Communication by means of sound waves is possible over short distances. If the sound waves are converted into electrical signals, then these signals can be made to travel long distances through transmission lines. This is termed as telephony. Telephony provides communication from person to person. Telephone lines have to be laid between different stations for transmission of telephony signals. One disadvantage of telephony communication is the need of telephone lines. Laying of telephone lines in hilly terrain and jungles is difficult and costly. Telephone communication cannot be used in all situations. Can the pilot of an airplane inform the airport authorities about the problems he is facing with his aero plane through telephone lines? Can the prime minister of a country appeal to his countrymen over telephone to donate generously for the flood victoms ?
All such situations led to the development of radio broadcast and wireless communication which provides very fast and long distance communication without telephone lines. The radio broadcast and wireless communication is carried out by radiation of electromagnetic waves through free space. These waves are picked up at the receiving end. Aerials are used for radiating the signal energy at the transmitting end and picking upon the signals at the receiving end. The signal frequencies lying in the audio frequency range cannot be transmitted through radiation due to the following reasons
(a) Antenna length. Length of the antenna is very important for effective radiation/ pick up of electrical signals. It has been found out through experiments that the length of the antenna should be approximately equal to the wavelength of the signal in order to obtain maximum radiation of the signal energy. Audio signals have frequencies lying in the range from 20 Hz to 20 kHz and the antenna length required for effective radiation of audio signals must have antenna length between 15000 Km to 15 Km. Construction of such a long antenna is not only costly but also a great engineering problem. If the frequency of the signal is raised to 500 kHz, the antenna length required is of the order of 600 m. Such an antenna is not difficult to fabricate.
(b) While the signal waves are travelling through free space between the transmitting end and the receiving end, they suffer certain losses and the signal strength is reduced. As a result of these losses, the range over which these signals can be picked up by a receiving antenna is restricted. It has been found that these losses are inversely proportional to the signal frequency. Low frequency signals suffer more losses during propagation as compared to signals of high frequencies. It is therefore necessary to translate the signal frequencies from the audio frequency range to a high frequency range before transmission to obtain long range communication without using telephone lines.
Block Diagram of Communication System
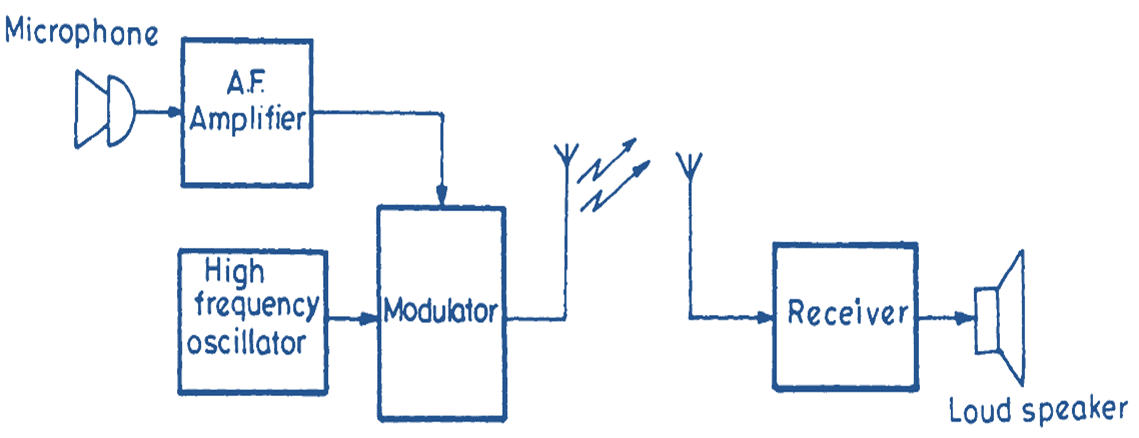
Fig. 1: Outlines of a radio communication system.
Fig. 1 shows the outlines of such a communication system. The radio communication system comprises of a transmitter which translates the audio frequency signals to a high frequency range and radiates these waves into free space. The radio receiver picks up these signals and converts these signals back into audible range. A brief description of the radio communication system is given below.
Transmitting system: In the transmitting section, a microphone is used to convert sound waves into audio current. The audio signal is amplified by an amplifier to suitable amplitude. The amplified audio signal is given as input to the modulator.
The modulator is also given the high frequency signal generated by a high frequency oscillator. The modulator translates the audio frequency signal to a high frequency signal by a process known as modulation. The modulated signal is given to the antenna for radiation into free space. The antenna converts the high frequency currents into electromagnetic waves which are radiated into free space. The electromagnetic waves travel at the velocity of light and provide very fast communication.
The electromagnetic waves reach the receiving and induce signal voltage in the receiving antenna. The receiving antenna picks up the signals from the free space and converts them into electrical currents. The electrical signal is given to the receiver. The receiver amplifies the signal received and demodulates it to recover the audio frequency signals. The audio frequency signal is given to the loudspeaker which produces sound waves.