High energy permanent magnets made up of rare earth or samarium-cobalt used for exciting the magnetic field of permanent magnet synchronous motors, enable them to be significantly smaller in size and weight. They have better efficiency because of the absence of a rotor winding and the small size of the rotor.
Construction of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor
Fig. 1 shows the circumferential cross-section of a typical two-pole permanent magnet synchronous motor. The stationary member of the motor, called stator can be of a wide variety of constructions and designs and can be wound for single-phase or polyphase excitation. The permanent magnets made up of high permeability and high coercivity materials like rare earth or samarium-cobalt form the poles of the rotor, equivalent to the wound field poles of conventional synchronous motors. Permanent magnet poles are inherently salient. Many permanent magnet synchronous motors may have physically smooth cylindrical rotors, but electrically each permanent magnet pole have a salient pole structure.
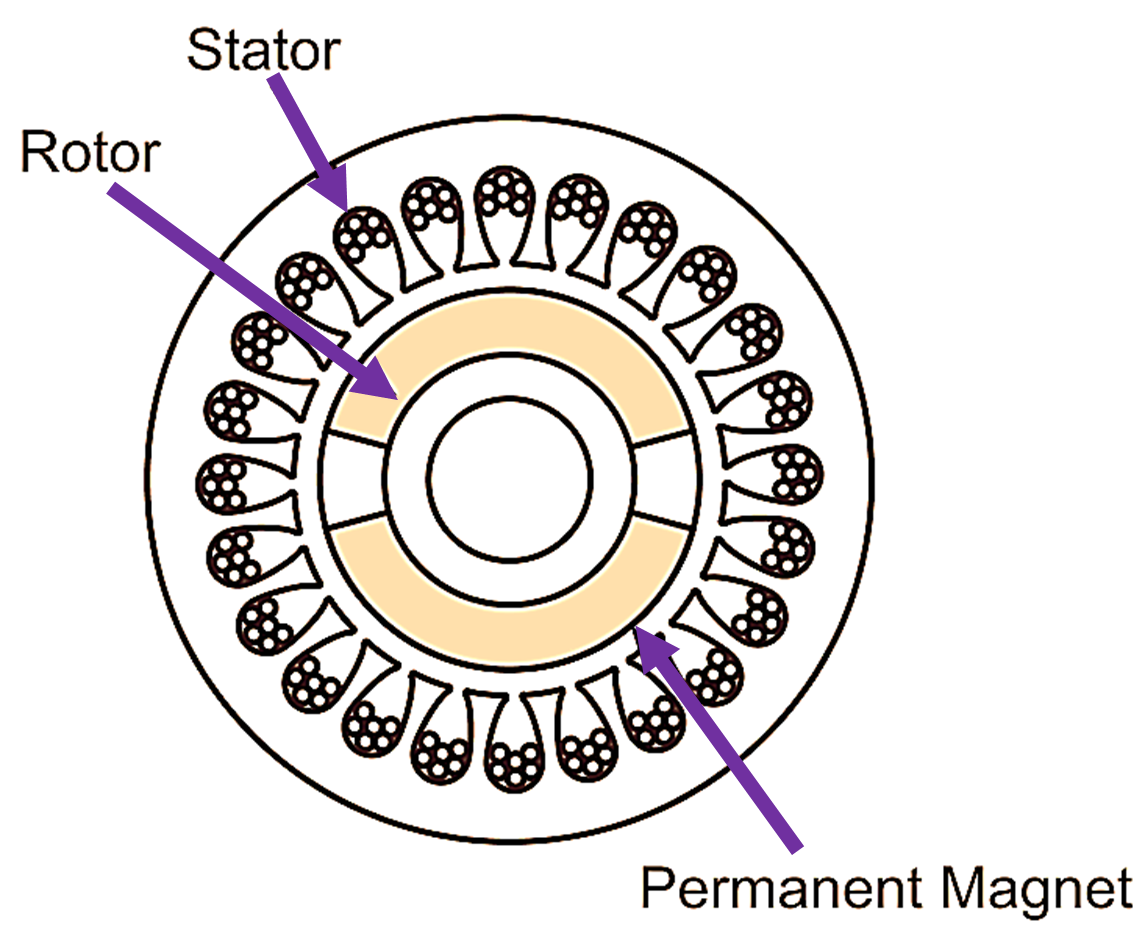
Fig. 1: Circumferential cross section of a two-pole permanent magnet synchronous motor
Apart from permanent magnet poles, rotor structure of the motor may include a number of other structural and magnetic components. Damper winding, forming the cage arrangement of conducting bars is provided in most of the motors (of power ratings above a few hundred watts) used in power applications. The principal purpose of damper winding is to dampen oscillations about the synchronous speed. It is also used to start the synchronous motor and bring it up to the synchronous speed.
Principle of Operation of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor
The principle of working of permanent magnet synchronous motor is same as that of conventional synchronous motor. Initially, the motor starts as a squirrel-cage induction motor with the help of damper winding. When a three-phase winding (if provided) of a stator is energized from a three-phase supply, rotating magnetic field is set up in the air gap. At synchronous speed, the rotor field poles get magnetically locked with the stator poles to produce torque and hence, rotor continues to rotate.
Characteristics of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor
Permanent magnet synchronous motors have same operating and performance characteristics as conventional synchronous motors.
Applications of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor
They are widely used in various industrial applications such as automobiles, compressors, blowers, conveyors, fans, pumps, machine tools, elevators, traction, aerospace, printed circuit motors, computers, robotics, textile and glass industries, steel rolling mills, fibre spinning mills, etc.