It is an electrical absorption type dynamometer.
Principle of Working of Eddy Current Dynamometer
Eddy Current Dynamometer works on the principle that, “when a conductor moves through a magnetic field, it induces eddy currents (called as local currents). These eddy currents flow in a short circular path around the conductor and are dissipated in the form of heat. ”
Construction of Eddy Current Dynamometer
Eddy Current Dynamometer consists of non-magnetic steel rotor mounted on the shaft, whose power is to be measured. It rotates inside a smooth cast iron stator. Clearance between stator and rotor is very small. Stator carries an exciting coil, which is energized by d.c. supply from an external source. The stator is mounted, such that, it permits free swing about its axis. Stator is provided with a torque arm, to which, a spring balance is attached.
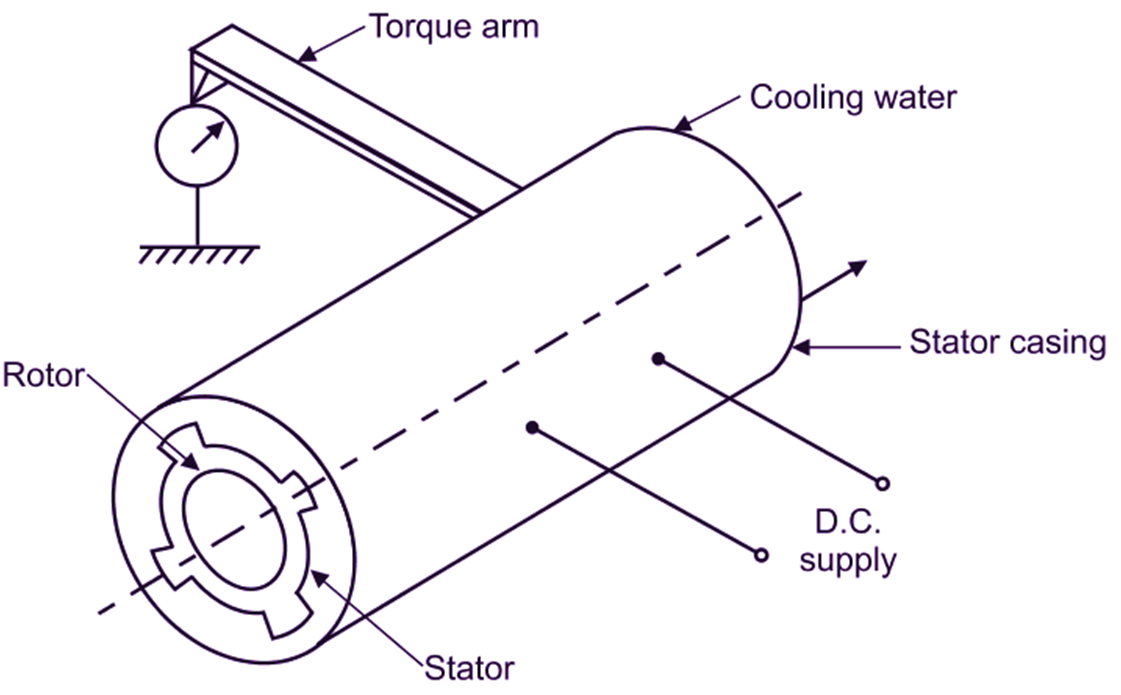
Fig. 1: Eddy Current Dynamometer
Working of Eddy Current Dynamometer
Stator winding is excited by a d.c. supply as shown in Fig. 1. When the solid rotor moves in the magnetic field produced by stator winding, an emf is produced in it, thereby inducing eddy currents. These eddy currents oppose the rotation of rotor. The moment of resistance is measured by torque arm or brake arm and then torque and hence, shaft power can be calculated. The mechanical power supplied to dynamometer is converted in the form of heat. This heat is dissipated or carried away partly by air circulation and partly by water. Therefore, cold water is circulated through the air gap between the stator and rotor.
Advantages of Eddy Current Dynamometer
- Good control at low rotating speeds.
- Suitable for high speed range.
- Ability to measure large power output at all speeds. Therefore, it is preferred in testing of automobile and aircraft engines.
- It is compact as compared to other dynamometers of same capacity.
- The torque developed is smooth and continuous under all operating conditions.
Disadvantages of Eddy Current Dynamometer
- It cannot produce torque at zero speed.
- Comparatively smaller in size, which reduces its strength and reliability.
Applications of Eddy Current Dynamometer
- Measurement of extremely large power in the range of 200 kW-225 kW.
- If the shafts are rotating at high speeds of 5000 to 6000 r.p.m., it is most suitable instrument for power measurement.