Moving Coil Microphone works on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, which states that, “when a conductor moves in a magnetic field, it cuts the flux line and an emf is generated.” Therefore, Electro-dynamic microphones are also called as Electro-magnetic microphones.
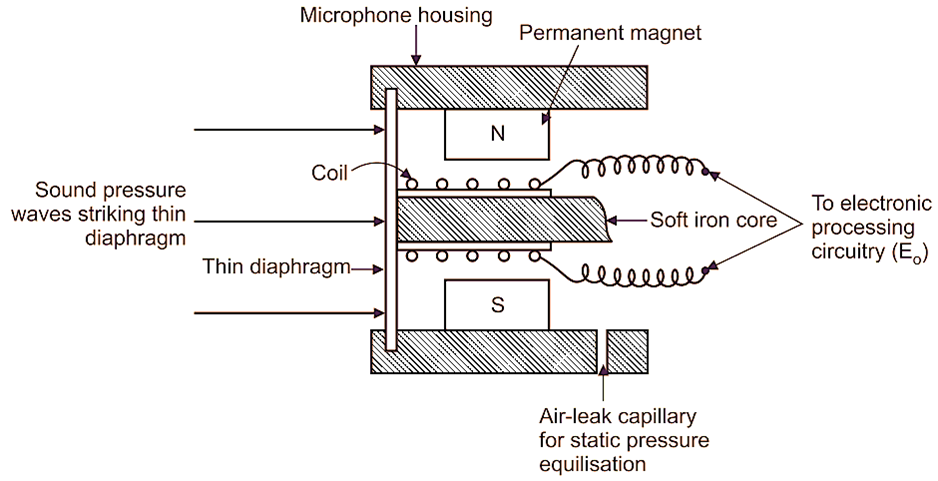
Fig. 1: Moving Coil Microphone.
Construction and Working of Moving coil Microphone
Moving Coil Microphone consists of a sensing diaphragm, which has small light weight coil attached to it. This sensing diaphragm acts as a primary transducer, which senses the sound pressure waves and convert them into displacement of diaphragm. The coil attached to diaphragm is free to move in and out of space between North and South poles of magnet. Sound pressure waves exert a force on diaphragm causing the coil to move in and out of the space between North and South poles of magnet. This induces an e.m.f. across the coil terminal. Magnitude of e.m.f. developed is direct result of motion of coil, which clearly depends upon the force exerted by pressure waves. This e.m.f. or voltage is calibrated in terms of pressure.
Output voltage of Moving Coil Microphone is given by,
E0 = B.L.V × 10-8 Volts
Where, B = Density of magnetic flux in ‘Weber/m2’
L = Length of the conductor in ‘m’
V = Velocity of conductor in ‘m/s’
Advantages of Moving coil Microphone
- They are self-generating type (i.e. no external power source is needed for their operation).
- They have high sensitivity and dynamic range.
- They do not require battery.
- Compact and light weight.
- Low cost.
Disadvantages of Electro-Dynamic Microphone
- Poor linearity.
- Poor frequency response due to high inertia of moving coil.
- Low output.
- Bulky in size.
Applications of Moving coil Microphone
- Voice communication in telephone lines.
- Precision sound measurements.