Carbon microphone consists of a thin moving diaphragm, used as primary (first) transducer, which senses the sound pressure waves and convert them into displacement of diaphragm. Moving diaphragm is connected to a capsule having flexible bellows to allow compression or expansion. A capsule containing granules of carbon acts as a secondary transducer in this microphone. The device is externally powered by a constant voltage source (battery). Therefore, carbon microphone is not a self-generating type instrument, like Electro-dynamic microphone (Fig. 1).
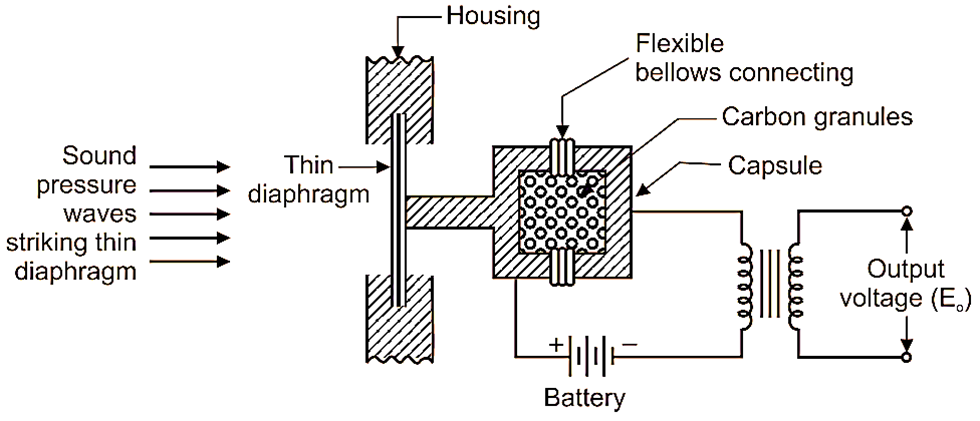
Fig. 1: Carbon Microphone.
Working of Carbon Microphone
When sound waves strike on thin diaphragm, the diaphragm gets displaced by some distance, compressing the capsule and hence, the carbon granules located in that flexible capsule. This leads to change in resistance, and hence change in output voltage. The output voltage obtained is calibrated in terms of sound pressure.
Advantages of Carbon Microphone
- Low cost.
- It withstands rough handling.
- Simple and rigid construction.
- It does not deteriorate due to
- hotness and coldness.
- It gives relatively high-power output as compared to other microphones.
Disadvantages of Carbon Microphone
- It requires an external power source to operate/work.
- Distortion of sound is more as compared to other microphones.
- It has a limited frequency response, not more than 5 kHz.
- Less accurate.
- Poor linearity.
Applications of Carbon Microphone
- In Telephone transmission circuits.
- In Telephone receivers.
- In Radio broadcasting.
- In Recording devices