Operating Range: More than 750°C.
Working Principle of Radiation Pyrometer
Radiation pyrometer works on the principle which states that, “Temperature of a body can be measured by measuring radiant energy emitted by that hot body“. According to Stefan Boltzmann’s law, total thermal radiation emitted by a body can be calculated by,
Q = σ · T4 (in Wm2)
Where,
σ = Stefan Boltzmann’s constant in Wm-2K-4
T = Absolute Temperature in Kelvin
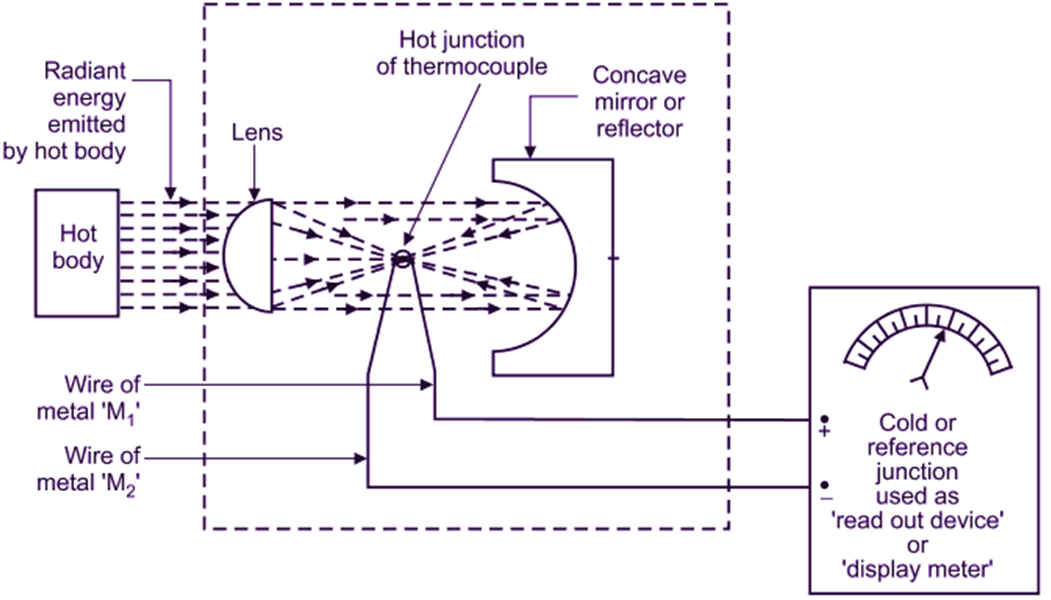
Fig. 1: Total Radiation Pyrometer
Construction of Radiation Pyrometer
Radiation pyrometer consists of three major components:
Lens: It is used to focus the radiated energy from the body (whose temperature is to be determined) on to a receiving element.
Receiving element: Resistance thermometer or thermocouple can be used.
Recording instrument: A temperature indicator, recorder or controller is attached with the receiving end to obtain reading.
Working of Radiation Pyrometer
When the total energy radiated by a hot body enters the pyrometer, it is collected and focused by lens on to the receiving element (thermocouple). Due to hot radiations incident on thermocouple, an emf is developed. This emf is measured by a milli-voltmeter, which is calibrated to show value of measured temperature directly. Concave mirrors are used to avoid reflection of radiations in unwanted directions. Concave mirrors reflect them back to receiving element as illustrated in Fig. 1.
Advantages of Radiation Pyrometer
- Ability to measure high temperature, unlike thermocouple, which may melt at high temperatures.
- No physical contact with object, whose temperature is to be measured.
- Fast speed of response.
- High output and moderate cost.
- It is less affected by corrosive atmosphere.
- High accuracy of 2 % of full scale.
Disadvantages of Radiation Pyrometer
- Non-linear scale.
- Possible errors due to presence of intervening gases or vapours, which absorb the radiations.
- Emissivity of hot body affects temperature measurement.
- Due to dirt or dust on the mirror or lens, instrument shows low value of temperature measured than actual temperature of body.
Applications of Radiation Pyrometer
- It is preferred for temperature measurement of components or applications like furnace, interiors, boilers etc., which are not easily accessible.
- It measures temperatures of places or components, which are not easy to access.
- It is used to measure average temperature of large surfaces.
- It is used to measure temperature of moving object or target.
- It is used to measure invisible rays from radiations.
- It is used to measure temperature in corrosive atmospheric conditions, temperature measuring instruments may be contaminated.