Internal gear pump differ from external gear pump in the arrangement of gears. An internal gear pump also consists of two gears, but one of the gear is internal gear and the other is commonly used spur gear. Both the gears rotate in the same direction.

Figure 1: Internal Gear Pump.
This gear pump consists of a stationary part called crescent shaped seal, which is used to separate the gears and also acts as a seal between the suction port and the discharge port (Figure 2).
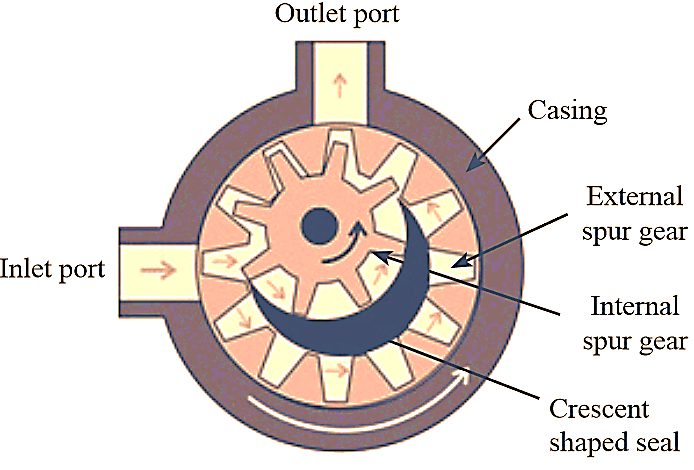
Figure 2: External Gear Pump.
Working of Internal Gear Pump
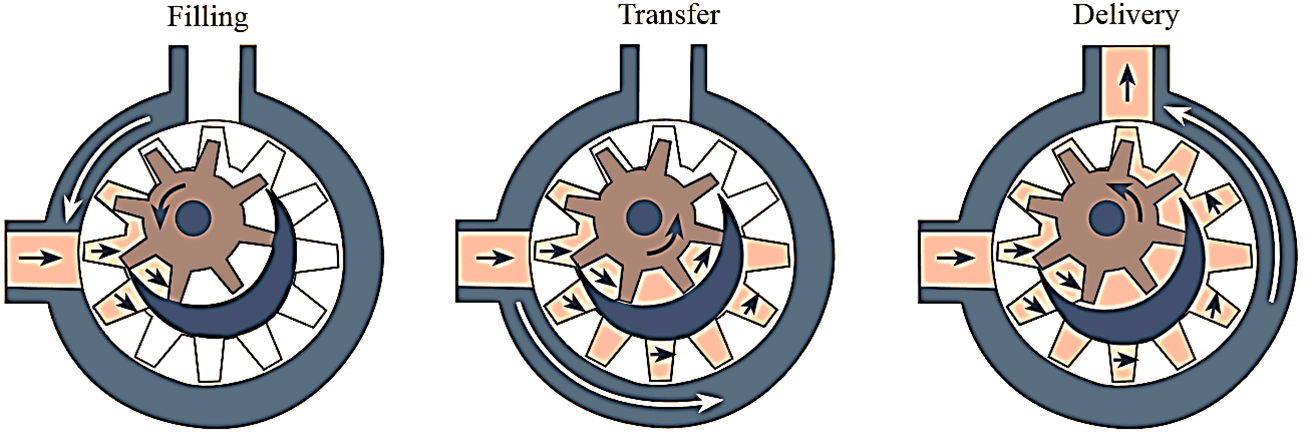
Figure 2: Internal Gear Pump working.
Among the two gears, the internal gear is connected to the driving shaft and power is transmitted to it. Therefore, the internal gear is the driving gear and the external spur gear is the driven gear. During the rotation of the two gears, they appear to be coming out of mesh at the inlet port. This creates the suction and causes the fluid to enter into the pump. The fluid is completely filled around the crescent seal and the gear spaces. The rotation of gears transfers the fluid from inlet port to outlet port.
At the outlet port, the two gears comes into mesh. This decreases the space between the two gears and increases the pressure. which forces the fluid outside the pump system.
Advantages of Internal Gear Pump
- It can be used for high viscosity fluids.
- Less moving parts.
- Uniform discharge irrespective of varying pressures.
- It is a bi-directional pump.
Disadvantages of Internal Gear Pump
- The parts used should have high dimensional accuracy.
- Lubrication is required.
- Shaft bearing experiences an overhung load.