The entire plan that directs the execution of particular HRM functional areas is called human resource management Strategy. The human resource decisions that are best for the organisation are directed by strategies of HRM. The organisational business strategy must be compatible with all the functional areas of HRM strategy. HR strategies are developed in order to cultivate talents, attitudes and behaviour in the staff members which will in turn help the organisation to meet its goals. It is devised of ideology for effectively handling the employees using HR practices and policies. The different areas of HRM like compensation, recruitment, performance management, employee relations, rewards and recognition and training are covered under this. HR strategies must be put in line With the organisational mission, vision, and goals. Analysing the features of the industry, establishing competitive advantage and identifying important people and processes is crucial for developing HR strategy. It is vital that diftürent strategies are developed for different group of employees in the organisation keeping in view their talents roles and knowledge. The strategy’ should focus on the organisation’s structure, system, culture, and people.
According to Dessler, “HR Strategy is defined as the courses of action HR uses to help the company achieve its strategic aims”.
Objectives of HR Strategy
HR strategy has numerous goals that should not be hidden but carefully broadcasted and internally as well as externally endorsed. Following are the different goals of HR strategy:
To Develop HR Services: HR strategies are motivating factors towards the betterment of HR services. It not only improves the prevailing HR practices but also introduces fresh HR services that affect employee’s satisfaction and also enhance the efflcieney of workforce in the organisation. One such HR strategy is the accurate analysis of HR processes, since a few processes have to be disregarded, few re-designed, while a new value-added processes need to be introduced in the organisation.
To Amalgamate Human Resources: One goal of the HR strategy is the amalgamation of human resources in the organisation since it has to bring in line HR and business strategy. Business strategy gives direction to the entire organisation whereas HR strategy focuses on the development of human capital. It emphasises on the organisation which is flexible, fast, and competitive in the industry.
To Introduce Perfect Manager: The best time to introduce the perfect manager is while discussing the HR strategy. A perfect manager is one who has a balanced approach towards hard and soft targets. He considers all their subordinates equal, which make him admirable. He is supportive towards the employees as well as the organisational growth, thus helping in the development of the organisation. The best time to declare such an objective is HR Strategy.
To Determine Required Behaviour: Desirable employee behaviour is determined by the HR strategy. The kind of behaviour that will be rewarded and recognised in the future is also determined which helps employees adapt to the revised norms. This goal is important since it enables employees to understand what is expected from them. HR manager coaches the managers so that they learn to make out desirable behaviour and drive them towards rewarding employees who follow the corporate culture whole heartedly.
To Enhance Employee Satisfaction: Another objective of HR strategy is to increase the employee’s satisfaction. Employees witness the difference between employers. A different employer is always perceived to give its employees more than they required.
Components of HR Strategy
Following are the different components of HR strategy:
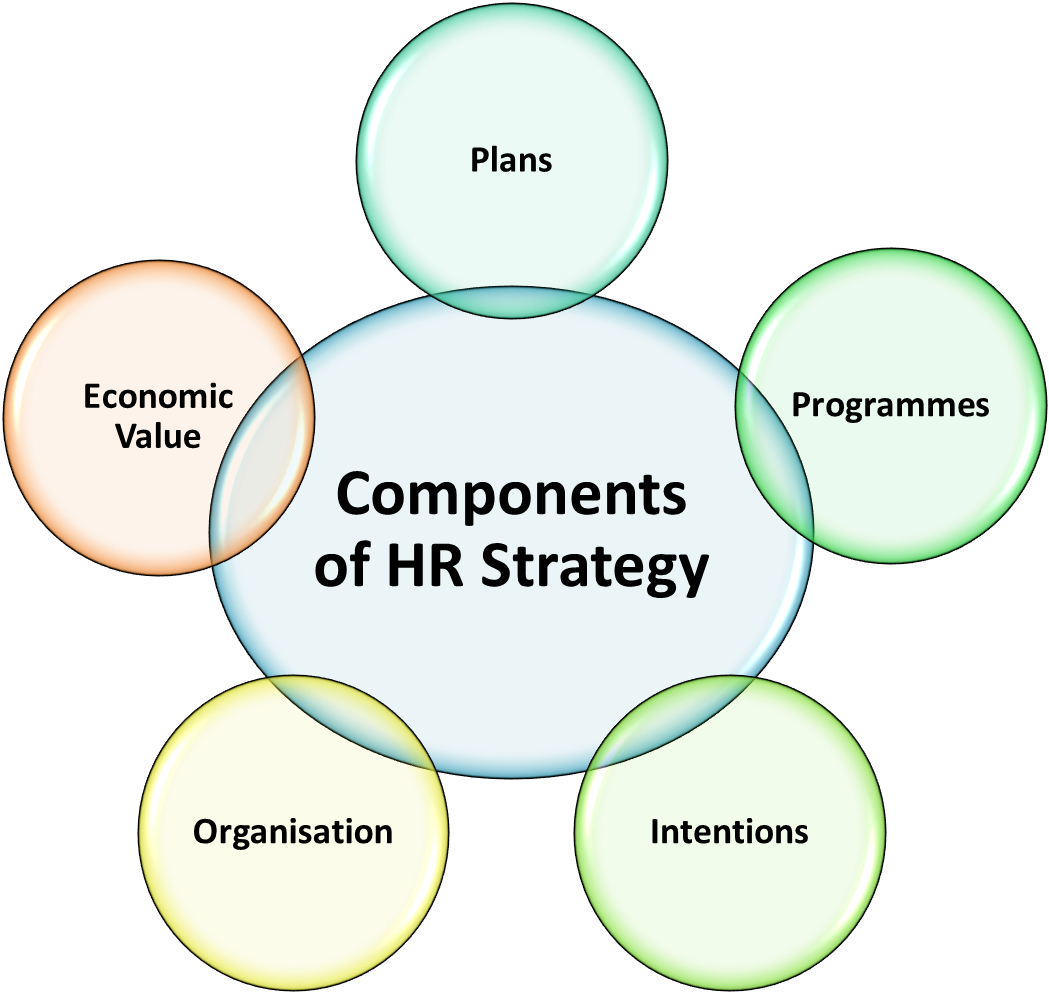
Plans: Plans involve the whole direction of the organisation regarding its size, style, scope of activities, talents and morals, as well as particular priority of supporting the developmental plans of the organisation.
Programmes: They are precise groups of HR projects that results in either organisational breakthroughs or enabling incessant improvement.
Intentions: It includes fields where the organisation intends to implement improvement but the plans have yet not materialised into definite projects.
Organisation: It holds the formal as well as informal preparations for constant exchange through dividing the lab-our internally. Outsourcing, virtual working and alliances are also a part of this, which lifts HR Strategy to greater heights, beyond the concrete definition of conventional organisational limits.
Economic Value: The extra cash now generated for awarding the better performing staff or for customers, a large part of which is accumulated finally for the shareholders is called the economic value of the firm. Although certain amount of economic value is intangible, it’s worth can still be calculated.
Types of HR Strategies
Following are the important kinds of HR strategies:
Overarching HR Strategies: These kinds of strategies give a general outline of the plan’s goal-specific strategy and also elucidate the department’s efforts to accomplish the plan’s goals. These strategies affect everything undertaken or to be achieved by the department. These strategies portray the universal and fundamental plan of the organisation regarding the management and development of human resources, steps taken to make Sure that organisation can draw and preserve its desired employees and make Sure that workforce is motivated, dedicated and involved. The overall organisational effectiveness ending up into getting human resource benefits by, utilising ‘better people in organisations with better process’, creating improved performance work processes and developing a great workplace in comparison with another competitors is the matter of concern. A few samples of this strategy are:
- “Since we are in search of both young as well as Old people, we will emphasise on the regional newspaper as well as on the Department website and media accessed by youth. The Communication officer will be in-charge of this event and a group of senior managers will support him. Monthly checks will be done to ensure the opportunistic hadling of the sources”.
- “Since we are targeting the latest migrant and immigrant workers, Spanish language media will be involved and the Heads of regional Mexican-American and Puerto Rican communities through continuous meetings, creating joint statements on a regular basis, e-mails, and bi-lingual excursions of our facility. We will also create a telephone hotline which will operate from 8am to 8pm every day, the entire month. Communications team will comprise of Nancy and Miguel who, for the next six months, will circulate the monthly updates.”
- “Since we are targeting to reach the maximum number of parents regarding the walk-to-school campaign, we Will put into use the editorial board conferences, a kick-off news conference which is strategised to increase broadcast and print media coverage, radio public service announcements, high profile student activities and a tagline and a visual image. All this will be incorporated on September 15. The communication consultant will work in close association with the deputy director and the steering committee will take all the important decisions.”
Specific HR Strategies: The grounds for what the organisation plans to do in certain areas are set by specific HR strategies. These areas are as follows:
Talent Management: The manner in which the organisation plans to develop its employees and exploit their maximum potential.
Continuous Improvement: Making available targeted and unending innovation coupled with individual development.
Knowledge Management: Acquiring, creating, sharing, capturing and putting in use knowledge to improve the employee’s learning curve.
Resourcing: Acquiring and sustaining highly talented employees.
Learning and Development: Providing the employees with an environment where they feel motivated to gain knowledge and develop.
Reward: Describing the long-term plans of the organisation regarding the growth and implementation or rewards policies, processes and practices, which enable the employees to accomplish the organisational goals and fulfil stakeholder’s need alongwith attaining employee satisfaction.
Employee Relations: Elaborating on the plans of the organisation regarding the need of employee involvement and the changes that should be incorporated for the effective management of relationships between the organisation and its employees and trade unions.
Importance of HR Strategy
Following are the ways in which the HR strategy is important to the organisation and employees:
Decision-Making Tool: Being a managerial decision-making tool, HR Strategy directs the management to tackle a specific HR project proposal. The project contract is evaluated against the HR strategy by the management team and the team will enable the human resources to implement the strategy’. During the existence of the HR strategy, the team will be able to create more project proposals. The management team needs to prioritise the proposals since it will not be possible for the HR department to implement all of them.
Useful in Setting Vision: Another important function of HR strategy is that it enables employees to take routine decisions since they can easily comprehend if their decisions based on HR strategy are of any use to the organisation or not. HR strategy defines the vision but it is put in use for the routine decisions. The Strategy directs the decision process.
Enhances Communication: HR strategy is vital for the discussion with managers regarding improvement of HR services convenient. HR team can display how department works and how HR will handle individual feedback, request or services provided.
Promotes Team Spirit: HR strategy promotes team spirit in human resources since it provides human resources a stage for communication and discussion regarding the future of human resources. The HR strategy must narrate an appealing Story since it develops a general understanding for the key words used in formulating the strategy and HR employees interpret them differently.
Functional HR Strategy
A strategy which addresses the key areas of HRM is called as functional strategy. For example, employee relation, pay and conditions, performance management, resourcing and development. Though these areas are treated here as a separate entity but normally they should not be treated as a separate entity. Every facet of HR strategy must be considered as a component of the entire SHRIM process. The connection between them, and the ways through which the practices and policies of one area may support the practices and policies of another area, must be considered and placed in the entire business strategy. The strategy that helps in the development of the perforrnance management process can be linked to the strategies of Other areas like reward and human resource development. It can also provide a contribution to any comprehensive strategies like strategies related to culture change. Thus, in other words, we can say that for SHRM there is a need to accept a holistic approach, which can be activated by configuring mutual consolidating aspects simultaneously. HR strategy may include some overall goals and objectives related to the organisational problems or issues; it can also set priorities in the core areas of HR strategy. For example, the overall aim of the strategy might be focused towards the improvement of employee’s performance. However, it can be achieved by giving preference to the development of strategies related with performance and reward, which will provide links to formulation and development of strategies, even if the detailed development programmes are set for a later stage.
Organisational HR strategy
An organisational strategy is the sum of the actions a company intends to take to achieve long-term goals. Together, these actions make up a company’s strategic plan. Strategic plans take at least a year to complete, requiring involvement from all company levels. Top management creates the larger organisational strategy, while middle and lower management adopt goals and plans to fulfill the overall strategy Step by Step. The business oriented HR Strategy is just a small subset of the general strategic journey of the enterprise. The principal purpose of the HR strategy is the differentiation from other competitors. The unique employee value proposition lets employees engage emotionally with the organisation. Copying the HR Best Practices does not cultivate the unique corporate culture. It does not support the development of the sustainable competitive advantage. Employees cannot recognise a difference between the organisation and key competitors. They cannot see how exceptional the company is on the job market. The applicants do not value the company because they do not see outstanding workplace conditions. The people want to work for the business that makes things differently. The organisation operates as a single company consisting of a diverse set of businesses and the HR infrastructure spans across and integrates with the various autonomous business units. The HR infrastructure comprises of the Group HR function which develops organisational wide HR strategy and policies; a shared services HR function which serves the various autonomous business units with organisational-wide HR services; HR functions within each business unit and finally the line managers, within the autonomous business units. As evidenced in the organisation’s HR strategy (Figure 1), the various business units each have their own strategies and actions, which are, interlinked with the organisation’s overall group HR strategy.
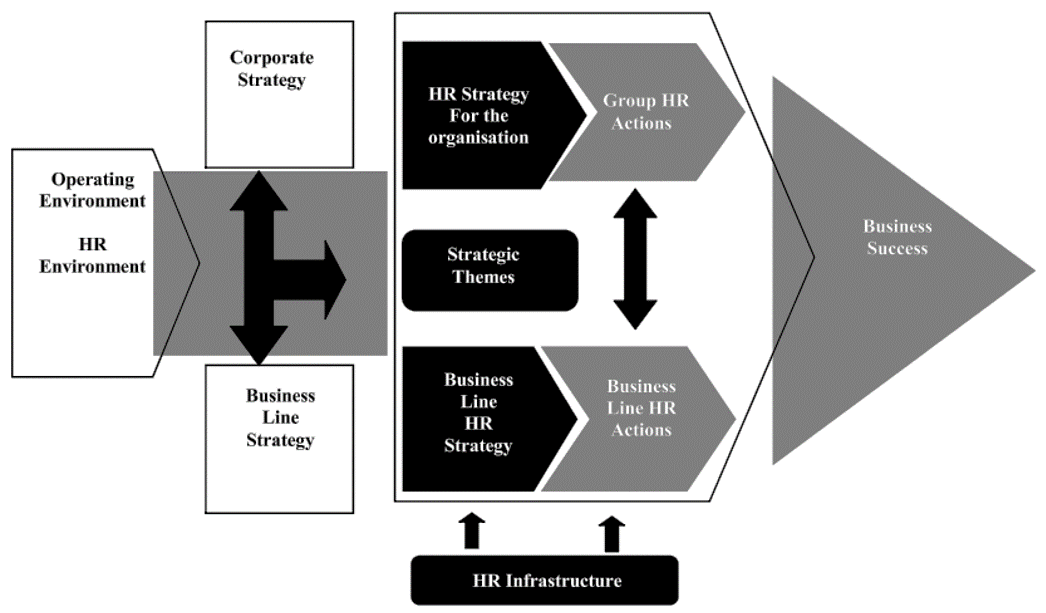
Figure 1: HR Strategy
The significance of an organisation’s HR strategy on measures of organisational effectiveness was well highlighted by Wang who reported that different HR strategies seem to deliver different organisational outcomes. For example; personnel strategy was found to increase the level of employee entrepreneurship while a systems HR strategy facilitated better technological innovation outcomes. The organisational HR strategy was linked to improved Outcomes in the development of a positive organisational culture and supporting high employee performance. Wang also noted that HR strategies such as the systems strategy’ enhance the outcomes of Knowledge Management (KM) initiatives.