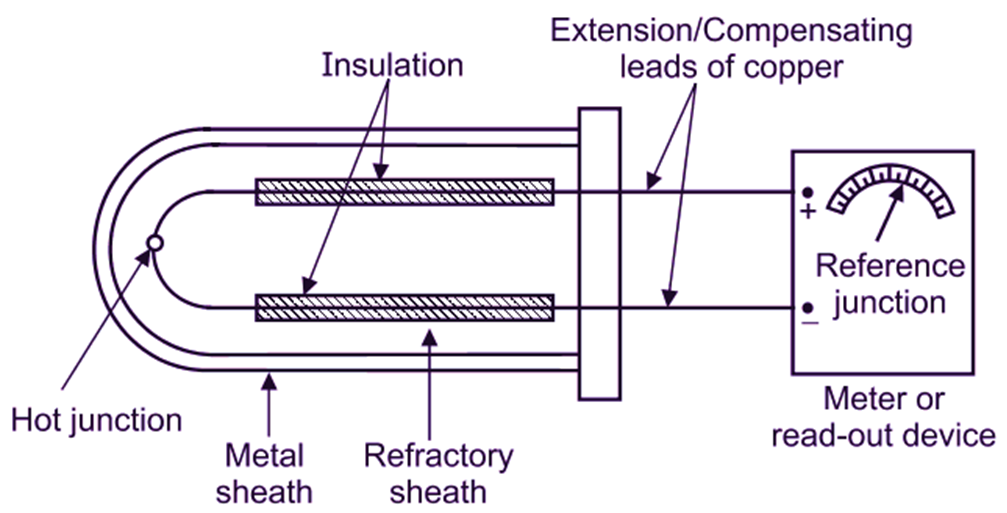
Fig. 1: Thermocouple
Working of Thermocouple
Thermocouple is mostly used to measure high temperatures in the furnaces. Junction kept near the hot source (furnace) is called as hot junction. Junction, at which, emf generated is measured, is called as cold junction (reference junction). The magnitude of emf generated depends upon the temperature difference of two junctions and type of metals used. Emf generated is directly calibrated in terms of temperature at read-out device or meter reader to indicate reading of temperature difference between two junctions.
Factors to be Considered While Selecting Thermocouples for Temperature Measurement
Various considerations in selection of thermocouples for measurement of temperature are:
- Construction, whether rigid.
- Strength.
- Atmospheric or ambient conditions.
- Type of insulation used.
- Sensitivity.
Desirable Characteristics of Thermocouple
- Emf generated per degree change in temperature must be sufficient for detection and measurement purpose.
- Temperature-EMF relationship should be linear and reproducible.
- Thermocouple should maintain its calibration without drift over a long period of time.
- Thermocouple should have a long life, so that, cost of measurement will be less for less frequent measurements.
- Thermocouple material should be able to withstand high and rapidly fluctuating temperatures.
- Thermocouple material should be highly resistant to oxidation, corrosion and contamination.
Desirable Properties of Thermocouple Material
- Thermocouple material should be able to give fast thermal response.
- Thermocouple material must have stability over a wide temperature range.
- Thermocouple material should not produce drift.
- Thermocouple material should have long life.
- Temperature-EMF relationship should be linear and reproducible.
- Thermocouple material should be able to withstand against high temperatures.
- Thermocouple material should be able to withstand against rapidly fluctuating temperatures.
- Thermocouple material should be highly resistant to oxidation, corrosion and contamination.
Thermocouple Materials
Commonly used materials are Copper, Iron, Platinum, Rhodium and Alloys like Constantan (60
Iron/Constantan: -200° to 900° C
Chromyl/Alumel: -200° to 1250° C
Platinum/Rhodium: 0° to 1600° C
Copper/Constantan: -200° to 400° C
Advantages of Thermocouple
- Wide measurement range of temperature from – 200°C to 1600°C.
- Cheaper than resistance thermometer (RTD).
- Accurate measurements.
- Good reproducibility.
- Low cost.
- No need of external supply.
- Rigid and robust in construct’ on, so it can be used in high vibration or adverse
environments. - Bridge circuits are not needed for measurements.
- Ability to get connected to suitable electrical equipment for measuring rapid or sudden changes in temperature.
Disadvantages of Thermocouple
- Thermocouple does not allow any compromise in essential requirements during temperature measurement, such as, Cold junction, Cable and Lead compensation.
- Output is very small, therefore, it needs signal amplification.
- At high temperatures, thermocouple shows non-linear relationship of Temperature-EMF.
- Not suitable in areas subjected to high radiation fields.
- Slower in response as compared to RTD. Therefore, it cannot be used for high sensitivity applications.
- Proper separation of extension leads from thermocouple wires is essential to avoid errors.
Applications of Thermocouple
- To monitor temperatures of liquids and gases in flowing pipes, ducts or storage.
- Industrial furnaces, hot baths, solutions in chemical reactors etc.
- For temperature measurement in cryogenic range (-150°C to 273°C).
- Measurement of subzero temperature in refrigeration system.