Rotameter is most commonly used type of variable area type flow meter. Here, flow area is varied by means of float kept in a tapered glass tube. Depending on the rate of flow, the float takes position in the tube, which increases or decreases size of area, thus keeping the pressure difference constant.
Principle of Working
“Pressure difference across an annular orifice is directly proportional to square of its flow area and square of flow rate. ”
Construction of Rotameter
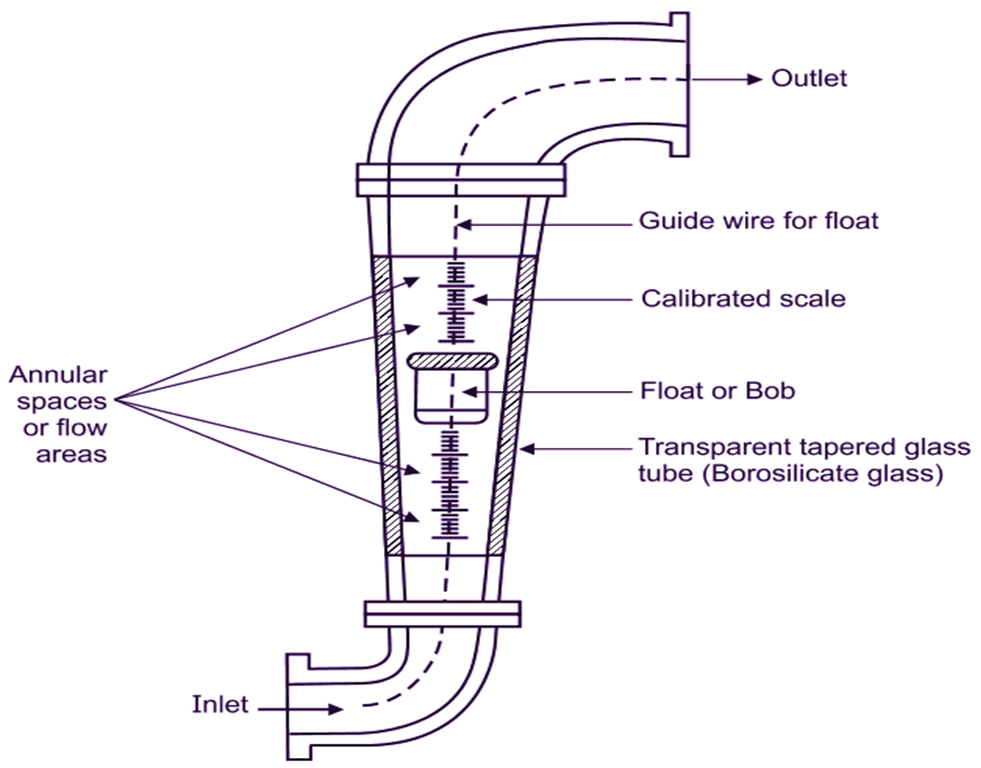
Fig. 1: Rotameter.
Rotameter consists of a transparent and tapered glass tube placed vertically in such a way that, the larger end is at top. A float is provided inside the glass tube, which is free to move up and down. Shape of float is selected, in such a way that, it creates minimal obstruction for flow. Density of float is more (nearly double) than the density of the fluid, whose flow rate is to be measured. Glass tube is made tapered to maintain constant pressure drop. This arrangement gives a linear relationship between the flow rate and position of float within the tube. Flow inlet is provided at bottom of the glass tube and flow outlet is at the top of tube. Under equilibrium, fluid force acting vertically upward is equal to weight of float acting vertically downward.
Weight of float = Mass of float × Gravitational acceleration = m × g
Fluid force = Pressure of fluid × Interna Cross-sectional area of Rotameter
= P . A
A linear scale is graduated or marked on the outer periphery of glass tube.
An annular orifice is the free area between the float and inside wall of tube.
Float adjusts its position according to discharge through the passage, i.e. float rises higher or lower depending on the flow rate.
Working of Rotameter
Fluid (whose flow is to be measured) enters the tube from bottom, then moves upward and escapes through the top. When there is no flow through rotameter, the float will rest at the bottom of glass tube. In this position, the maximum diameter of float is approximately same as the inside diameter of glass tube.
When the fluid enters in the metering tube, the float moves upwards, increasing the flow area of annular orifice. Float is pushed upwards, until, the lifting force produced due to pressure difference across its upper and lower surface becomes equal to weight of float. Now, if the flow rate increases, the pressure difference and hence, lifting force increases temporarily. Due to this, float moves upward and increases the area of annular orifice, so that, the Increased lifting force will decrease and fluid force will be equal to weight of float. Thus, the pressure difference remains constant by changing the area of annular orifice in proportion to the flow rate.
Every float position corresponds to one particular flow rate for a fluid of given density and viscosity. Calibrated scale marked on the glass tube provides the direct indication of flow rate.
Material used for float: Heavier metals like Stainless steel , Gun metal, Brass etc.
Material used for tube: Non-corrosive materials such as Glass, plastic etc.
Characteristics of Rotameter
- Simplicity of construction and low cost.
- Possibility of remote indication and record.
- Essentially a linear scale with most of the meters.
- Easy to install.
- Accuracy Within 2% of the maximum reading.
Advantages of Rotameter
- Pressure loss is nearly constant and small.
- It can handle any corrosive fluid.
- Suitable for measurement of gases as well as liquids.
- Good accuracy at low flow rates.
- Provides linear scale.
- Condition of flow is easily visible.
- Relatively low cost.
- Good range of measurement.
- Gives direct visual indication of flow rate.
- Minimum piping required.
- Easily equipped with data transmission, indicating and recording devices.
Disadvantages of Rotameter
- It must be installed in vertical position only.
- It becomes expensive in case of high pressure and high temperature applications.
- When opaque (Non-transparent) fluid IS used, float may not be visible.
- It is not rigid in construction as compared to venturimeter or orifice meter, due to use of glass tube.
- Not good to use in pulsating flow cases (i.e. fluctuating flow rates).
- Limited to small pipe sizes and capacities.
- Less accurate than venturimeter and orifice meter.
- Not suitable for liquids carrying suspended solid particles.
Applications of Rotameter
Rotameter is used for measurement of flow of liquids and gases in,
- Laboratories.
- Testing and production lines.
- process industries.
- Oil industries.
- Oxygen flow rate measurement in medical applications.
- For metering purge flows (i.e. viscous fluids having suspended particles).