A bevel protractor is a precision measuring instrument used to measure angles accurately.
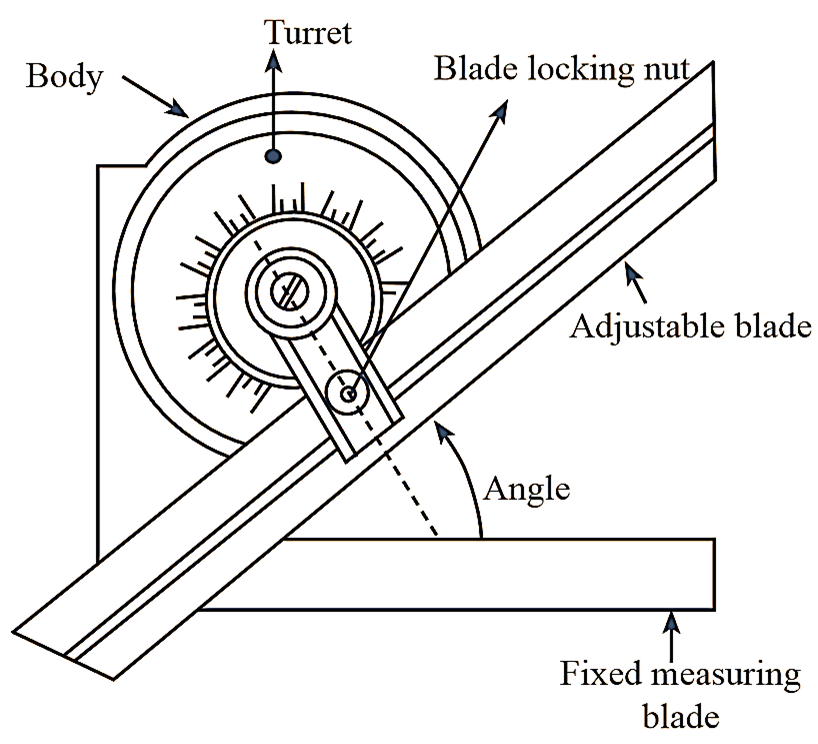
Figure 1: Bevel Protector.
Construction of Bevel Protector
A bevel protractor is an angle measuring instrument, consisting of the following parts as shown in figure 1
Body: The main part that houses the measuring components and provides a stable reference.
Turret: A rotatable circular disk graduated in degrees, allowing for angle measurements.
Adjustable Blade: A movable blade that pivots around the turret and is used to align with the edge of the surface to measure angles.
Fixed Measuring Blade: A fixed blade attached to the body that serves as a reference point for measuring angles.
Blade Locking Nut: A locking mechanism to secure the adjustable blade at the desired angle.
Graduations: The turret is marked with angular graduations (typically in degrees and fractions of a degree).
Working of Bevel Protector
A bevel protractor is used to measure angle between the two faces of a component. The fixed measuring blade and the adjustable blade is set along the faces of the component whose angle is to be measured. as shown in figure 1. The blades are then locked by a locking nut, to tighten the component for accurate measurement. The body consists of a circular scale and extends to form one of the blades. The circular scale can measure angles upto 360 degrees. The adjustable blade also slides and can be locked at any position along its length. to the rotating turret mounted on the body. Thus, accurate angular measurements of any component can be easily done by a bevel protractor.
Types of Bevel Protractors
- Vernier Bevel Protractor: Includes a vernier scale for enhanced precision (up to 1/12th of a degree).
- Digital Bevel Protractor: Features a digital display for direct angle readings with high accuracy.
- Mechanical Bevel Protractor: Basic model without a vernier scale, suitable for general purposes.
Advantages of Bevel Protractors
- High Accuracy: Vernier and digital bevel protractors provide precise measurements of angles.
- Versatility: Can measure both acute and obtuse angles.
- Ease of Use: Simple to operate, with a direct reading mechanism.
- Durability: Made of robust materials like stainless steel, ensuring long life.
- Compact Design: Lightweight and portable, suitable for field use.
Disadvantages of Bevel Protractors
- Limited Range: Typically measures angles within 0° to 180° (though some models can measure up to 360°).
- Skill Requirement: Accurate readings require careful handling and alignment.
- Susceptible to Wear: Graduations and moving parts can wear out with frequent use.
Applications of Bevel Protractors
- Machining and Tool Making: Measuring and setting precise angles on machine parts and tools.
- Construction: Ensuring correct angles in structural elements like beams and trusses.
- Metalworking: Inspecting and verifying angles during fabrication.
- Quality Control: Checking angular tolerances in manufactured components.
- Layout and Drafting: Used in technical drawings and layout marking.
Least Count of a Bevel Protractor
The least count of a bevel protractor refers to the smallest angle that it can accurately measure or read. It depends on the type of bevel protractor:
- Vernier Bevel Protractor: Least count: 5 minutes (1/12th of a degree) or 0.0833°. This is achieved using the vernier scale, which divides one degree into smaller increments.
- Digital Bevel Protractor: Least count: Typically 0.1° or 0.01°, depending on the model.
- Mechanical (Basic) Bevel Protractor: Least count: Typically 1°, as it lacks finer graduations or a vernier scale.