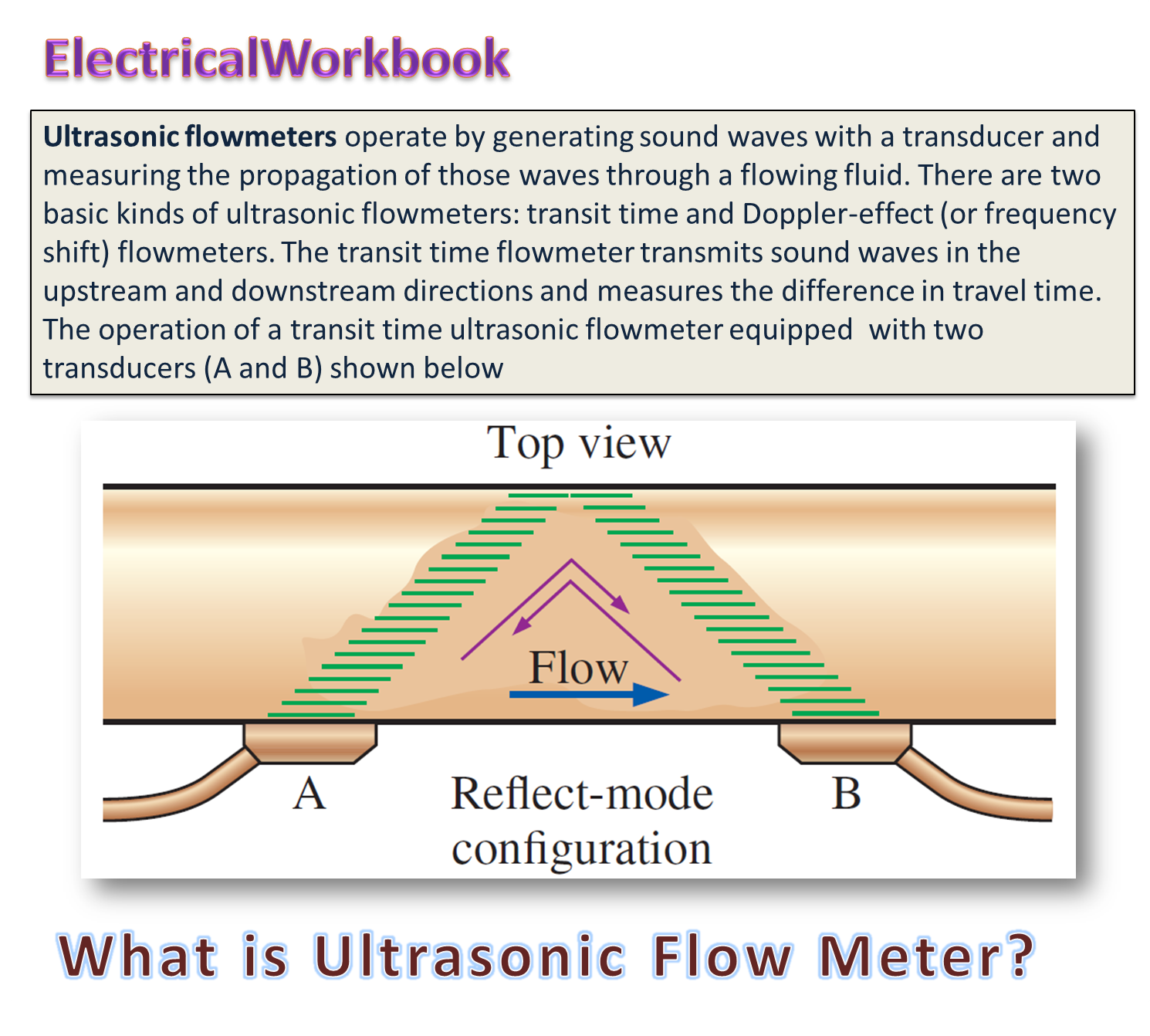
Ultrasonic flow meter works on the basis of Acoustic method of flow measurement, which states that, “Velocity of an acoustic wave and flow velocity can be added algebraically or summed vectorially”.
Principle of Operation
“It is based on the apparent change in the velocity of propagation of ultrasonic wave pulses in a fluid with a change in velocity of fluid flow”.
Construction of Ultrasonic Flow Meter
Ultrasonic transducer may be mounted in a direction parallel to the pipe wall or in an inclined direction, making some angle across the pipe wall. Ultrasonic transducer consists of two transmitters and two receivers. They are separated by a distance “L” and mounted as shown in Fig. 1. Transmitter “A” & “B” are piezoelectric crystals or devices transmitting short duration ultrasonic signals through the fluid flowing through pipe at a velocity “V”. Similar types of piezoelectric crystals or devices are used as receivers. Therefore, they are also labeled or referred as “A” and “B”.
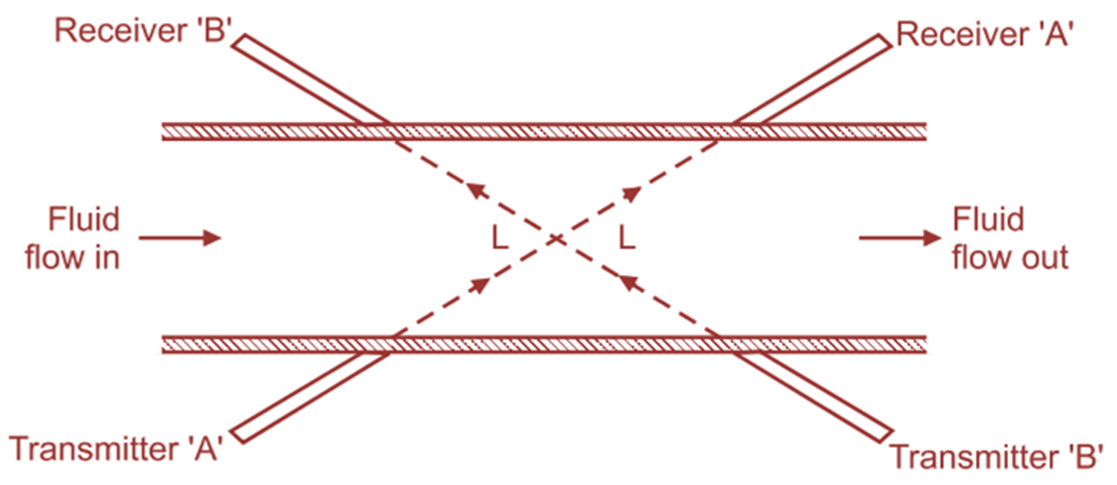
Fig. 1: Ultrasonic Flow Meter.
Working of Ultrasonic Flow Meter
Transmitter “A” transmits wave pulses of short duration in the direction of receiver “A”. This transmission is favoured, because, it occurs in the direction of flow of fluid. Transmitter “B” transmits wave pulses of short duration in the direction of receiver “B”. This transmission is not favoured, because, it occurs in opposite direction of flow of fluid. In short, velocity of ultrasonic waves is increased or decreased by the fluid velocity depending upon the direction of flowing fluid. Velocity of ultrasonic signal transmitted by transmitter “A” and received by receiver “A” will increase, due to the fluid velocity “V” (Same direction). Whereas, velocity of ultrasonic signal transmitted by transmitter “B” and received by receiver “B” will reduce due Transmitter ‘A’ to fluid velocity “V” (Opposite direction). Since, transducers are used as both, transmitters and receivers, the difference in travel time can be determined with same pair of transducers.
In this device, the detector measures the time taken by ultrasonic wave to cross the pipe along the direction of flow and opposite to the direction of flow.
VS = Velocity of sound in fluid in m/s
V = Velocity of fluid in m/s
L = Distance between transmitter and receiver in metres
t1 = Transit time along the fluid flow in seconds
t2 = Transit time against the fluid flow in seconds
Velocity of flow,
\[\text{V}=\frac{\text{V}_{\text{S}}^{\text{2}}\left( {{\text{t}}_{\text{2}}}-{{\text{t}}_{\text{1}}} \right)}{2\times \text{L}}\]
Range of ultrasonic Meter: 0 to 180 km/hr on air with an accuracy of ±0.5
Advantages of Transit Time Ultrasonic Flowmeter
- No need of obstructing fluid flow.
- No moving parts.
- It can be used for bi-directional flows as well as rapidly varying/ pulsating flows.
- High accuracy.
- Fast response.
- Linear relationship between velocity of fluid flow and the output obtained.
- Flow measurement is not affected by fluid viscosity, pressure and temperature variation.
- Suitable for flow measurements of liquids as well as gases.
Disadvantages of Transit Time Ultrasonic Flowmeter
- Complex in construction (complex circuit).
- Relatively high cost.
- Limited use in industry.
- Close tolerances (small tolerance zone) are required in manufacturing of mechanical and electronic components, which leads to increase in manufacturing cost.
Applications of Transit Time Ultrasonic Flowmeter
- To measure the flow rate of any liquid, through which, sound can be transmitted.
- To measure ocean currents.
- To measure water flow and gas flow in large conduits (pipes).
- To measure flow of various industrial fluids, which cannot be measured by other meters.