In this topic, you study Circuit Breaker definition, Working, Diagram, Symbol, Types, & Selection.
A switching device, which can be used to make or break a circuit manually, automatically, or with the help of remote control, all conditions i.e. no-load, full load, and fault conditions, is known as a circuit breaker.
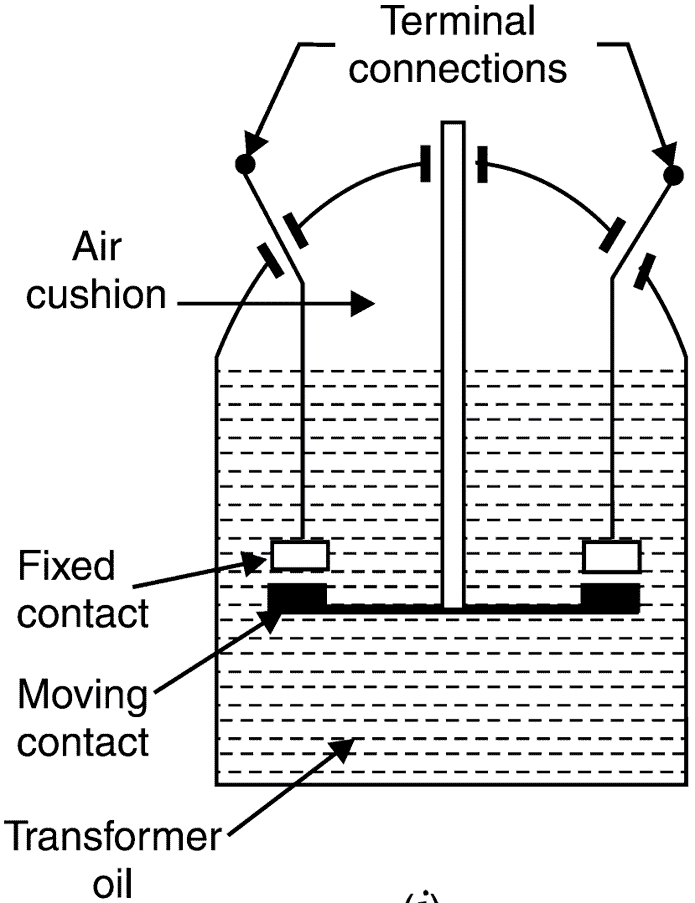
Figure 1 Oil circuit breaker.
Working of Circuit Breaker
The circuit breaker consists of two contacts namely “fixed” and “moving contacts” which touches each other normal condition i.e. when the circuit breaker is closed. Whenever a fault occurs, the trip coils get energized the moving contacts get pulled by some mechanism, and therefore, the circuit breaker is opened and the circuit is broken. Figure 1 shows the parts of a typical oil circuit breaker.
Symbol of Circuit breaker
The circuit breaker symbol is shown below

Types of Circuit breaker
The circuit breaker can be classified into the following categories as given in table1.
Table. 1. Types of Circuit Breaker
| Type | Arc Quenching Medium | Voltage Range |
| Miniature circuit breakers | Air at atmospheric pressure | 400-600V |
| Air break circuit breakers | Air at atmospheric pressure | 400V-11kV |
| Minimum oil circuit breakers | Transformer oil | 3.3 kV-220 kV |
| Vacuum circuit breakers | Vacuum | 3.3 kV-33 kV |
| SF6 circuit breakers | SF6 gas at 5 kg/cm2 pressure | 3.3 kV-765 kV |
| Air-blast circuit breakers | Compressed air at high pressure | 66 kV-1100 kV |
Selection of circuit breaker
The selection of circuit breakers for different ranges of voltage is given in table 2.
Table. 2. Selection of Circuit Breakers choice
| Choice of Circuit Breakers | Rated Voltage | Remark |
| Air break circuit breaker | Below 1 kV | |
| Vacuum, SF6, minimum oil circuit breakers | 3.3 kV – 33 kV | Vacuum preferred |
| Air blast, minimum oil, SF6 circuit breakers | 132 kV – 220 kV | SF6 preferred |
| Air blast, circuit breakers, SF6 circuit breakers | 400 kV – 760 kV | SF6 preferred |