Cooling Tower is a direct heat exchanger, through which heat of the water is transferred to the atmospheric air. The water is cooled up to the wet bulb temeperature of air (see Figure 1). The rate of evaporation depends on the following factors.
- Amount of water surface exposed.
- The direction of air flow.
- The line of exposure.
- Humidity of air.
The Fig. 1. shows the use of cooling towers.
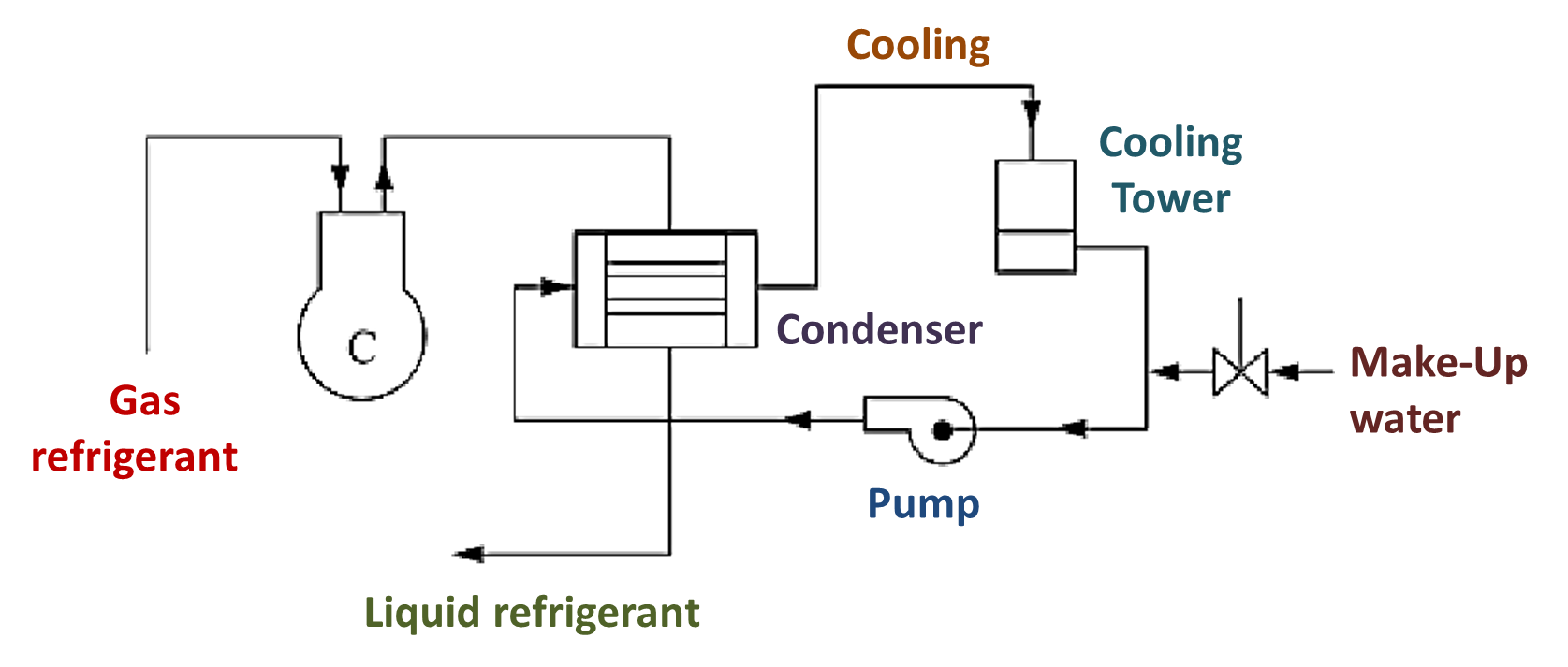
Fig. 1: Use of Cooling towers
Types of Cooling Tower
On the basis of air circulation the cooling towers are of the following types:
- Natural draft cooling towers
- Mechanical draft cooling towers
Natural Draft or Atmospheric Cooling Tower
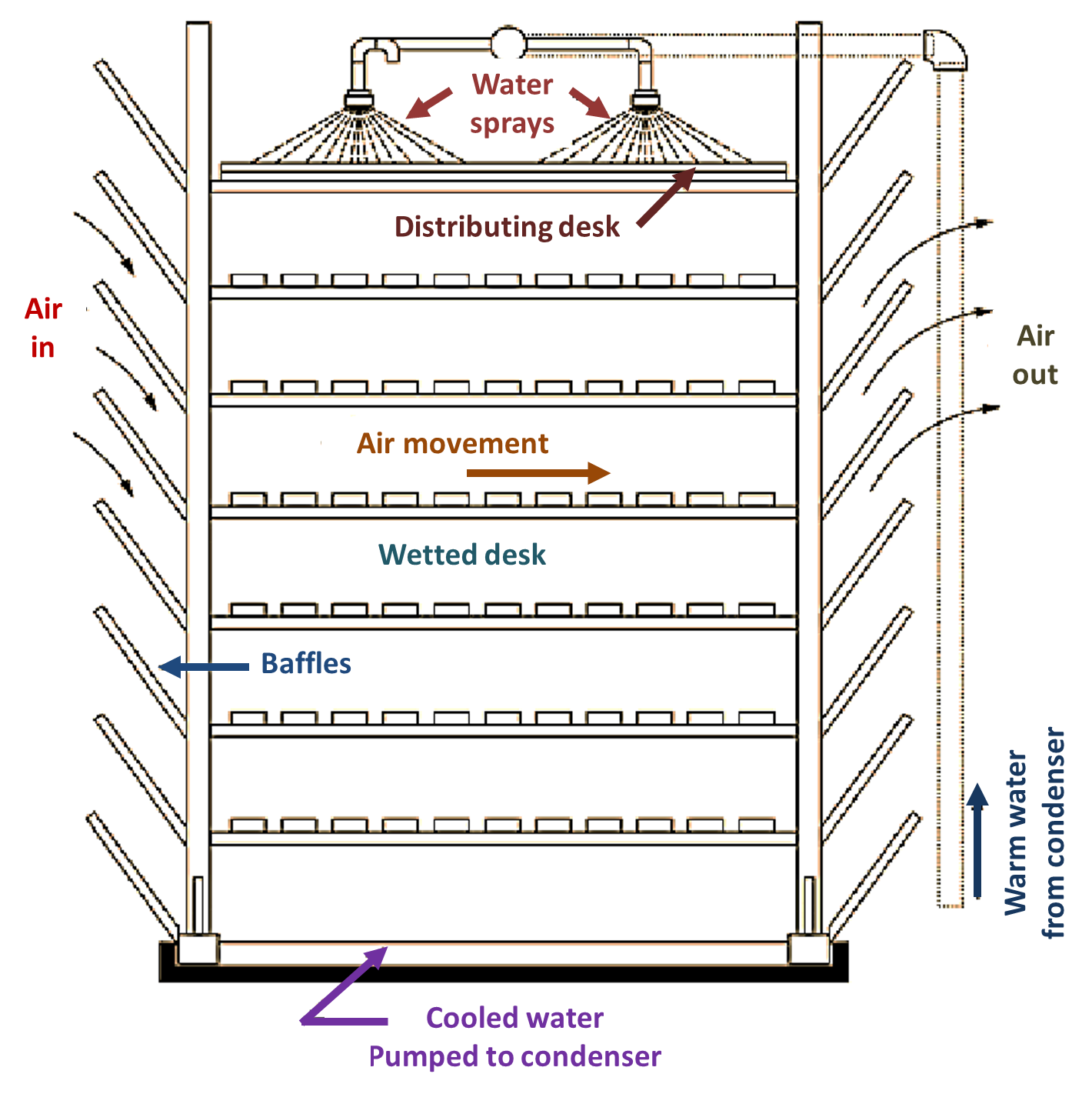
(a)
(b)
Fig. 2: Natural Draft Towers.
In this tower, the circulation of air through the tower is by natural convection. The hot water is pumped to the top of the tower and is sprayed down through nozzles. The water gives its heat to the air, cools down and is collected at the bottom of the tower, from which is sent to the condenser for reuse. Such a tower has been shown in Fig. 2 (a). Another design of natural draft tower has been shown in Fig. 2 (b). These are high and are installed in an open place. These are provided with distributing decks, whichhave grroves to have to have an even distribution of water over the whole tower. The water flows down through these decks as a ‘spray’ and cools down, when comes in contact of air. Natural draft cooling is a cheap method, but if temperature of atmospheric air is high, it takes much time for the cooling.
Mechanical Draft Cooling Towers
In mechanical draft towers, the movement of air (draft) is mechanical, i.e., created by fans – water falls from top to the bottom of a vertical shell and collected in a basin at the bottom. The draft of air is made to circulate from bottom to top of the shell either by ‘forced’ or ‘include’ draft fans. As the air passes against the flow of water it can pick up more heat as compared to natural draft towers, so less air is required to cool the same amount of water. They are of two types:
- Forced draft cooling towers
- Induced draft cooling tower
Forced draft cooling towers
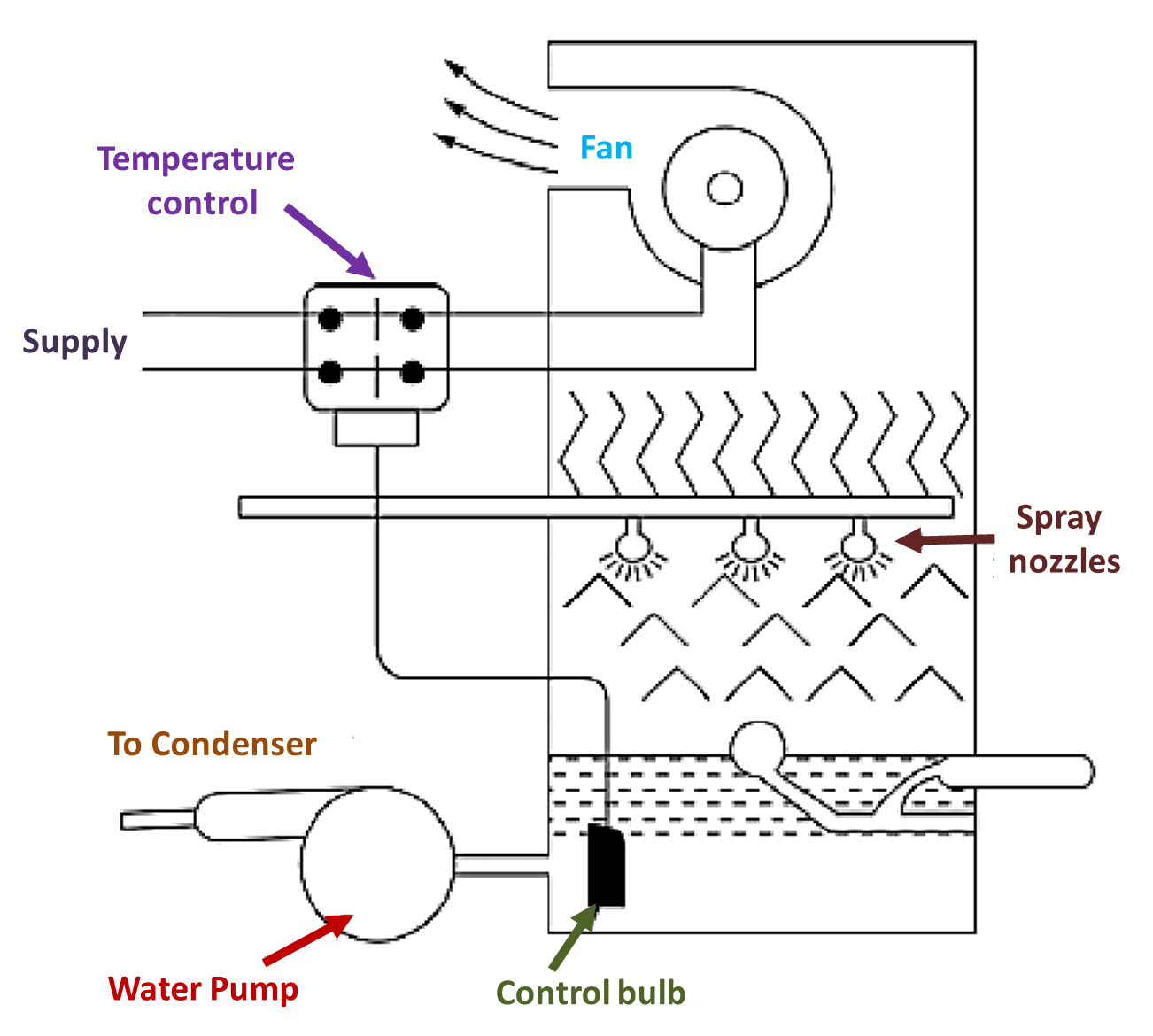
Fig. 3. Forced draft cooling tower.
The fan in these towers is installed at the top. The maintenance cost of the equipment is high. The tower is closed from all sides (see Figure 3). The air moves from top to bottom. The spray eliminators are used to ‘filter’ out of the air. The water comes through nozzles and cools water, which is accumulated at the bottom.
Advantages of Mechanical Draft Cooling Towers
- This is more efficient than induced draft tower.
- The vibration and noise are minimum as mechanical equipments are set on a solid foundations.
- As it handles dry air, problems of fan blade erosion are less.
Disadvantages of Mechanical Draft Cooling Towers
- There is posibility of recirculation of hot, humid exhaust coming out from the top of the tower through the low pressure air intake region.
- During cold weather, ice is formed on nearby equipment.
- The fan size is limited to 4 meters.
- The power requirement of forced draft fan is approximately double that of induced draft system for the same capacity.
Induced draft cooling tower
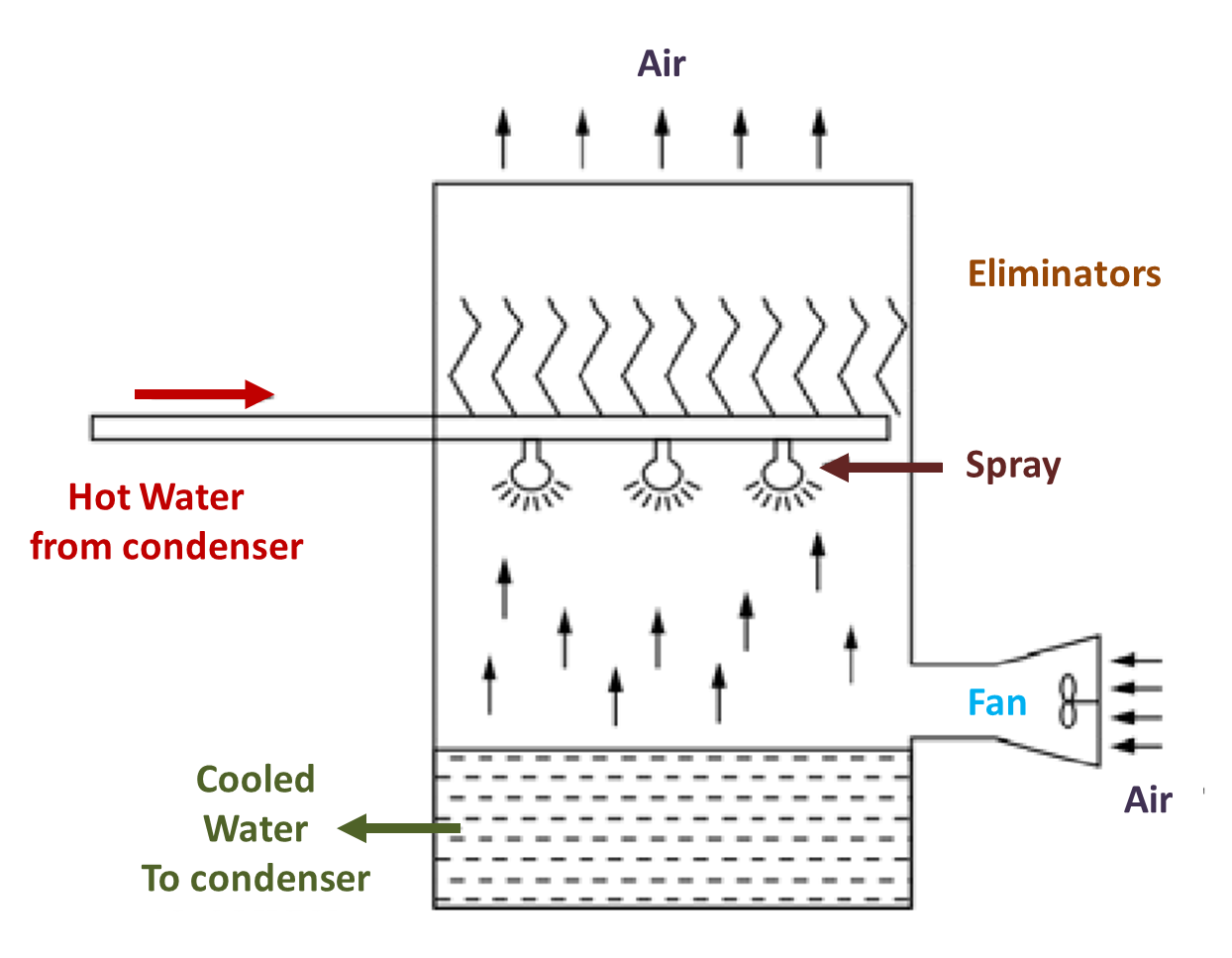
Fig. 4. Induced draft cooling tower
Fig. 5: Outer look of Induced draft cooling tower
This is similar to the forced tower, with a difference that fam may be installed near ground and the air flows from bottom to the top. The water eliminators are also installed to prevent loss of water with the out going air, i.e., to “filter out” the air. The Fig. 5. shows outer look of the tower. The induced draft fan is more desirable than a forced draft fan as
- It provides an even air distribution
- It eliminates the chance of recirculating discharged hot air, which is possible with a forced fan.
Advantages of Induced draft cooling tower
- The main advantage is that coldest water comes in contact the driest air and warmest water comes in contact with the most humid air.
- The size upto 20 m in diameter can be used.
- The initial cost is lower due to the reduction in pump capacity required and smaller length of water pipes.
Disadvantages Induced draft cooling tower
- This requires higher power motor to drive the fan compared with forced draft fan handling same air water flow.
- The air velocities through the packings are unevenly distributed.