Spring balance is a force measuring device which works on the principle of Hooke’s law. According to Hook’s law, the force acting on the spring (along the axis of the spring) is directly proportional to the displacement of the spring, in the direction of the force.
Construction of Spring Balance
Spring balance is made up of a coiled spring. The spring is suspended freely from a fixed support (i.e., one end of the spring is fixed to a support and the other end is movable). The schematic diagram of a spring balance is shown in below figure 1.
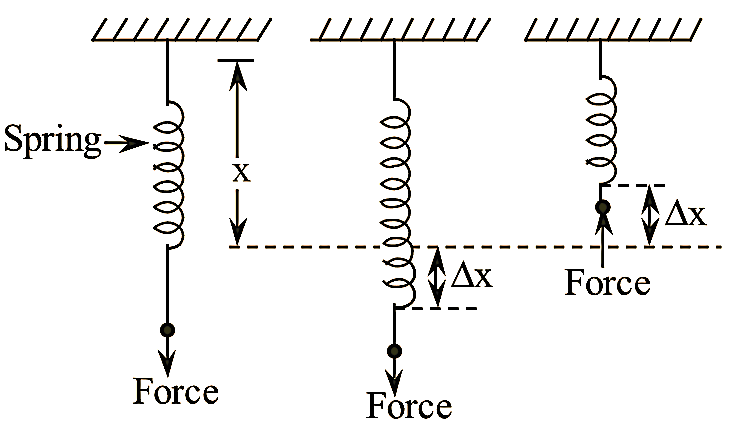
Figure 1: Spring Balance.
The force to be measured is applied at the movable end of the spring along the axis of the spring. When the spring is subjected to a force in the downward direction, the spring expands along its length If the force is applied in the upward direction, the spring contracts along its length.
Let, the actual length or the equilibrium position of the spring balance be ‘x’, and ‘Δx’ be the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position. When force is applied to the spring, Δx is positive when force acts downwards and Δx is negative when force acts upwards.
From the principle of spring balance, the displacement (Ax) is directly proportional to the applied force (F).
i.e., F ∝ Δx
F = k.Δx
Where,
k is Spring constant or stiffness (force unit displacement)
Advantages of Spring Balance
- It is simple in construction and working.
- It has linear input-output characteristics.
- It is economical.
Limitations of Spring Balance
- It has low measurement accuracy because spring is sensitive to environmental conditions such as temperature.
- It is not suitable for measurement of dynamic forces.