In this topic, you study Stepper Motor – Working, Diagram, Types, Characteristics & Applications.
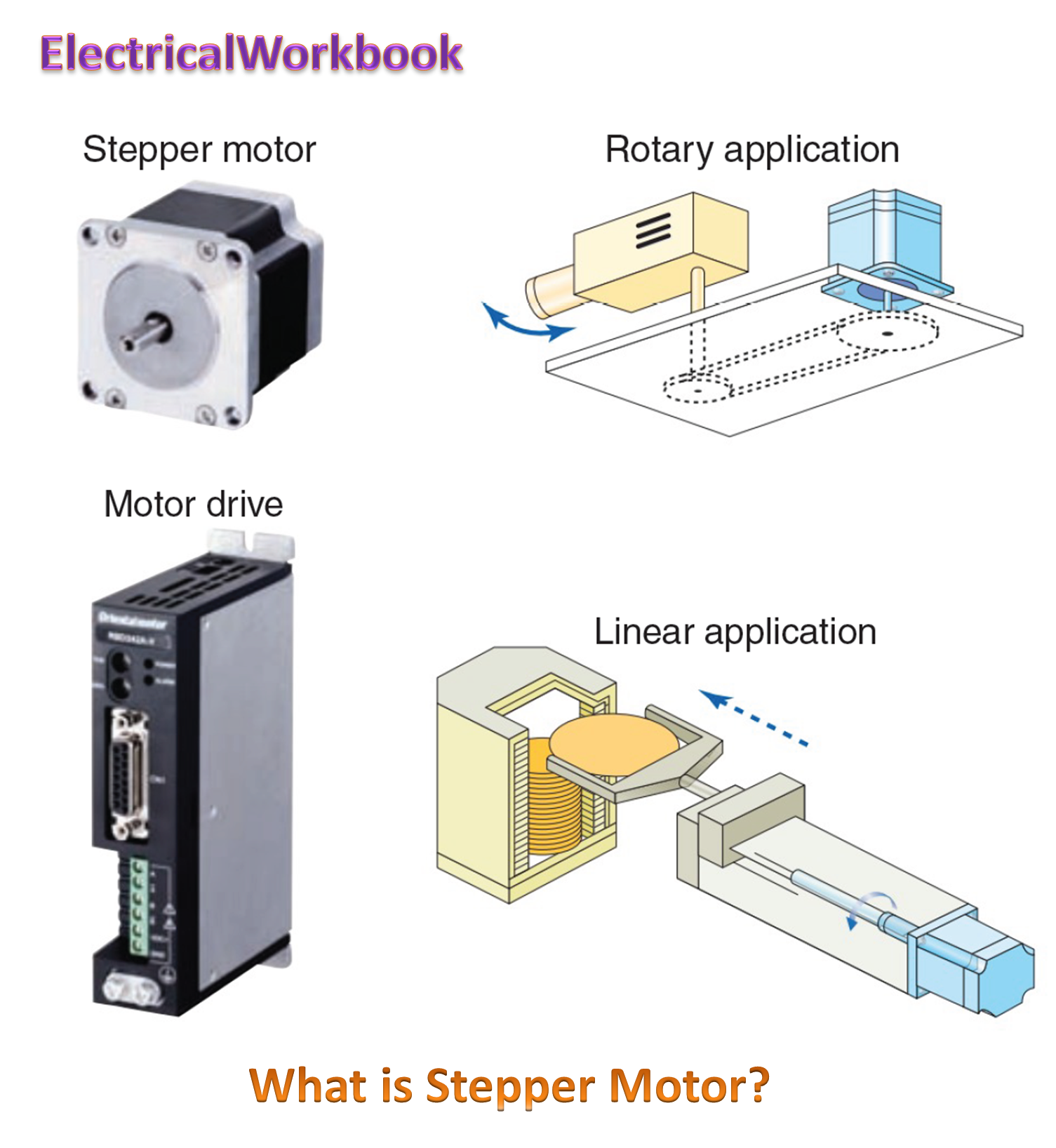
A stepper motor is an electrical motor which converts electrical input in the form of series of pulses into discrete angular movements, commonly called as steps. This conversion is on one to one basis i.e. the motor moves through one step for each input pulse. The pictorial view of the stepper motor is shown in Figure 1.

Fig. 1: Stepper Motor.
Principle of Operation of Stepper Motor
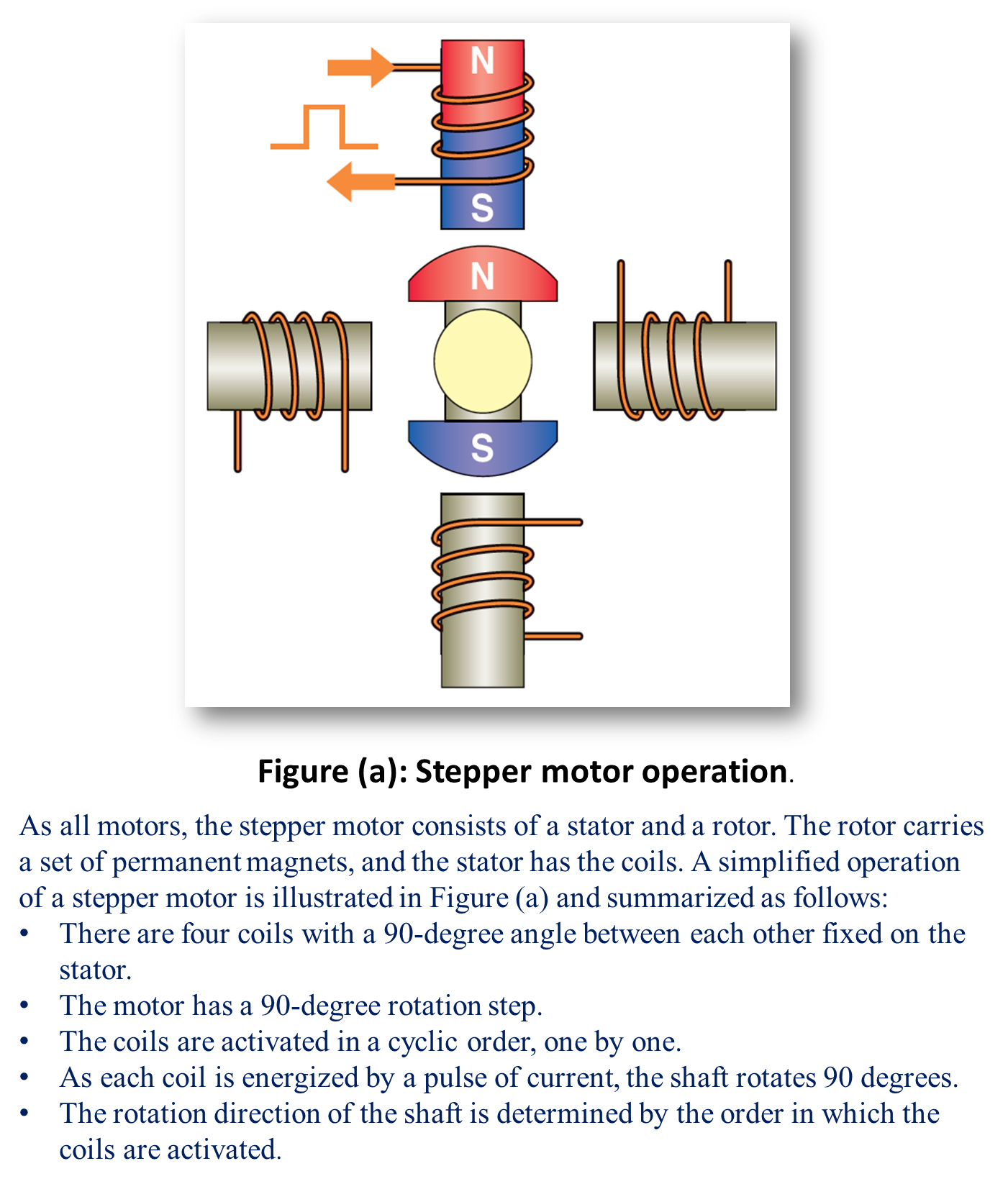
Thus, the basic principle of operation of stepper motor can be explained by considering a series of electromagnets arranged in a circle. These electromagnets are energised in sequence by the train of pulses. The magneto motive force developed in them and interact with the rotor (iron piece) and cause it to turn in clockwise or anticlock wise direction depending upon the energised electromagnet position.
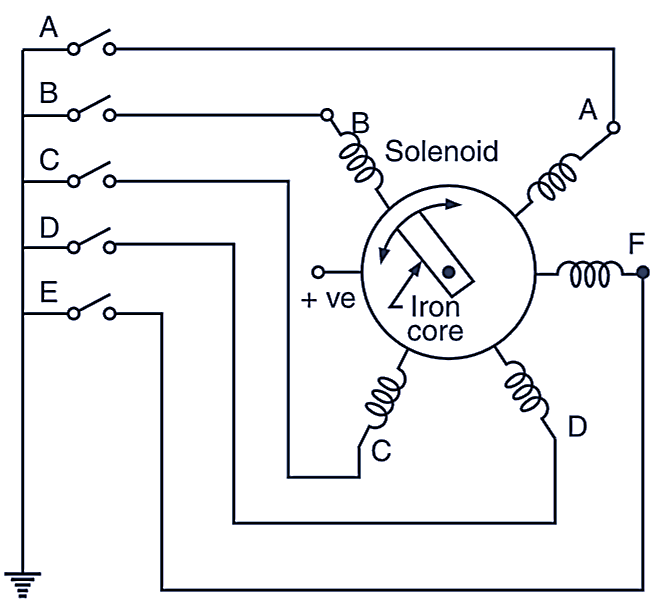
Fig. 2: Stepper motor working principle.
Working of Stepper Motor
Generally, stepper motors are operated by electronic circuits, mostly on a dc power supply. The drive systems of stepper motors are classified into open-loop and closed-loop drives. Fig. 3 illustrates the block diagram of a modern driving system for a stepper motor in open-loop mode. The input controller consisting of integrated circuits or microprocessor perform various functions such as generating and governing the number of step command pulses and their timings, logic sequencing, etc. The output signals of the input controller are transmitted to the input terminals of a power driver by which the turning on/off of the motor winding is governed. The power driver may be called a motor driver or simply a driver.
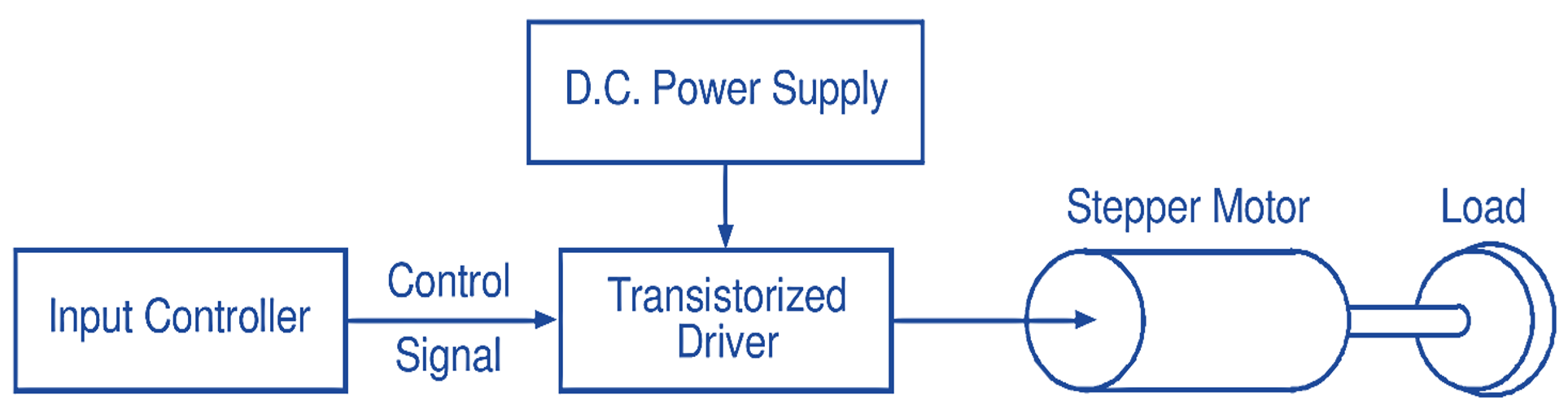
Fig. 3: Modern driving system for a stepper motor in open-loop mode
The open-loop drive is an economically advantageous driving method and widely accepted in applications of speed arid position controls. However, there are certain limitations to this type of drive. For instance, a stepper motor driven in the open-loop mode may fail to follow a pulse command when the stepping rate is too high or the inertial load is too heavy. Moreover, the motor motion tends to be oscillatory. The performance of a stepper motor can be improved to a great extent by employing position feedback and/or speed feedback to determine the proper phase(s) to be switched at the proper timings. This type of control is called the closed-loop drive. For this, nowadays, a rotor position sensor such as an optical encoder usually coupled to the rotor shaft is used (Fig. 4). Closed-loop control not only prevents step failure but it also gives motor motion much quicker and smoother.
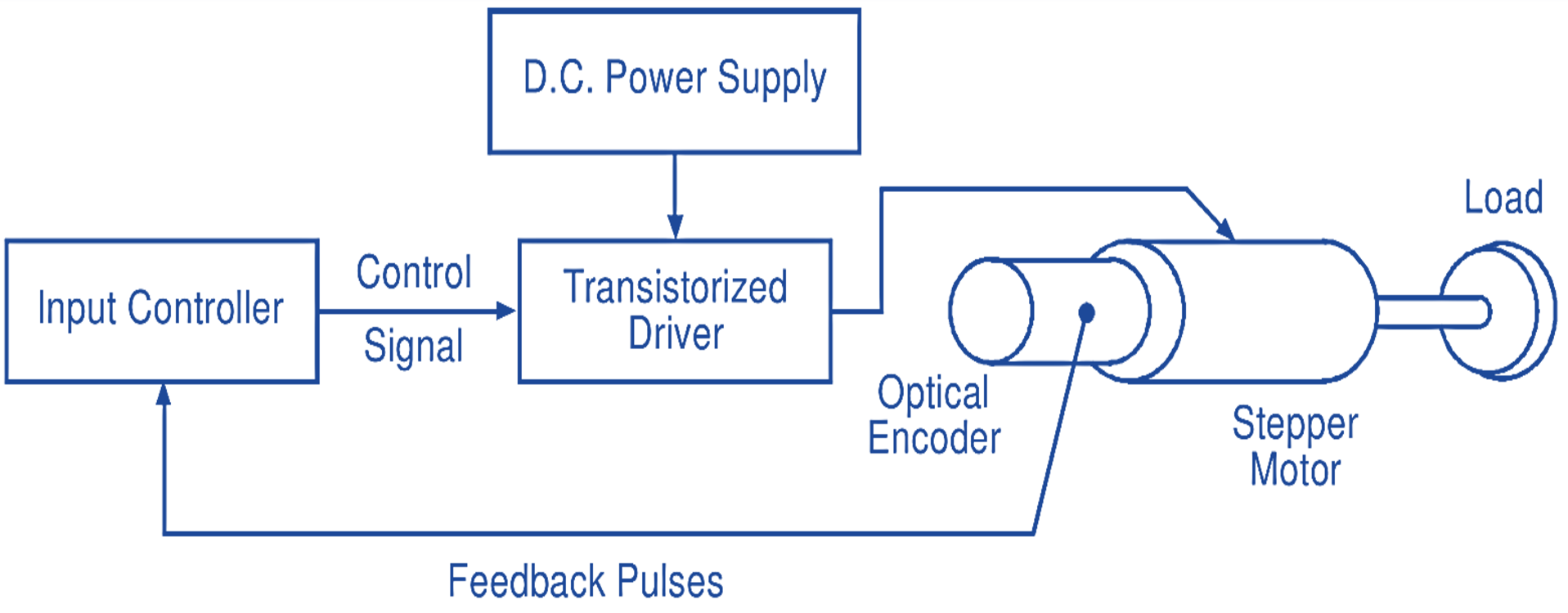
Fig. 4: Block diagram of closed-loop drive for a stepper motor
Stepper Motor Characteristics
Figure 5 shows the characteristics of torque stepping rate. As the stepping rate is increased, the motor can provide less torque because the rotor has less time to drive the load from one position to the next position. The start range is that in which load position follows the pulse without losing steps. On the other hand slew range is that in which the load velocity follows the pulse rate without losing steps but cannot start or reverse on signal. The maximum torque point is the point at which the torque is maximum.
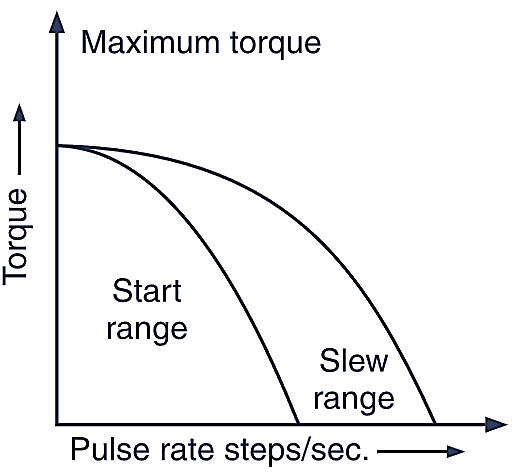
Fig. 5: Torque pulse rate characteristics of stepper motor.
The characteristics of the stepper motors are classified as
- Static characteristics,
- Dynamic characteristics.
Static Characteristics of Stepper Motor
The characteristics relating to a motor under stationary condition are called its static characteristics. They include:
- Torque-displacement characteristics,
- Torque-current characteristics.
Dynamic Characteristics of Stepper Motor
The characteristics relating to a motor under running condition or which is about to start, are called its dynamic characteristics. The dynamic characteristics of a stepper motor include:
- Pull-in torque characteristics,
- Pull-out torque characteristics.
Advantages of Stepper Motor
- Low cost.
- Small in size.
- It is available in wide range of step angles i.e. from 1.8° to 90°.
- Excellent torque at low speeds.
- Low maintenance (brushless).
- The starting current is low.
- Excellent for precise positioning control.
- It has low speed without reduction gears.
Disadvantages of Stepper Motor
- Overall efficiency is low
- Limited size available
- Noisy
- Torque decreases with speed.
Applications of Stepper Motor
The stepper motors are very widely used in computer peripherals such as serial printers, floppy disc drives, etc. Another big application field for stepper motors is found in the numerical controls of machine tools and workpieces. Other applications include process control systems. facsimiles, space-crafts. watches, semi-automatic wiring machines for printed circuit boards. etc.
Types of Stepper Motor
Following three types of stepper motors are in common use:
- Variable reluctance motors,
- Permanent-magnet motors.
- Hybrid motors.