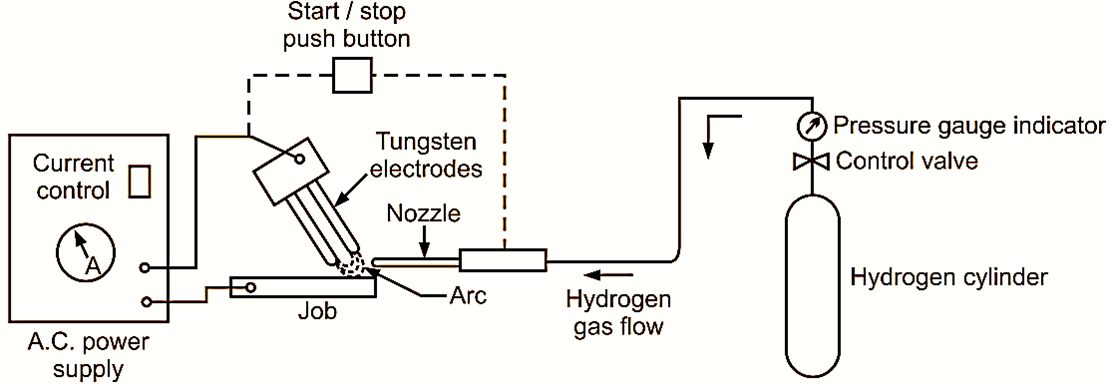
Figure. 1: Atomic Hydrogen Welding.
The atomic hydrogen welding process consists of two tungsten electrodes, hydrogen gas and filler rod, as shown in figure 1. In this process, heat is generated by an alternating current. The heat is passed between the two tungsten electrodes in the envelope of hydrogen gas. As it passes through the arc, the molecules of hydrogen gas are broken down into atoms. When these atoms encounters the cooler base metal, they reform and produce sufficient amount of heat. Thus, this heat along with the filler rod (if used) melts the surface to be welded. The purpose of using hydrogen gas is to protect the molten metal from oxygen and nitrogen. It also saves the metal from failure.
Advantages of Atomic Hydrogen Welding
- There is no requirement of flux shielding gas.
- This process can be carried out at faster rates with least number of distortions.
- Thin metals can also be welded.
Limitations of Atomic Hydrogen Welding
- High operating cost as compared to other welding processes.
- Welding of large amount of metal is not possible.
- Welding speed is relatively lower.
Applications of Atomic Hydrogen Welding
Atomic hydrogen welding is mostly used for high grade work on stainless steel and non-ferrous metals.