A shell and coil condenser consists of one or more water coils enclosed in a welded steel shell. The water coils may be provided with fins in order to increase surface area for better heat transfer rate. Refer Fig. 1. The shell and coil condenser may be either vertical (as shown in the Fig. 3.13) or horizontal. In this type of condenser, the hot vapour refrigerant enters from the top side of the shell and surrounds the water coils. The cold water absorbs the heat from vapour refrigerant. Due to heat rejected, the vapour refrigerant is cooled and condensed. The condensate (liquid refrigerant) drops to the bottom of the shell. Most vertical type shell and coil condensers use counter flow water system, as it is more efficient than parallel flow water system. In the shell and coil condensers, coiled tubing is free to expand or contract and therefore, it responds to wide range of rapidly fluctuating temperatures, because of its spring action. These coils can withstand any strain caused by changing temperatures. Since the water coils are enclosed in a welded steel shell, therefore the mechanical cleaning of these coils is not possible. The coils are cleaned with chemicals.
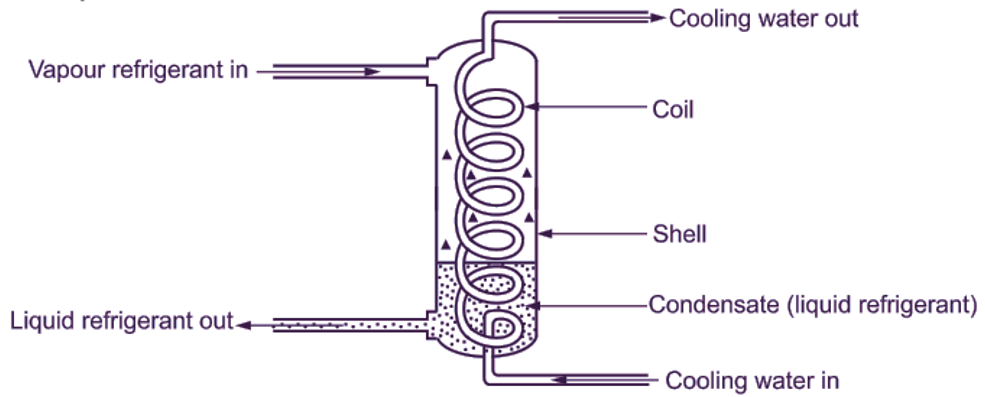
Fig. 1: Shell and coil condenser
Applications of Shell and Coil Condenser
Suitable for plants having refrigeration capacity below 50 TOR.