The Eddy Current Heating effect is produced due to eddy currents induced in the mass to be heated. Alternating current cutting the conducting substance induces eddy currents in it and the loss of energy due to eddy currents is “eddy current loss” which appears to be in the form of heat. This eddy current loss,
We = K × B2 × f2 × volume
where,
k is constant
f is supply frequencty
B is magnetic fied intensity.
Since We ∝ B2 and also We ∝ f2 and hence eddy currents principle is used in heating a conducting substance.
Nature of Supply Used in Eddy Current Heating
Very high frequency (about 10,000 Hz to 40,000 Hz) AC supply is used with the frequency control and flux density control equipment.
Working of Eddy Current Heating
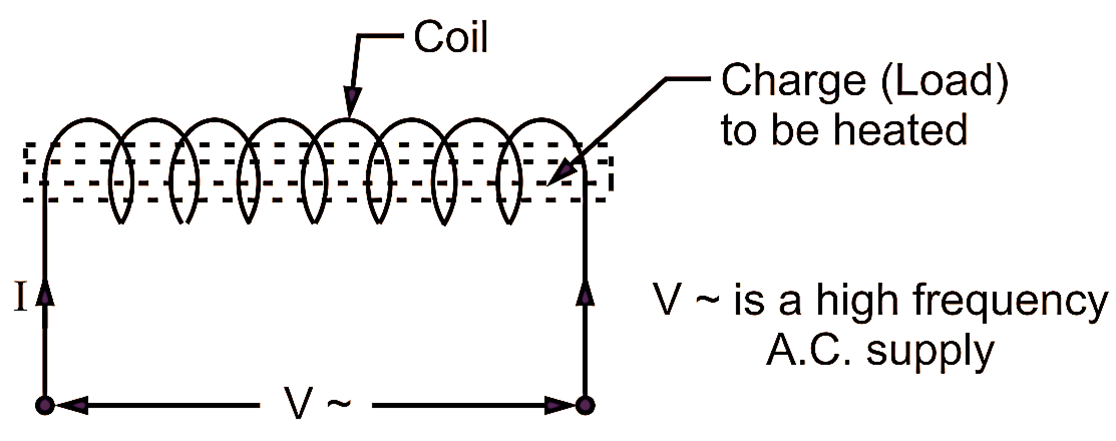
Fig. 1: Eddy current heating.
Charge or load to be heated is placed inside the coil arrangement (coil surrounds the charge). The heat, so produced, by eddy currents in the articles or charge penetrates the charge upto a sufficient depth and outside on the surface of the charge.
Advantages of Eddy Current Heating
- State advantages and disadvantages of eddy current heating.
- Control is smooth and very easy.
- Heat can penetrate to desired depth.
- Method is very quick and convenient.
- Process is clean.
- Heat loss is minimum as it is produced in the matenal to be heated.
- Process can be carried out In ordinary place, no effect of surroundings/ atmosphere etc.
- Process is very easy to be handled, hence semi-skilled person can carry the work.
- Temperature can be controlled by simple method.
- Automatic control can be employed.
- Coil spacing need not be charged for different objects. Air gap between coil and object does not affect the process.
Disadvantages of Eddy Current Heating
- The system of heating is comparatively costly than other types of heating.
- Initial cost of equipment is more.
- Efficiency is less upto 40 to 50
- It is difficult to heat to a great depth of the material.
- The requirement of frequency is very high from 10 kHz to 400 kHz.
Applications of Eddy Current Heating
The heating effect is produced due to eddy currents induced in the mass to be heated. Alternating current cutting the conducting substance induces eddy currents in it and the loss of energy due to eddy currents is eddy current loss” which appears to be in the form of heat.