An industrial robot has the basic parts like arm, sensor, actuator, controller etc. These subsystems communicate among themselves via interfaces, whose function consists basically of decoding the transmitted information from one medium to another. Fg. 1 shows the block diagram representation of a typical robotic mechanical system. The input is a prescribed task, which is defined earlier. The output of a robotic mechanical system is the actual task, which is monitored by the sensors. These sensors sense and transmit the information in the form of feedback signals.
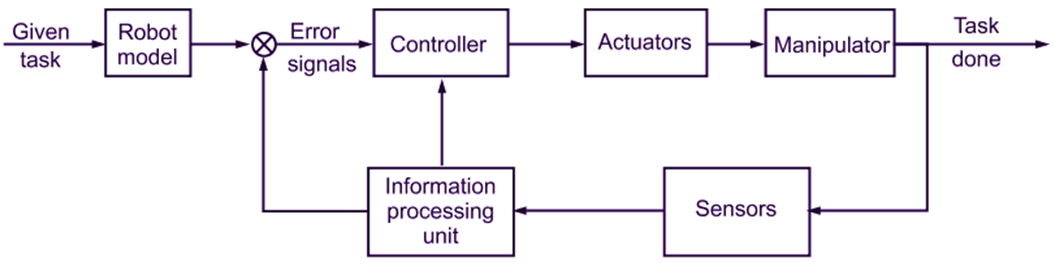
Fig. 1: General Structure of Robotic Mechanism
This is compared with the predefined task given to the controller. The errors between the prescribed and the actual task are then fed back into the controller, which then synthesizes the necessary corrective signals. These are in turn fed back to the actuators, which then drive the mechanical system through the required task. Thus, the given task is performed by the robot.