The air cooler works on the principle of refrigerant. The refrigeration used is simple water. Small-sized coolers are called ‘room coolers’, which use blowers. Big size coolers are called ‘desert coolers’, which use exhaust fans. The outer appearance and section of a room cooler are shown in Fig. 1 (a) & (b).
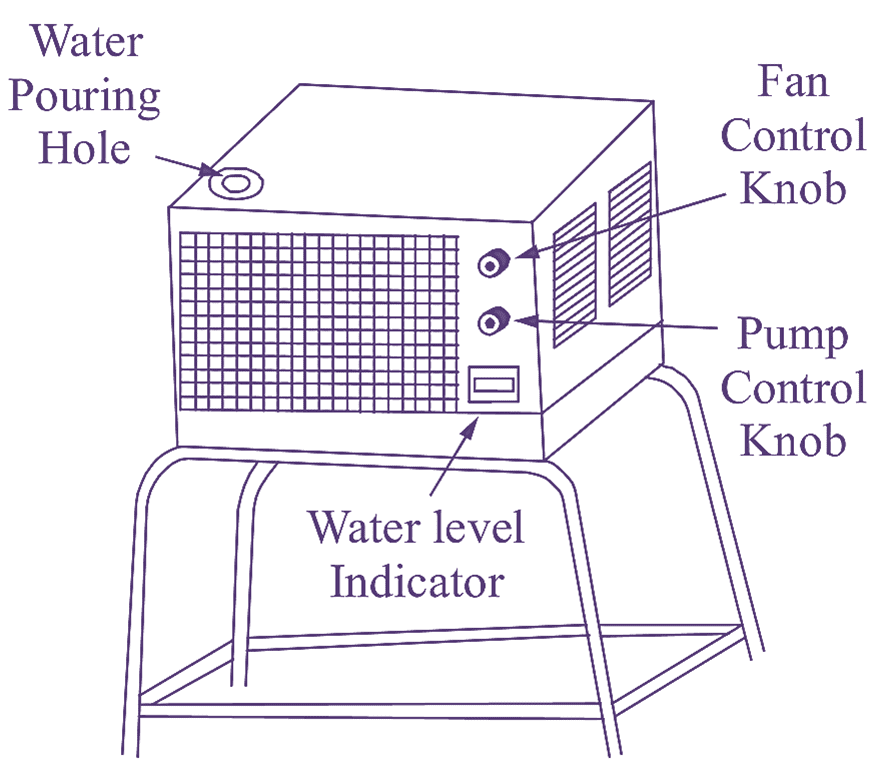
(a) Outer view of Air Cooler.
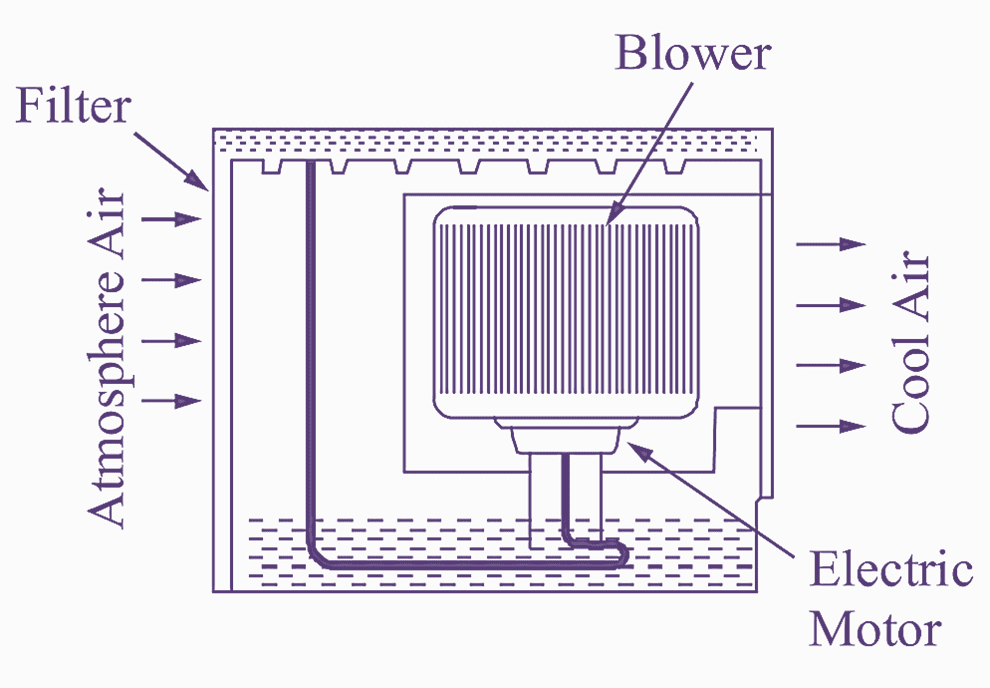
(b) Cross section of air cooler.
Fig. 1: Air cooler.
Water is filled in the tank of the cooler, the level of water in the tank may be controlled by floats. A pump is installed, which is run by a motor, to lift water from the tank. The waterfalls on pads are made of wood fibers. Such pads are provided on three sides of the cooler. The pads also act as an air filters.
A blower draws in hot air from the atmosphere through the wetted pads. This cooled air is thrown into the room or the space to be cooled through the fourth side of the cooler, which is kept, and opened.
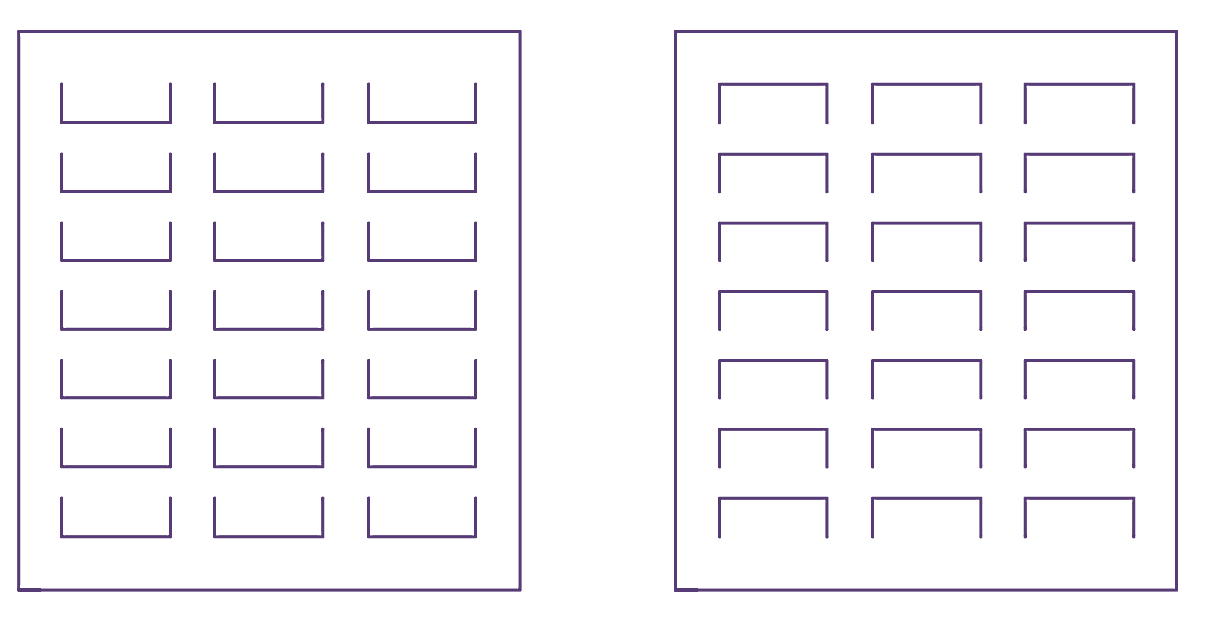
(a) Cooler Shutters.
(b) Cooler kit.
Fig. 2: Cooler Shutters and Kit.
The coolers may have a single blower, double blower, and a single motor for blower and pump, or separate motors for both, etc. Fig. 2 shows two designs of cooler shutters and the cooler kit.
Difference between Air conditioner and Cooler
|
Air cooler |
Window air-conditioner |
| Its main components are motor, fan and pump. | It contains a complete refrigeration system compressor, condenser, evaporator, etc. |
| It is cheap. | It is costly. |
| It is used to cool air only in dry seasons. | In can be used to cool in summer and heat in winter. |
| It increases humidity. | It controls humidity to a comfortable value. |
| It has more power consumption per unit cooling. | It consumes less power per unit cooling. |
| It can only ‘cool’ and increases humidity. | It controls all factors of human comfort, viz., temperature, humidity, air movement and air purification. |
| It uses water as refrigerant. | It uses freon as refrigerant. |
| Its components are motor, pump and fan. | Its components are motor compressor condenser and Evaporator |