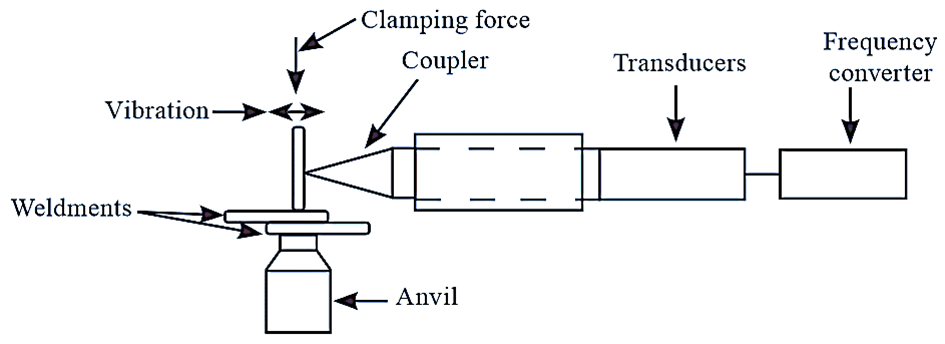
Figure. 1: Ultrasonic Welding.
The major components of ultrasonic welding are frequency converter and a transducer. The power source of frequency converter is used for converting 50 Hz or 60 Hz line power into high frequency electric power. The transducer transforms the high electric power into vibratory energy. A line diagram of ultrasonic welding is shown in figure 1.
The workpieces to be welded are held between the anvil and the welding tip. The pressure is maintained such that it holds the workpieces in close contact. The bonding or welding is obtained by transferring the vibratory energy to the joint for a specific period of time. This method, neither requires external heat nor the filler rod. Thus, welding is done by means of very high frequency ultrasonic vibrations.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Welding
- Rate of production is high
- It can be used for welding of both thin and thick workpieces.
- The welds are free from foreign contaminants.
- The amount of time consumed in welding is relatively low.
- It usually does not require cleaning of workpiece after Welding.
- Preparation of weld is quite easy.
Disadvantages of Ultrasonic Welding
- The maximum thickness is limited to 0.3 to 0.25 mm
- Large-sized workpieces cannot be welded in a single operation
- Ultrasonic vibrations can damage the electric components.
- Specifically designed joints are required.
- The cost of tooling fixtures is relatively high.