In this topic, you study Thermal Power Plant – Working, Diagram, Construction, Advantages & Disadvantages.
Those power stations which convert chemical energy of fuel (coal, gas etc.) into electrical energy are called thermal power stations. The fuel used in thermal power stations is coal or gas. The heat of combustion of coal is utilised to convert water into steam which runs the steam turbine coupled with the alternator produces electrical energy.
Schematic diagram of Thermal Power Plant
The schematic diagram of steam power station is shown in Fig. 1.
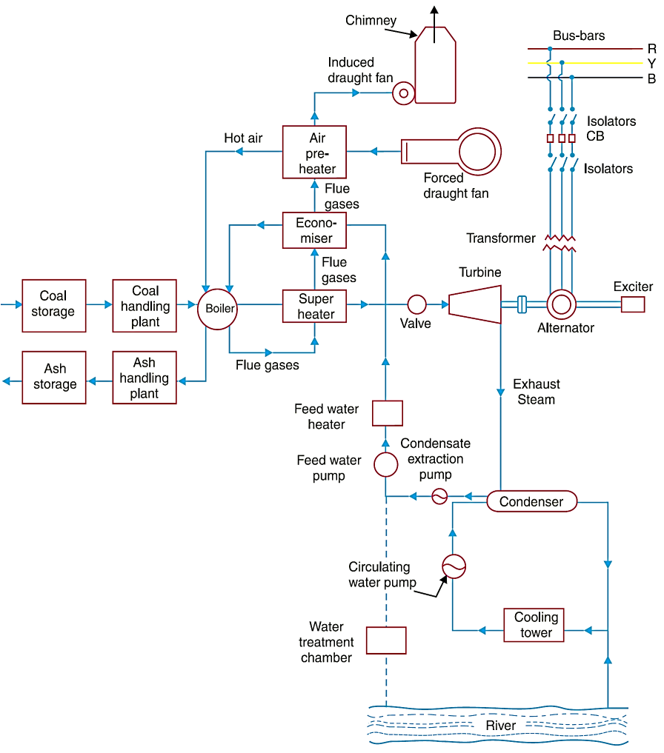
Fig. 1: Elementary block diagram of modern steam power station.
Working and Construction of Thermal Power Plant
It consists of the following stages:
Coal and Ash Handling Arrangement: The coal and ash handling plant generally consists of: (i) Coal storage, (ii) Coal handling plant, (iii) Ash handling plant, and (iv) Ash storage.
The coal is stored in a coal storage plant from where it is delivered to the coal handling plant. In coal handling it is crushed into small pieces for proper burning. The coal in the powdered form is burnt in the boiler. The ash produced after burning of coal is removed to ash storage plant
Boiler: The heat of combustion produced by burning coal in the boiler is used to heat up water for producing steam. The steam produced is wet, therefore it is passed through a superheater where it is dried and superheated.
Superheater: The wet steam from the boiler is passed through the superheater and superheated by the flue gases on their way to the chimney. This steam is then injected into the steam turbine blades through the main steam value.
Economizer: The function of economizer is to preheat the feed water by utilizing the heat of flue gases.
Air Preheater: The air is drawn from atmosphere by a forced draught fan and passed through air preheater, where it is heated by flue gases and then admitted to the furnace for the burning of coal.
Steam Turbine: The dry and superheated steam from the superheater is fed to the steam turbine to convert heat energy of steam into mechanical energy.
Condenser: The used up steam is exhausted to the condenser where it is converted to water which is again fed to the boiler.
Alternator: The alternator and turbine are coupled together. The mechanical power is converted to electrical energy by alternator. The output electrical energy is delivered to the bus through transformers, circuit breakers and isolators.
Water Treatment Chamber: Clean and soft water is needed for the boilers for their long life. The water taken from the river is given chemical treatment to make it soft and clean. This water is fed to the boiler by a feed water pump.
Advantages of Thermal Power Plant
- The fuel used is quite cheap.
- It can be located near the load centres.
- Less space is required as compared to hydroelectric power plants.
Disadvantages of Thermal Power Plant
- Costlier as compared to hydroelectric power stations in running cost
- Atmosphere polluted due to smoke and fumes.
Site Selection of Thermal Power Plant
- The site selected should be near the coal mines to reduce transportation cost.
- Ample supply of water should be available for cooling.
- The land should be cheap.
- The site selected should have adequate transportation facilities.
- Some land must be available for future expansion.