In this topic, you study Inverter (DC to AC converter) – Definition & Theory.
An inverter is an electrical circuit, converts a fixed voltage DC to a fixed (or variable) voltage AC with variable frequency. Inverters can be used to control the speed of three-phase induction and synchronous motors.
Applications of Inverter
Some of the applications of inverters are:
- Generation of 50 Hz, fixed voltage AC from a DC source obtained from wind power, solar generation or batteries
- Uninterrupted power supply (UPS)
- Induction heating
- Standby power supply
Figure 1 is a block diagram of the closed loop speed control system of a three-phase induction motor.
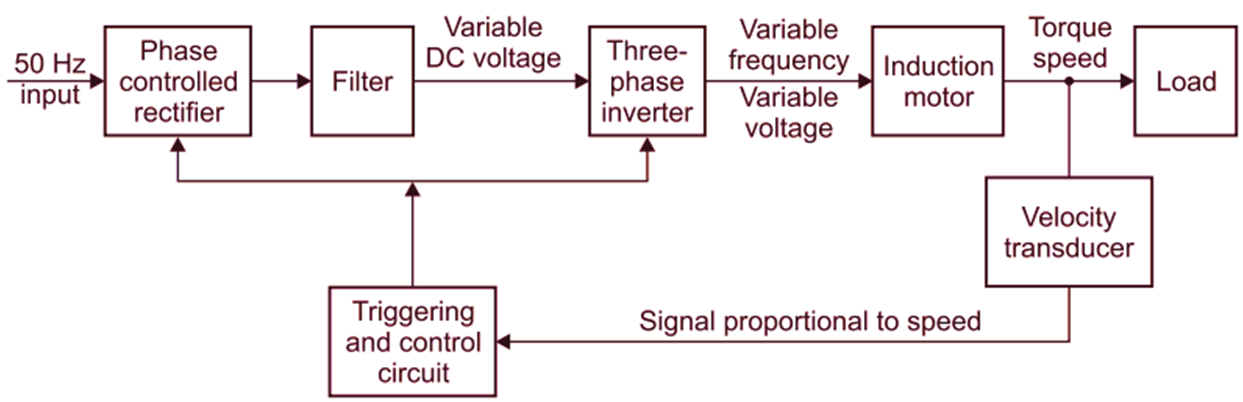
Fig. 1: Closed loop speed control system for a three-phase induction motor
Figure 2 shows the scheme for an UPS application uninterrupted power supply when the power failure is of longer duration and unlimited protection time is required for domestic industrial applications.
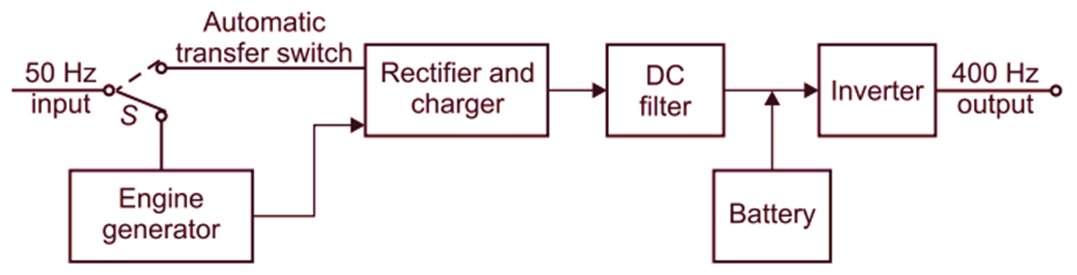
Fig. 2: Uninterrupted power supply system