In this topic, you study how to design Gray to Binary Code Converter Circuit and draw the logic diagram.
Truth table
The conversion of 4-bit input Gray code (A B C D) into the Binary code output (W X Y Z) as shown in truth table 1. The 4-bit input so 16 (${2^4}$) combinations are possible and all of them are valid so no don’t care condition.
Table 1: Gray to Binary Code Code Converter.
| Gray Code (Input) | Binary Code (Output) | ||||||
| A | B | C | D | W | X | Y | Z |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
Drawing of K-map for each output
From this truth table, the K-maps are drawing shown in Figure 1, to obtain a minimized expression for each output.
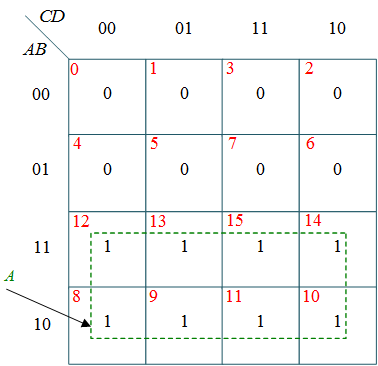
(a) k-map for W
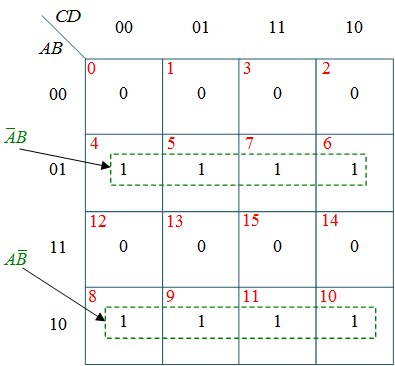
(b) k-map for X
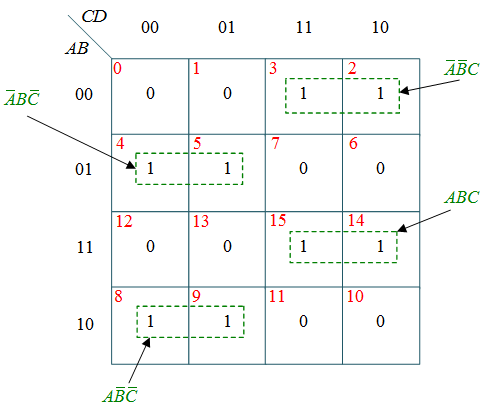
(c) k-map for Y
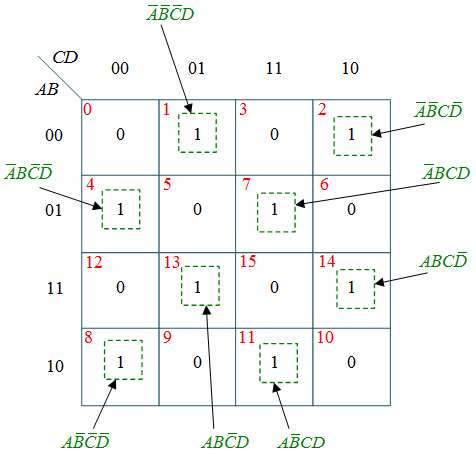
(d) k-map for Z
Figure 1: k-maps for Gray to Binary Code Converter.
Minimized Expression for each output
The minimized expression for each output obtained from the K-map are given below as
$W = A$
$X = \bar A B + A \bar B = A \oplus B $
$Y=\bar{A}\bar{B}C+\bar{A}B\bar{C}+ABC$
$+A\bar{B}\bar{C}$
$=A\oplus B\oplus C$
$Y = X \oplus C$
$Z = \bar A\bar B\bar CD + \bar A\bar BC\bar D + \bar AB\bar C\bar D $
$+\bar{A}BCD\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }+AB\bar{C}D+ABC\bar{D}$
$+A\bar{B}\bar{C}\bar{D}+A\bar{B}CD$
$Z=A\oplus B\oplus C\oplus D$
$Z = Y \oplus D$
Logic Circuit Diagram
Based on the above given minimized expression for each output, a logic circuit can be drawn as shown in Figure 2.
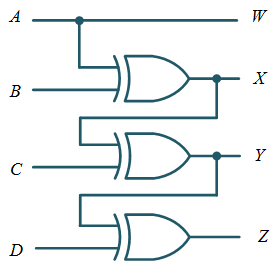
Figure 2: Gray to Binary Code Converter logic diagram.