Rotary Potentiometer is used for measurement of angular displacement.
Construction of Rotary Potentiometer
Resistive elements are circular in shape in case of rotational type potentiometer. The resistive elements of potentiometer are metal alloys wound on a cylindrical ceramic former. Wiper (slider) is made up of phosphor bronze and it’s gold plated for good electrical contact.
Working of Rotary Potentiometer
The resistance wire is wrapped around a circular former, so that, wiper may be rotated along with the various turns along an arc (angular movement). The circular former is also called a mandrel (Figure 1). The wiper always maintains an electrical contact with the resistance wire wound on a circular former made up of plastic or ceramic (i.e. any insulating material) and rotates over it. The resistance element is excited with either AC or DC voltage. The output voltage generated is a linear function of angular displacement (θi) to be measured (Figure 2).
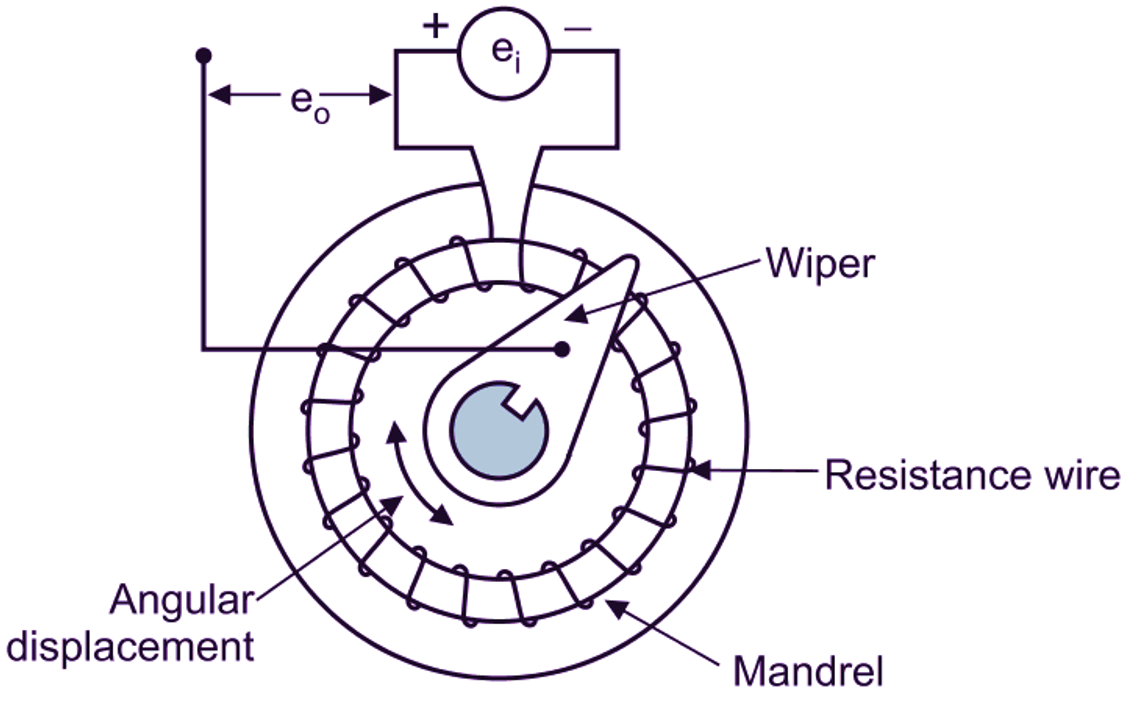
Fig. 1: Rotary Potentiometer
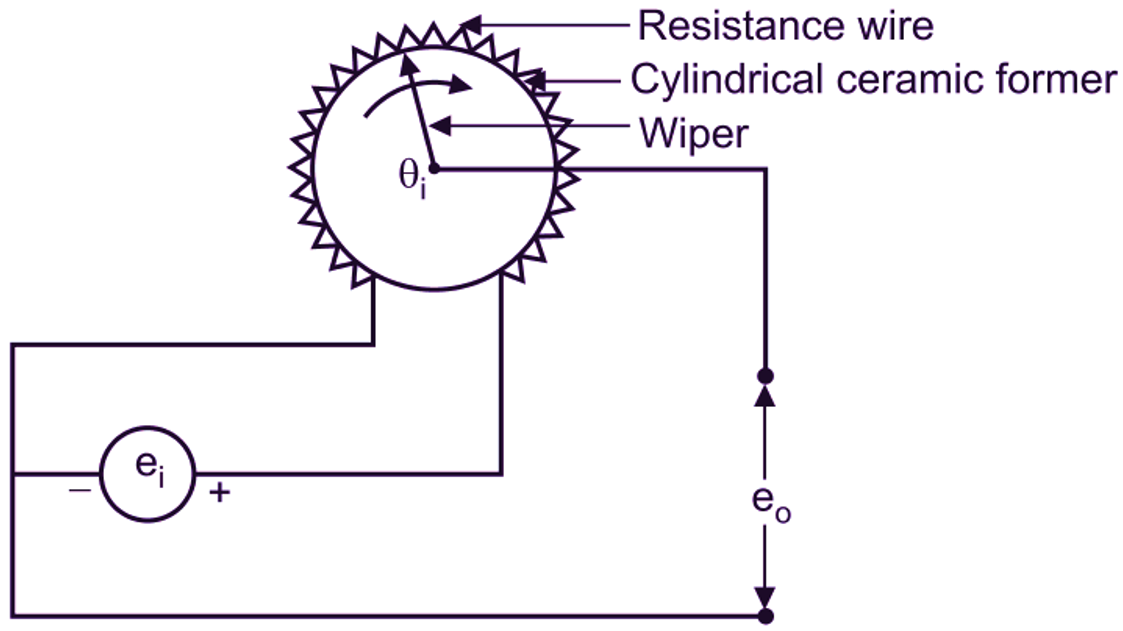
Fig. 2: Rotary Potentiometer working
Materials used for Rotary Potentiometer
Resistance Wire
- Commonly used material for resistance wire is alloy metal.
- However, depending upon the specific requirements and applications, it is also made up of platinum, chromium, nickel, copper etc.
- Resistance wire has to carry large current at high temperature. Therefore, temperature coefficient of resistance wire material should be small.
Wiper or Slider
- Wiper (slider) is made up of phosphor bronze.
- For good electrical contact, it is gold plated.