In this topic, you study Hydroelectric Power Plant – Working, Diagram, Construction, Advantages & Disadvantages.
Those power plants which convert the energy of falling water into electrical energy and called hydroelectric power plants.
Schematic diagram of Hydroelectric Power Plant
The schematic diagram of Hydroelectric Power Plant is shown in Fig. 1.
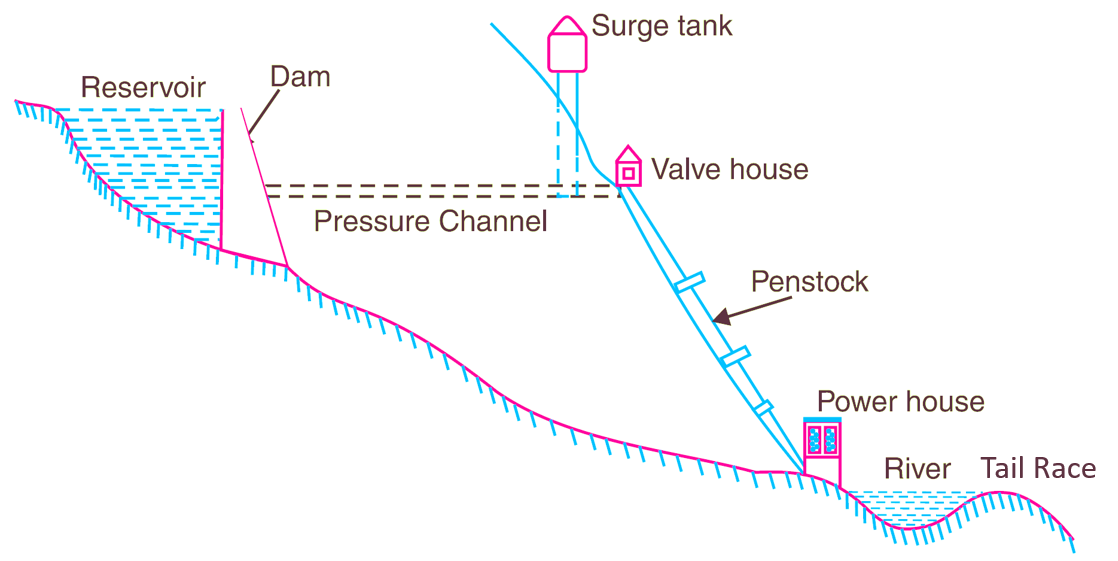
Fig. 1: Schematic diagram of hydroelectric power plant.
Working and Construction of Hydroelectric Power Plant
It consists of the following major components:
- Catchment Area
- Water Reservoir
- Dam
- Valve house
- Penstock
- Water Turbine
- Surge Tank
- Pressure channel
- Alternator
- Tail Race
- Spillway
Catchment Area: It is the area over which rainfall is collected and led to the reservoir.
Water Reservoir: A dam is constructed across a river at a suitable place and water is stored in the catchment area from where it is led to the water reservoir. The main sources of water are rainfall and melting of ice in the mountains.
Dam: It is generally a masonry structure and its functions are to create a water head and to store water in the catchment area. The dam should be able to resist failure against sliding, overturning and rupturing. The water from the reservoir is brought to the surge tank through the pressure channel.
Valve House: At the start of the penstock there is a valve house which contains main sluice Valves for controlling the water flow. In addition to this there are also provided automatic isolating valves which come into operation when the penstock bursts, which cuts off further supply of water.
Penstock: The huge steel or concrete pipe that conveys the water from valve house to water turbine.
Water Turbine: From the penstock water is taken to the turbine. The turbine converts the water energy into mechanical energy.
Surge Tank: It is an open tank built just before the valve house. It acts as the storage of water which is sufficient for one day or for a specific period of time. Surge tank is also helpful in reducing the thrust of water on penstock in case of sudden closing fixed gates of a water turbine.
Pressure Channel: A pressure channel is constructed between reservoir and valve house to carry water from reservoir to valve house.
Alternator: To the turbine is coupled the alternator which converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Tall Race: After the water has done its useful work in the turbine, it is discharged to the tail race which may lead it to the same stream.
Spillway: It is normally constructed at the top of the dam acting as a safety valve by discharging the overflow of water to the down-stream when the reservoir is full during the rainy season. This is generally constructed of concrete and provided with water discharge openings shut off by metal control gates. By changing the degree to which the gates are opened the discharge of water head can be accomplished in order to maintain the water level in the reservoir.
Classification of Hydroelectric Power Plant
- Low head power plant below 60 m.
- Medium head power above 60 m and below 300 m.
Types of Turbines Used in Hydroelectric Power Plant
- Impulse turbine,
- Reaction turbine,
- Propeller
Advantages of Hydroelectric Power Plant
- It is quite neat and clean.
- It is economical in large sizes.
- Running costs are less since no fuel is required.
- It can be started in no time.
- It is simple in construction, robust and requires low maintenance.
- It has higher efficiency and long life.
- It helps in irrigation and controlling floods.
Disadvantages of Hydroelectric Power Plant
- High capital cost.
- High cost of transmission lines.
- Power supply may be affected during the dry season.
- Skilled and experienced hands are required to build the plant.
Site selection of Hydroelectric Power Plant
- It should be selected where sufficient water at a reasonable head is available.
- Reservoir should have a large catchment area.
- Transportation facilities should be adequate.
- Possibility of constructing the dam should be there.
- The land should be cheap.
- The bearing capacity of the soil should be sufficient so that heavy equipment can be installed.