In this topic, you study Open Circuit – Definition, Diagram & Theory.
The conceptual understanding of open circuits and short circuits is very important in the analysis of electrical networks. Otherwise, they can cause a lot of confusion while applying some of the methods for the solution of electrical networks.
An open circuit exists between two isolated terminals of a network which are not connected by an element of an kind.
Under this condition, these terminals can have a potential difference across them but the current flowing through them is always zero amperes.
For example, consider the battery of e.m.f. E volts and internal resistance of r ohms shown in Fig. 1.
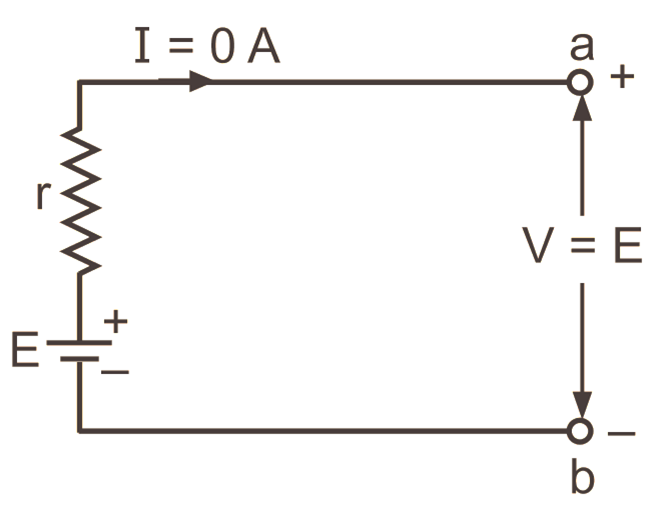
Fig. 1: A battery on open circuit
An open circuit exists between the terminals a and b. There is a voltage of V (= E) volts between these two terminals, but the current flowing between them is zero due to the absence of a closed path for its flow.