In this topic, you study Electrical Circuit (or Electrical Network) – Definition, Types & Theory.
The electrical circuit serves as a means of energy transfer from the source of electrical energy to the load with the help of the connecting wires or in simple words, provides a path for the current flow from the source to the load.
Parts of Electrical Circuit
The basic parts of simple electrical circuits are (see Figure 1):
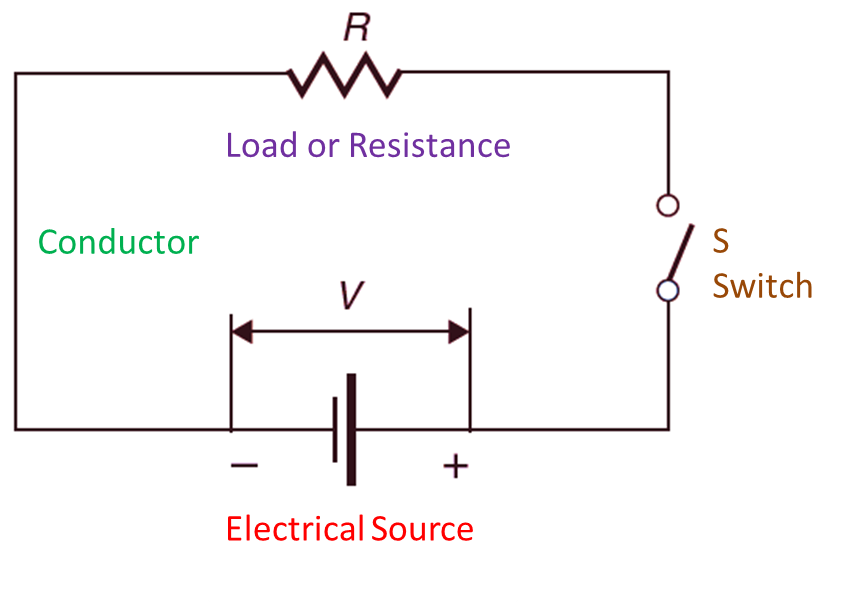
Fig. 1: Simple Electrical Circuit.
- Electrical Source (ac or dc).
- The switch (For opening and closing the circuit).
- Load (any electrical appliances).
- Cables and wires (or conductor).
Classification of Electrical Circuit
An electrical circuit or network is a combination of various elements consisting of sources of energy and components like resistors, capacitors and inductors, either in lumped or distributed form. The behaviour of entire network depends on the behaviour of its individual elements and accordingly, they can be classified as follows:
Linear Circuits: A circuit whose parameters are always constant irrespective of variations in voltage or current is known as a linear circuit. The current flowing in each parameter of such a circuit is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it.
Non-linear Circuits: A non-linear circuit is one whose parameters change with voltage or current.
Bilateral Circuits: It is that circuit whose characteristics are the same irrespective of its direction of operation, e.g. a transmission line. It has the same relationship between the current and the voltage for the current flowing in either direction.
Unilateral Circuits: A circuit whose characteristics are dependent on the direction of its operation is called a unilateral circuit, e.g. circuits containing elements like vacuum diodes, silicon diodes, selenium rectifiers, etc., which allow the current to pass only in one direction.
Active Networks: When a network contains a source of energy, it is said to be active. An energy source may be a voltage or a current source.
Passive Networks: A network is said to be passive if it contains no source of energy.
Definition of Some Important Terms Related to Electric Circuits
Incidentally, some important terms related with electric circuits are defined below.
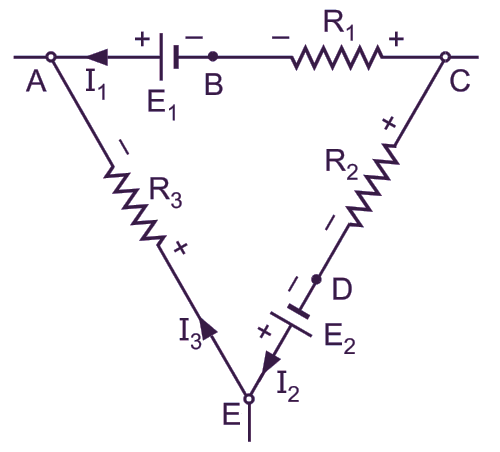
Fig. 1: Electrical Circuit.
Branch: A branch is a part of the network with two terminals across which different circuit elements (like energy sources, resistances, Inductances and capacitances) are suitably (in series or in parallel) connected. In Fig. 1, AC, CE and EA are the branches of a given network.
resistor R which carries no current due to its short circuit can be safel
Mesh or Loop: A set of branches, forming a closed path in a network is called a mesh orloop. In Fig. 1, the closed path ACEA is a mesh or loop.
Junction: It is a common point in a network at which two or more circuit elements are connected. In Fig. 1, the points A, B, C, D and E are the junction points.
Node: Every junction point in a network where three or more branches meet is called anode. In Fig. 1, A, C and E are the nodes.