In this topic, you study Hybrid Stepper Motor – Working, Circuit Diagram & Construction.
These motors operating under the combined principles of the permanent magnet and variable reluctance motors are widely employed for small Step angles.
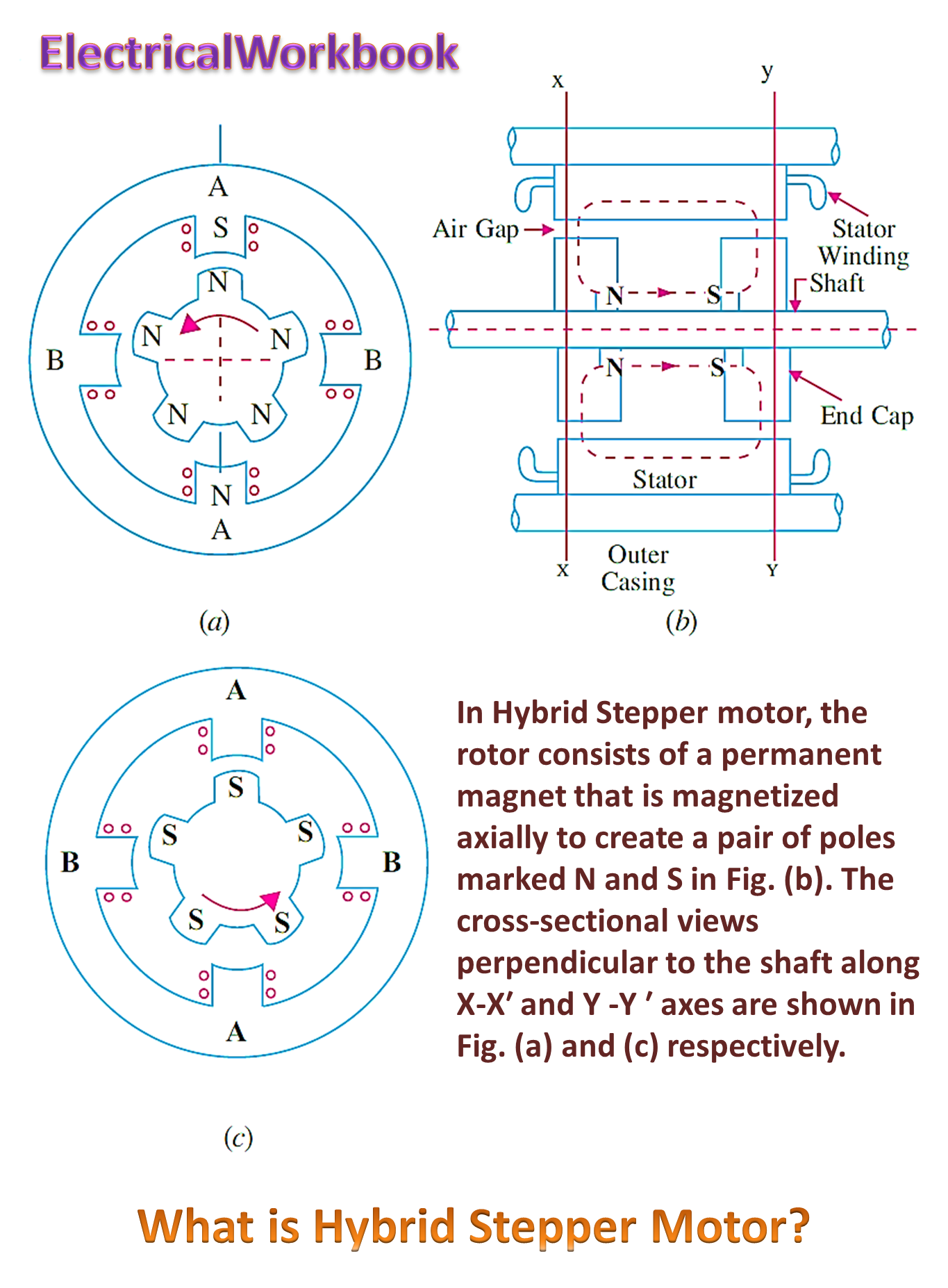
Construction of Hybrid Stepper Motor
Fig. 1 shows cross-sectional view of a typical hybrid motor. The stator core structure is similar to that of the variable reluctance motor. The stator is generally wound for two or four phases. Important feature of the hybrid motor is its rotor structure. The rotor consists of cylindrically shaped permanent magnet magnetized parallel to the shaft axis. Each pole of this magnet is covered with laminated silicon steel end caps. These end caps uniformly toothed. The teeth on the two end caps are misaligned with respect to each Other by a half tooth pitch.
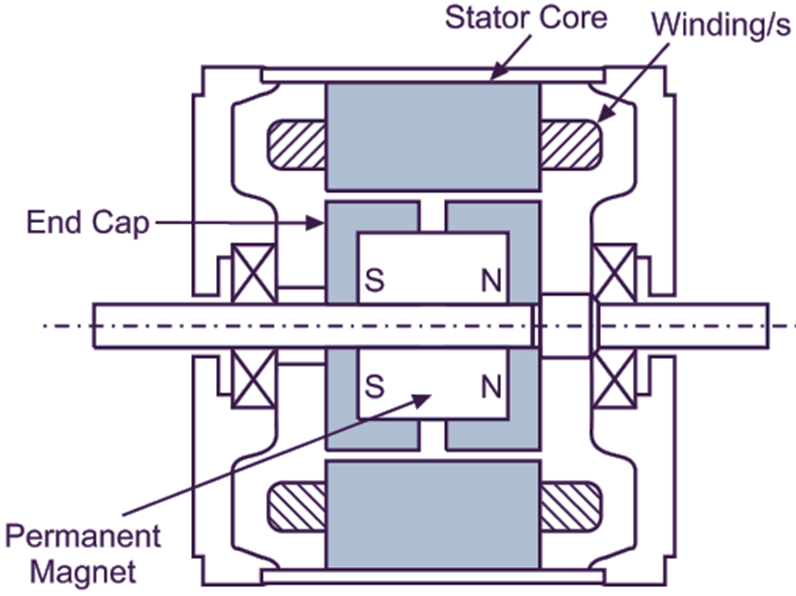
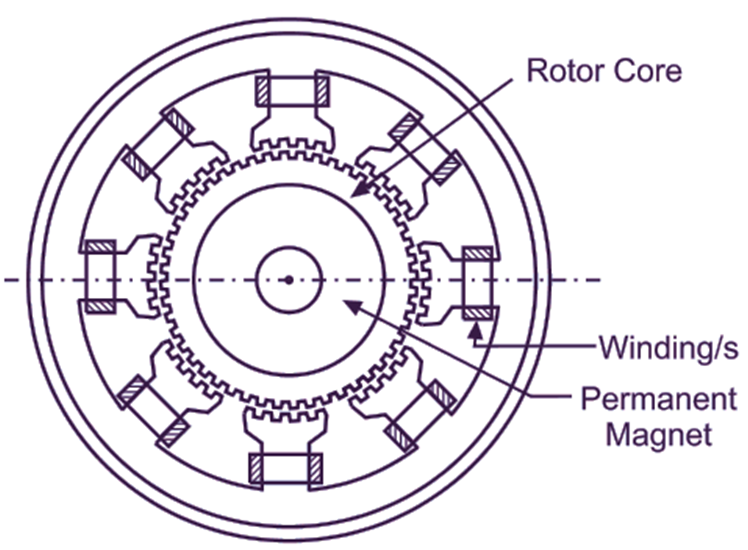
Fig. 1: Construction of a typical hybrid stepper motor
Working of Hybrid Stepper Motor
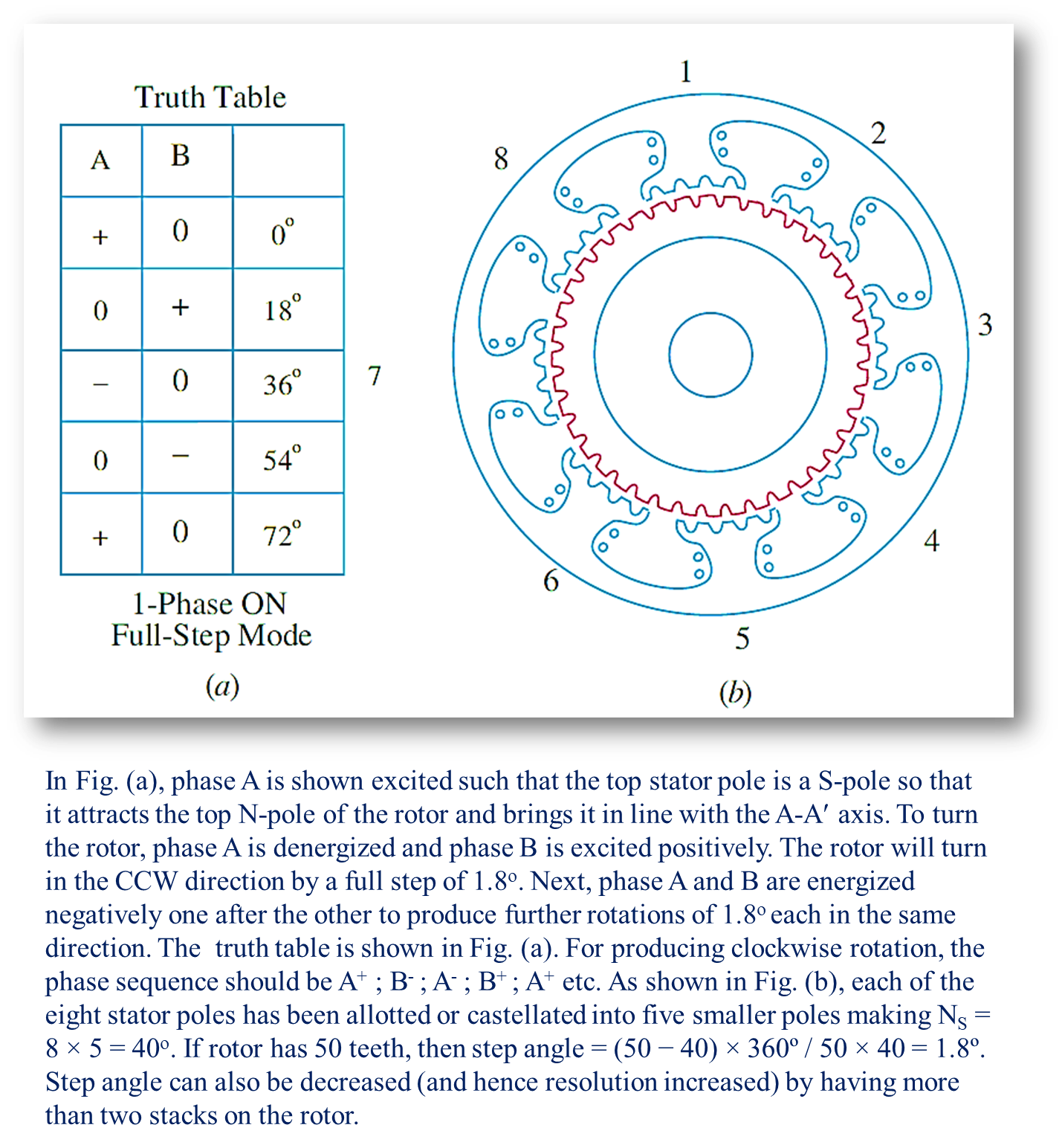
The permanent magnet in the rotor structure of the motor produces a unipolar field, while the Stator of the motor produces a distributed magnetic field due to the currents supplied to its windings. The torque is created by the interaction of these two magnetic fields in the toothed Structure in the air-gaps. In this type of motor, by studying the resultant field pattern in the toothed structure in the air-gaps, it can be shown that no effective torque is generated by the stator magnetic field alone in the variable reluctance motor but the permanent magnet in the rotor plays an important role in creating the driving force. Thus the motor works on the combined principles of the permanent magnet and variable reluctance motors. The stepping action of the motor is caused by the sequential switching of supply to the phases of the motor. In order to raise the torque, multi-stack hybrid motors are employed.
Advantages of Hybrid Stepper Motors
Following are the main advantages of the hybrid stepper motors:
- Step angle as low as 1.8o
- High torque per unit volume.
- Availability of some detent torque due to the presence of permanent magnet in the rotor structure.