Tube in tube type or double tube condenser consists of two tubes arranged in such a manner that, one tube is inside the other. In this type of condenser, the hot vapour refrigerant enters from the top side of the condenser. This vapour refrigerant is circulated through outer tubes. The cold water enters from the bottom side of condenser and circulates through the inner tubes. The water absorbs the heat from the vapour refrigerant and the condensed liquid refrigerant flows towards the bottom. Since the refrigerant tubes (outer tubes) are exposed to atmospheric air, therefore, some amount of heat is also absorbed by atmospheric air due to natural convection. The cooling water in the inner tubes can be circulated in either direction i.e. top to bottom or bottom to top (which is shown in Fig. 1). When the water enters from the bottom and flows in the direction opposite to the flow of refrigerant, it is said to be a counter flow system. Refer Fig. 1. On the other hand, when the water enters from the top and flows in the same direction as the refrigerant, it is said to be a parallel flow system. The counter flow system is preferred in all types of water cooled condensers, because it gives high rate of heat transfer.
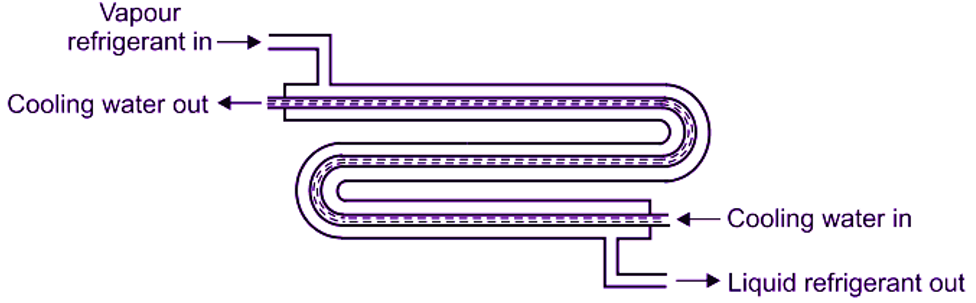
Fig. 1: Tube in tube type or Double tube condenser