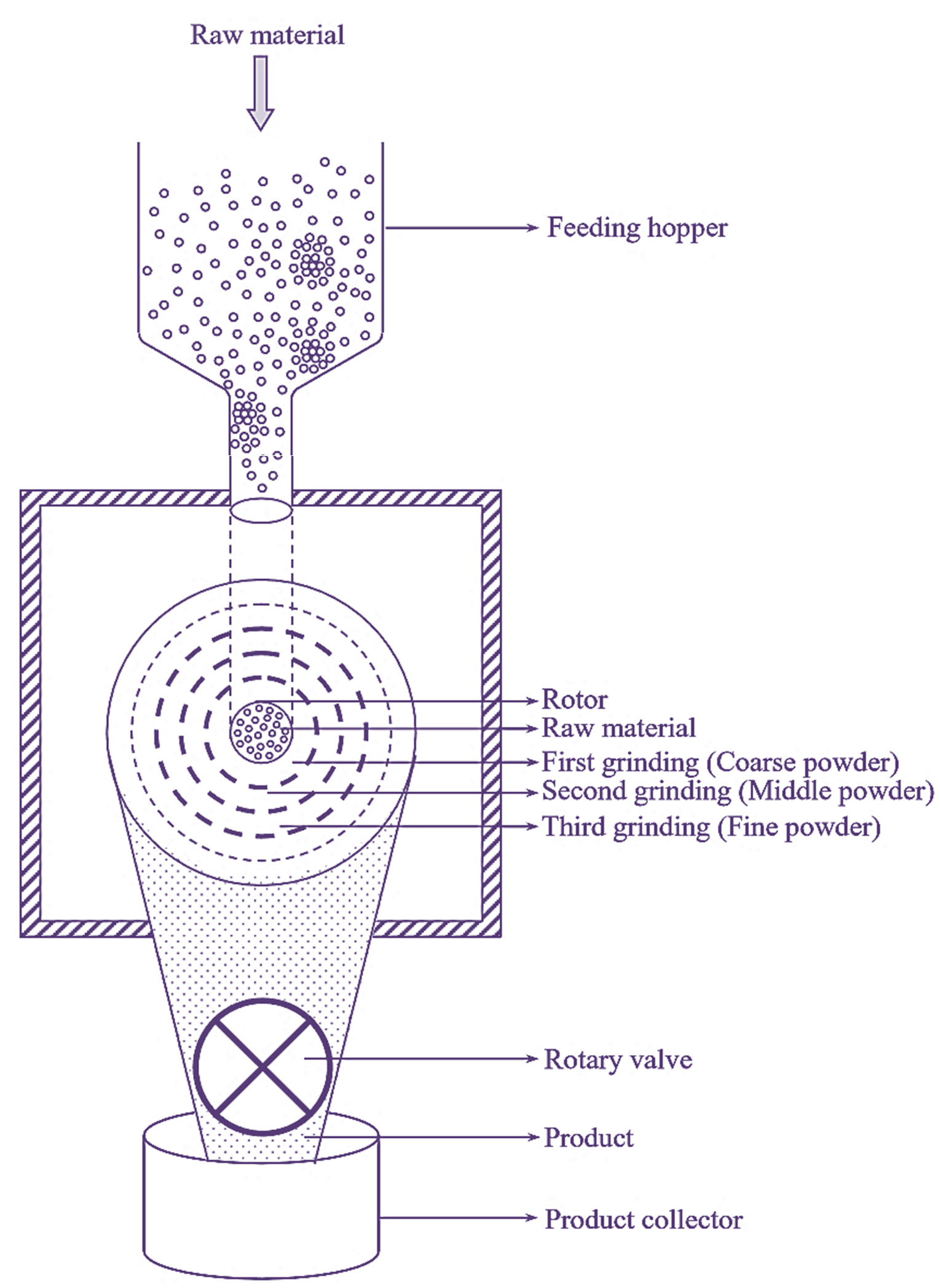
Figure 1: Pin Mill.
Working Principle of Pin Mill
Pin mills or centrifugal impact mills (CIM) function on the principle of impact and are used for the achievement of fine and ultra (micro) fine particles. At slower speeds, they are used for dismantling clusters of particles. They work without the use of external knives, hammers, screens or rolls.
Construction & Working of Pin Mill
Weighed quantity of raw material to be milled is fed into the machine through the feeding hopper (feeding valve). Due to gravitational pull, the material passes down through the feeding hopper, undergoes centrifugal acceleration and reaches the impact zone. Pin type or knife type rotor is used at a speed of a few hundred to 5,400 rpm. The pins attached to the rotor rotate beat the material to yield small particles. First grinding of coarse powder is carried out in the inner part of the rotor. The resultant of first grinding i.e., middle powder is remilled and finally third grinding is done at the periphery until the powder easily passes through the screens. Fine or ultrafine powder is collected as product from the rotary valve.
Advantages of Pin Mill
- Easy to clean and operate.
- Components can be changed periodically.
- Most of the components can be used lifelong (durable).
- Consumes less power and time and works with higher efficiency.
- Solids as well as semisolids can be milled.
- Wastage is low.
Disadvantages of Pin Mill
- Components are costly
- The screen and the mill may get affected by the abrasive materials to be size reduced.
- The screen possesses the risk of clogging.
Applications of Pin Mill
Pin mills are used for size reduction of the following,
- Non-abrasive materials
- Soft materials
- Oily materials.